
Ensuring optimal performance in fuel delivery systems is crucial for the efficiency of any engine. Regular upkeep and troubleshooting can significantly enhance longevity and reliability. This section delves into the intricacies of maintaining these essential components, focusing on common issues and effective solutions.
Understanding the mechanisms involved is vital for anyone looking to enhance their knowledge in this field. Proper diagnostics and proactive measures can prevent costly failures and ensure smooth operation. Here, we explore various strategies and best practices that will assist you in achieving proficiency in maintaining these intricate systems.
Whether you’re a seasoned technician or a novice enthusiast, familiarizing yourself with the nuances of these units will empower you to tackle challenges confidently. With the right approach, you can not only resolve issues but also improve the overall functionality of your equipment.
This section aims to provide a comprehensive overview of essential components and their roles within a fuel delivery system. Understanding how these elements interact is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Components of the System
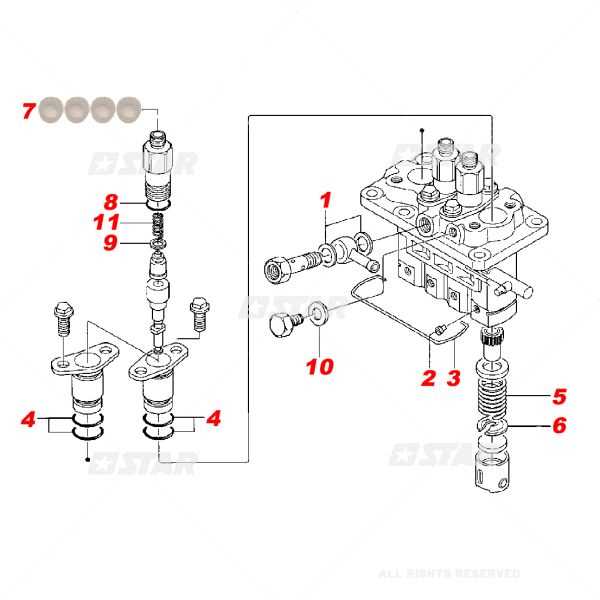
- Fuel Delivery Mechanism
- Control Systems
- Flow Regulators
- Pressure Management Devices
Operational Principles

Recognizing the fundamental operational principles is vital. This includes the methods of fuel transfer, timing mechanisms, and the role of pressure in ensuring efficiency.
Understanding these aspects will facilitate a more profound knowledge of the system’s functionality and longevity.
Common Signs of Injector Pump Issues

