
The functionality and longevity of any vehicle’s power unit depend on regular upkeep and timely interventions. Understanding the complexities involved in maintaining your engine can significantly enhance its performance and reliability. This section aims to provide essential insights and methodologies for managing various aspects of your unit’s functionality.
By familiarizing yourself with the integral components and their interactions, you can proactively address potential issues before they escalate. This guide will explore various techniques and approaches that ensure your power unit operates at peak efficiency. Emphasizing hands-on knowledge, you will gain confidence in managing repairs and adjustments effectively.
Furthermore, this resource will highlight common challenges faced during maintenance and present practical solutions to overcome them. Whether you are a seasoned enthusiast or a newcomer, the information provided here will equip you with the necessary tools to tackle maintenance tasks with assurance.

This section addresses typical problems encountered in specific automotive engines, along with their associated indicators. Recognizing these issues promptly can aid in effective troubleshooting and maintenance, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the engine.
Frequent Problems
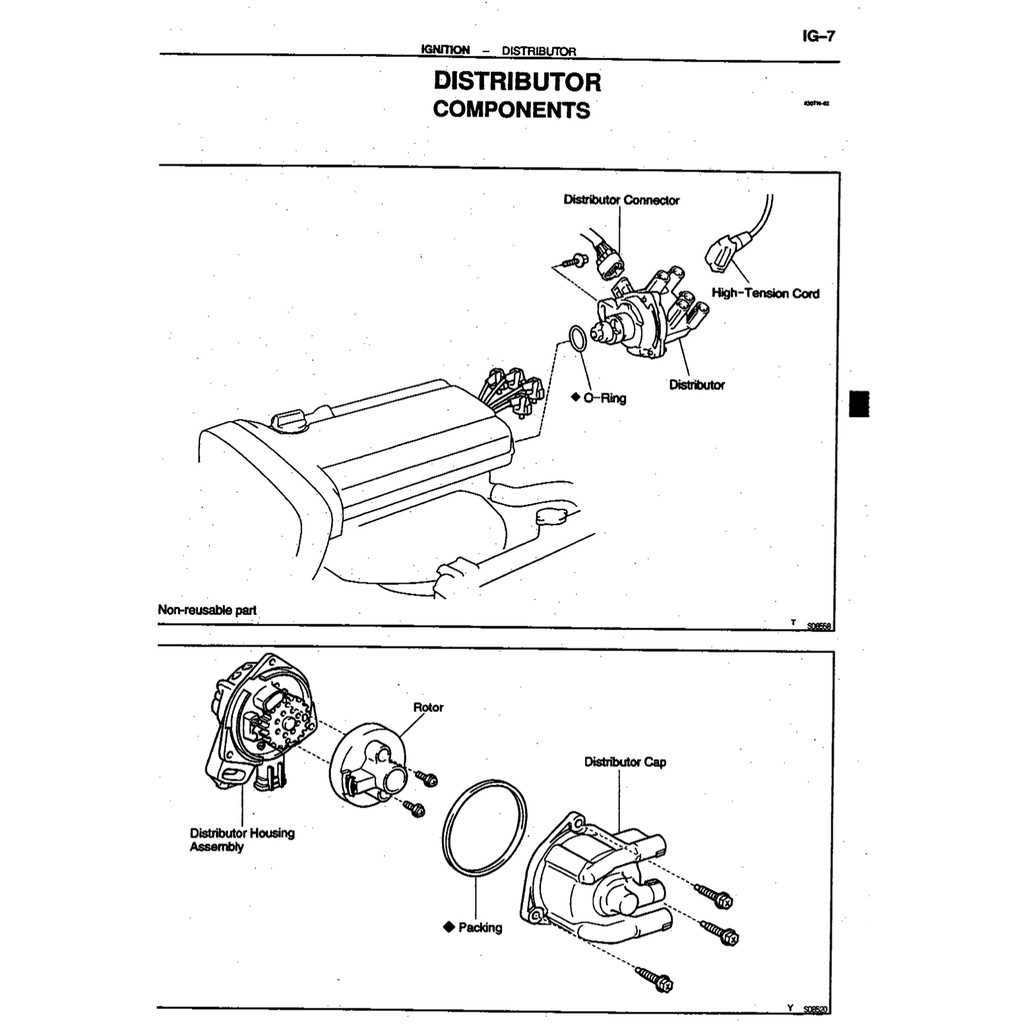
- Overheating: High engine temperatures can indicate a cooling system malfunction.
- Rough Idling: Unstable idle may suggest fuel delivery or ignition issues.
- Oil Leaks: Visible oil spots under the vehicle could point to seal or gasket failures.
- Poor Acceleration: Lack of power during acceleration may be related to fuel supply problems or air intake restrictions.
Indicators to Watch For
- Engine warning lights on the dashboard.
- Unusual noises, such as knocking or ticking sounds.
- Increased fuel consumption beyond normal levels.
- Excessive exhaust smoke, which may vary in color.
Monitoring these signs can lead to timely interventions, potentially saving time and resources while enhancing overall engine reliability.
Essential Tools for Repairs