Identifying problems with fuel delivery mechanisms is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance. Various symptoms may indicate underlying complications that require immediate attention.
Decreased Engine Performance: A noticeable drop in power during acceleration can suggest that the fuel delivery system is not functioning properly. This may result in sluggish responses and reduced efficiency.
Unusual Noises: Uncommon sounds, such as knocking or whining, can indicate internal issues within the system. These noises often signify that components are not operating smoothly.
Fuel Leaks: Visible leaks around the system can lead to serious safety hazards and should be addressed promptly. Monitoring for any signs of leakage is essential for preventing further damage.
Increased Exhaust Smoke: An unusual amount of smoke emitted from the exhaust may point to incomplete combustion due to improper fuel supply. This not only affects performance but can also lead to environmental concerns.
Starting Difficulties: If the engine struggles to start or requires multiple attempts, it may indicate issues with the fuel delivery mechanism. This symptom is often an early warning sign of potential failures.
Essential Tools for Repair Work
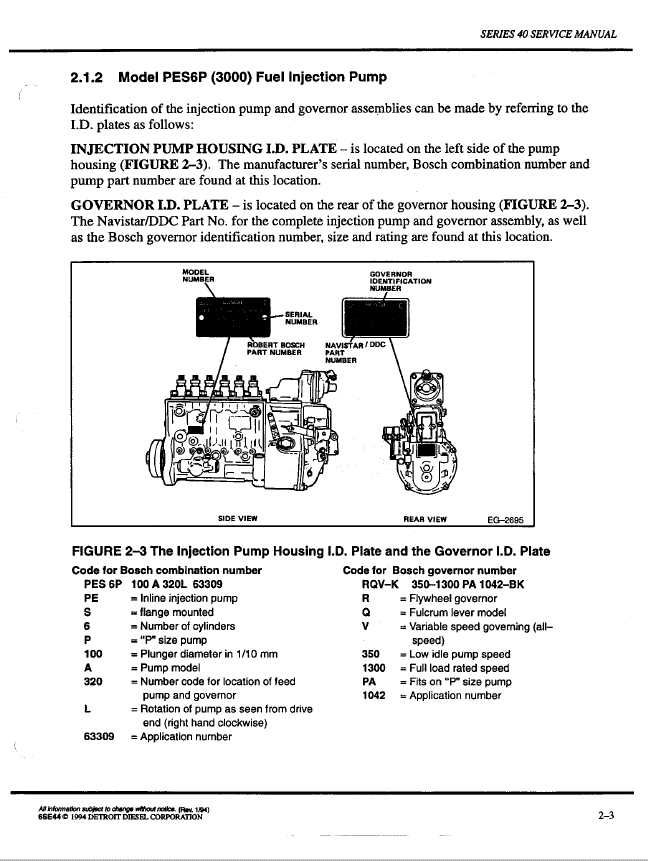
Undertaking maintenance tasks requires a set of specific instruments that enhance efficiency and accuracy. These essential devices not only facilitate smooth operations but also ensure that each procedure is executed with precision.
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Socket Wrench Set | For loosening and tightening fasteners in confined spaces. |
| Torque Wrench | To apply a precise amount of force to nuts and bolts. |
| Pliers | Useful for gripping, twisting, and cutting wires or other materials. |
| Screwdriver Set | Essential for driving screws of various types and sizes. |
| Multimeter | For measuring electrical parameters, ensuring optimal functioning. |
| Cleaning Kit | To maintain components and ensure longevity of tools. |
Step-by-Step Disassembly Process
This section outlines the essential steps for safely taking apart the component in question. Following a methodical approach ensures that each part is handled carefully, minimizing the risk of damage and facilitating easier reassembly.
Preparation and Tools
Before beginning the disassembly, gather all necessary tools and materials. A clean workspace is crucial to keep track of components. Common tools required include wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers. Make sure to wear safety gear to protect yourself during the process.
Disassembly Steps
Start by removing any external covers or shields. Carefully unscrew and detach each section, keeping components organized. Use a labeling system for small parts to avoid confusion during reassembly. Take notes or photos to document the arrangement of components as you progress.
Important: Handle all parts with care, as some may be delicate or easily damaged. Following these steps will provide a clear path toward successful disassembly and future maintenance.
Inspecting Components for Damage
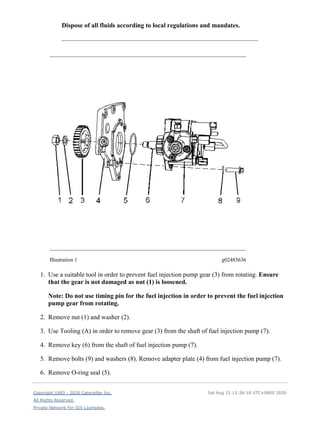
Thorough examination of mechanical parts is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Identifying any signs of wear, corrosion, or malfunction can prevent further complications during operation. Regular inspections should be part of any maintenance routine to maintain efficiency.
When inspecting components, consider the following aspects:
- Visual Assessment: Look for obvious signs of damage such as cracks, dents, or excessive wear.
- Surface Condition: Check for rust or corrosion that may indicate deterioration.
- Clearances: Measure gaps and tolerances to ensure they fall within acceptable limits.
- Functionality: Test each part to verify its proper operation and responsiveness.
After the initial visual check, it’s important to delve deeper into the integrity of each element:
- Disassemble: Carefully take apart the assembly to access internal components.
- Inspect Seals and Gaskets: Look for any signs of leakage or wear that could compromise functionality.
- Check for Debris: Remove any contaminants that could obstruct movement or cause damage.
- Documentation: Keep records of any findings to track the condition over time.
By systematically evaluating these areas, you can ensure all components function harmoniously, enhancing the overall efficiency of the system.
Cleaning Techniques for Injector Parts

Proper maintenance of essential engine components is key to ensuring optimal performance and longevity. The cleaning process, when done correctly, can help to eliminate debris and prevent wear, ultimately supporting smoother operation.
- Preparation: Begin by carefully disassembling each part, laying them out in a clean, organized workspace. This step helps prevent cross-contamination and allows for easier access to each element during cleaning.
- Soaking Method: For components with visible residue, a safe solvent soak is recommended. Submerge parts in the solvent for a set period, allowing the cleaner to break down hardened buildup.
- Brush Cleaning: Use soft-bristled brushes to remove any remaining particles without damaging delicate surfaces. Ensure that all crevices and narrow areas are thoroughly cleaned.
- Rinsing and Drying: After scrubbing, rinse each item with a gentle spray of water or compressed air. Pat them dry with a lint-free cloth to prevent any moisture from lingering.
- Final Inspection: Before reassembling, inspect each part ca
Reassembling the Injector Pump
In this section, you’ll learn the essential steps to carefully assemble each component back into its original position, ensuring everything fits and functions as expected. Following a meticulous approach will prevent potential issues and support reliable operation once reassembled.
- Check Component Alignment: Align each part precisely to ensure smooth movement and optimal performance. Misalignment can lead to wear or malfunction.
- Install Seals and Gaskets: Properly place all seals and gaskets to avoid leaks. Make sure each gasket fits snugly, as these prevent fluid escape and maintain pressure.
- Secure Fasteners: Tighten bolts and screws following recommended torque specifications. Over-tightening can damage parts, while under-tightening can cause instability.
- Begin by positioning the primary assembly parts in their designated areas.
- Gradually add smaller components, ensuring that each one is properly aligned and secure.
- Once all parts are in place, double-check that everything is correctly aligned and stable.
Completing these steps with attention to detail will prepare the unit for consistent performance and longevity.
Testing Functionality After Repair