Having the right equipment is crucial for successful maintenance tasks. Whether you are working on engines, transmissions, or other components, specific instruments can significantly enhance your efficiency and accuracy. This section highlights the necessary tools to ensure a smooth process, enabling you to tackle various challenges with confidence.
Basic Hand Tools
Hand tools form the foundation of any repair kit. From tightening bolts to adjusting fittings, a variety of instruments are essential for efficient work. Below is a list of fundamental hand tools that every technician should consider:
| Tool Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Wrenches | For loosening or tightening nuts and bolts |
| Screwdrivers | To drive screws into various materials |
| Pliers | For gripping and bending objects |
| Torque Wrench | To apply a specific torque to fasteners |
Specialized Instruments
In addition to basic tools, specialized instruments can help diagnose and resolve specific issues. Investing in the right equipment can save time and prevent damage. Consider the following specialized tools:
| Tool Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Multimeter | For measuring voltage, current, and resistance |
| Compression Tester | To check the compression of engine cylinders |
| OBD-II Scanner | For diagnosing electronic issues and reading trouble codes |
| Oil Filter Wrench | To remove and install oil filters |
Step-by-Step Disassembly Process
This section provides a detailed guide for carefully dismantling a complex engine assembly. Following these steps will ensure that each component is properly handled and can be reassembled without issues. A systematic approach is essential to avoid damage and to maintain organization throughout the process.
-
Gather necessary tools and materials, including:
- Wrenches of various sizes
- Screwdrivers (flathead and Phillips)
- Torque wrench
- Container for small parts
- Shop manual for reference
-
Begin with disconnecting the battery to ensure safety. Remove any electrical connections that may hinder disassembly.
-
Drain fluids, including oil and coolant, to prevent spills and maintain cleanliness.
-
Remove external components, starting with:
- Air intake system
- Exhaust manifold
- Cooling hoses
- Accessory belts
-
Carefully detach the valve cover, checking for any signs of wear or damage.
-
Proceed to remove the timing belt or chain, ensuring to note the alignment for future reassembly.
-
Remove the cylinder head, taking care to follow the specific bolt removal sequence to avoid warping.
-
Continue by disassembling the remaining components, such as:
- Piston assembly
- Crankshaft
- Oil pump
-
Place all removed parts in clearly labeled containers to ensure organization and ease during reassembly.
By following these steps methodically, the disassembly process will be efficient and organized, setting a solid foundation for any necessary repairs or modifications.
Rebuilding the Engine Block
Revitalizing an engine block is a critical process that requires attention to detail and a solid understanding of the mechanical components involved. This procedure involves disassembling the unit, cleaning, inspecting for wear, and making necessary modifications to restore its performance capabilities. A thorough approach not only enhances reliability but also extends the life of the entire power unit.
Disassembly and Cleaning
The first step in the rebuilding process involves carefully disassembling the block to access its internal parts. Each component should be labeled and organized to facilitate reassembly. After disassembly, cleaning is essential to remove grime, carbon buildup, and other contaminants. Using a suitable solvent and brushes ensures that all surfaces are prepared for inspection and machining.
Inspection and Machining
Once cleaned, inspect the block for cracks, warping, and other signs of damage. Pay special attention to the mating surfaces and cylinder bores. If any issues are found, machining may be necessary to restore these surfaces to their original specifications. Precision measurements using calipers and micrometers are critical during this phase to ensure optimal fitment of the new components.
Replacing Timing Belts and Chains
Replacing the timing components is essential for maintaining optimal engine performance. These components ensure that the engine’s valves open and close at the correct intervals in relation to the position of the pistons. Neglecting this task can lead to severe engine damage, decreased efficiency, and costly repairs. This section outlines the necessary steps for replacing these vital parts.
Before beginning the replacement process, it is important to gather the necessary tools and materials. Proper preparation ensures a smooth and efficient workflow. Below is a list of essential items:
| Tools | Description |
|---|---|
| Socket Set | Used for removing bolts and nuts |
| Torque Wrench | Ensures proper tightening of bolts |
| Timing Tool Kit | Helps align the timing components correctly |
| New Timing Belt/Chain | Replacement component for the old one |
| Lubricant | To reduce friction during installation |
Start by disconnecting the battery and removing any components obstructing access to the timing area. Carefully follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for disassembling parts, noting the order and orientation for reassembly. Once you have access to the timing system, check for wear on the old belt or chain, including any signs of cracking or fraying.
After removing the old timing mechanism, compare it with the new one to ensure compatibility. Install the new component, ensuring it is aligned correctly with the timing marks. Use the torque wrench to fasten all bolts to the manufacturer’s specifications to avoid future issues.
Finally, reassemble any components that were removed and reconnect the battery. Start the engine to verify that it runs smoothly, and listen for any unusual noises that may indicate improper installation. Regularly scheduled maintenance will extend the lifespan of the timing components and enhance overall engine performance.
Diagnosing Electrical Problems
Electrical issues can be some of the most challenging to troubleshoot in any mechanical system. Identifying the root cause often requires a systematic approach, utilizing a variety of tools and techniques to pinpoint the malfunction. Understanding the electrical layout and components involved is essential for effective diagnosis.
Common Symptoms of Electrical Faults
Several indicators can suggest an electrical fault. These may include inconsistent engine performance, flickering dashboard lights, or the inability to start the engine. Conducting preliminary checks on fuses and wiring can provide insight into the source of the problem.
Steps for Effective Troubleshooting

To systematically address electrical malfunctions, begin with a visual inspection of all connections and wiring. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or loose connections. Next, utilize a multimeter to test voltage and continuity in circuits. Recording measurements during this process will help track down any anomalies. If necessary, consult wiring diagrams to ensure all components are properly configured and functioning.
Fuel System Maintenance Tips

Maintaining the fuel delivery system is essential for optimal performance and longevity of your vehicle. Regular care ensures that the engine receives a clean and steady supply of fuel, which can improve efficiency and reduce emissions. Here are some key practices to keep in mind.
Regular Inspections

- Check fuel lines for leaks or cracks.
- Inspect fuel filters and replace them as needed.
- Ensure connections are tight and secure.
Fuel Quality Management
- Use high-quality fuel from reputable suppliers.
- Avoid allowing the fuel level to drop too low, which can lead to sediment buildup.
- Add fuel stabilizers if the vehicle will be stored for an extended period.
By following these maintenance tips, you can help ensure that the fuel system operates smoothly and efficiently, enhancing overall vehicle performance.
Cooling System Troubleshooting
The effectiveness of a vehicle’s thermal management system is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance. Identifying and addressing issues within this system can prevent severe damage and enhance longevity. This section outlines common problems and diagnostic steps to help ensure efficient cooling.
- Overheating: This can be caused by low coolant levels, a malfunctioning thermostat, or a blocked radiator.
- Coolant Leaks: Look for signs of leakage around hoses, the radiator, and the water pump.
- Insufficient Heating: If the cabin heat is inadequate, the issue may lie with the thermostat or air in the system.
- Unusual Noises: Hissing or bubbling sounds may indicate trapped air or a failing water pump.
To diagnose these issues effectively, follow these steps:
- Check the coolant level in the reservoir and refill if necessary.
- Inspect hoses for wear or damage, ensuring secure connections.
- Test the thermostat’s operation by observing temperature fluctuations.
- Examine the radiator for blockages and clean as needed.
- Look for signs of leaks and monitor engine temperature during operation.
By systematically addressing these areas, one can enhance the performance of the cooling system and avoid further complications.
Performance Upgrades and Modifications

Enhancing vehicle performance involves a range of modifications aimed at boosting power, improving efficiency, and optimizing overall driving experience. Various components can be upgraded to achieve desired results, whether for competitive racing or everyday driving. Understanding these enhancements can lead to significant improvements in both speed and handling.
Key Modifications
Several areas can be targeted for upgrades, including the engine, exhaust system, and suspension. Each of these components plays a crucial role in the vehicle’s performance, and optimizing them can yield substantial benefits.
Comparison of Upgrades
| Upgrade Type | Description | Expected Gain |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Air Intake | Increases airflow to the engine for improved combustion. | 5-10% increase in horsepower |
| High-Performance Exhaust | Reduces back pressure and improves exhaust flow. | 5-15% increase in horsepower |
| ECU Tuning | Reprograms the engine control unit for better fuel maps and ignition timing. | 10-20% increase in horsepower |
| Suspension Upgrades | Enhances handling and stability during cornering. | Improved cornering speed and control |
When planning modifications, it is essential to consider compatibility and the balance between various components. Comprehensive upgrades can lead to a significant transformation in vehicle dynamics, resulting in a more thrilling and responsive driving experience.
Testing and Quality Assurance

Ensuring the reliability and performance of an automotive engine requires a systematic approach to evaluation and validation. This section focuses on methods and practices to verify that components meet the necessary standards before installation. Quality assurance is crucial in maintaining high-performance levels and preventing potential issues.
Various testing techniques can be employed to assess different aspects of engine components. Here are some common methods:
- Visual Inspection: Examine parts for any signs of wear, damage, or manufacturing defects.
- Dimensional Analysis: Measure components against specified tolerances to ensure proper fit and functionality.
- Functional Testing: Run the engine under controlled conditions to evaluate its performance metrics, such as power output and fuel efficiency.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Utilize techniques like ultrasonic or magnetic particle testing to detect internal flaws without damaging the parts.
Implementing a comprehensive quality assurance program involves the following steps:
- Develop clear specifications and standards for all components.
- Train personnel on testing procedures and quality control measures.
- Document all testing results to track performance over time.
- Continuously review and update testing protocols based on technological advancements and field feedback.
By adhering to rigorous testing and quality assurance practices, automotive professionals can enhance the reliability and longevity of engine components, ultimately ensuring optimal performance on the road.