Ensuring proper functionality following component maintenance is essential to verify that all systems operate smoothly and as intended. This section outlines the key steps for evaluating the performance and detecting any potential issues that may have emerged during the process.
Initial Assessment

Start by visually inspecting the assembly, checking connections, seals, and structural integrity. Confirm that all parts are correctly aligned and secured in their respective positions. Observing any irregularities early can prevent further complications and ensure accurate test results.
Performance Testing
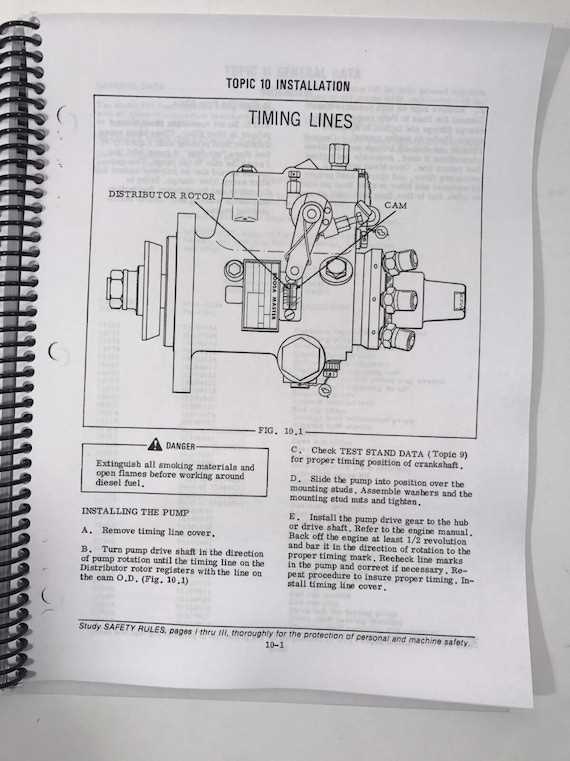
Once the visual inspection is complete, initiate the system and monitor its performance closely. Pay attention to sound patterns, responsiveness, and output consistency, as these can indicate the overall operational health. Use diagnostic tools to assess performance metrics and identify any deviations from optimal standards. This step is crucial for confirming the functionality and reliability of the assembly after maintenance.
Note: Minor adjustments may be necessary to fine-tune the system. Make sure to perform these carefully, following established procedures to avoid compromising component longevity.
Troubleshooting Common Problems

This section provides guidance on identifying and resolving frequent issues encountered in fuel delivery systems. By recognizing specific signs, you can better understand the root causes and choose suitable solutions for restoring functionality.
- Starting Difficulties: If the engine struggles to start, consider checking the fuel intake and flow consistency. Blockages, air in the system, or clogged lines may be affecting performance.
- Inconsistent Power: Uneven or reduced engine power can indicate problems with the fuel mixture. Assess the system for any irregularities in fuel distribution or pressure drops.
- Strange Noises: Unusual sounds, such as knocking or rattling, often point to wear or air entry in the components. Inspect for loose connections, worn parts, or air leakage.
- Excessive Exhaust Smoke: Dark or unusually colored exhaust may signal incomplete fuel combustion. This could be due to imbalances in fuel flow, which can often be corrected with a thorough inspection of the fuel delivery system.
- Identify signs indicating a potential issue.
- Examine fuel connections, lines, and flow controls.
- Resolve each issue promptly to maintain smooth operation.
When to Seek Professional Help
Some maintenance tasks can be handled independently, but certain technical issues may require specialized knowledge and tools. Recognizing these moments is essential to avoid potential damage and ensure the equipment continues functioning optimally. Even a minor oversight can lead to complex issues, making professional assistance a valuable option.
Signs that Professional Assistance is Needed: If unusual sounds, inconsistent performance, or other irregularities arise, it may indicate deeper technical issues. In such cases, a professional’s expertise can quickly identify and address the underlying causes, preventing costly repairs in the future.
Ensuring Longevity and Safety: Trusting a skilled technician when technical expertise is needed safeguards the system’s longevity and maintains a higher level of safety. While personal troubleshooting is beneficial, certain challenges demand the precision and experience only a qualified specialist can offer.