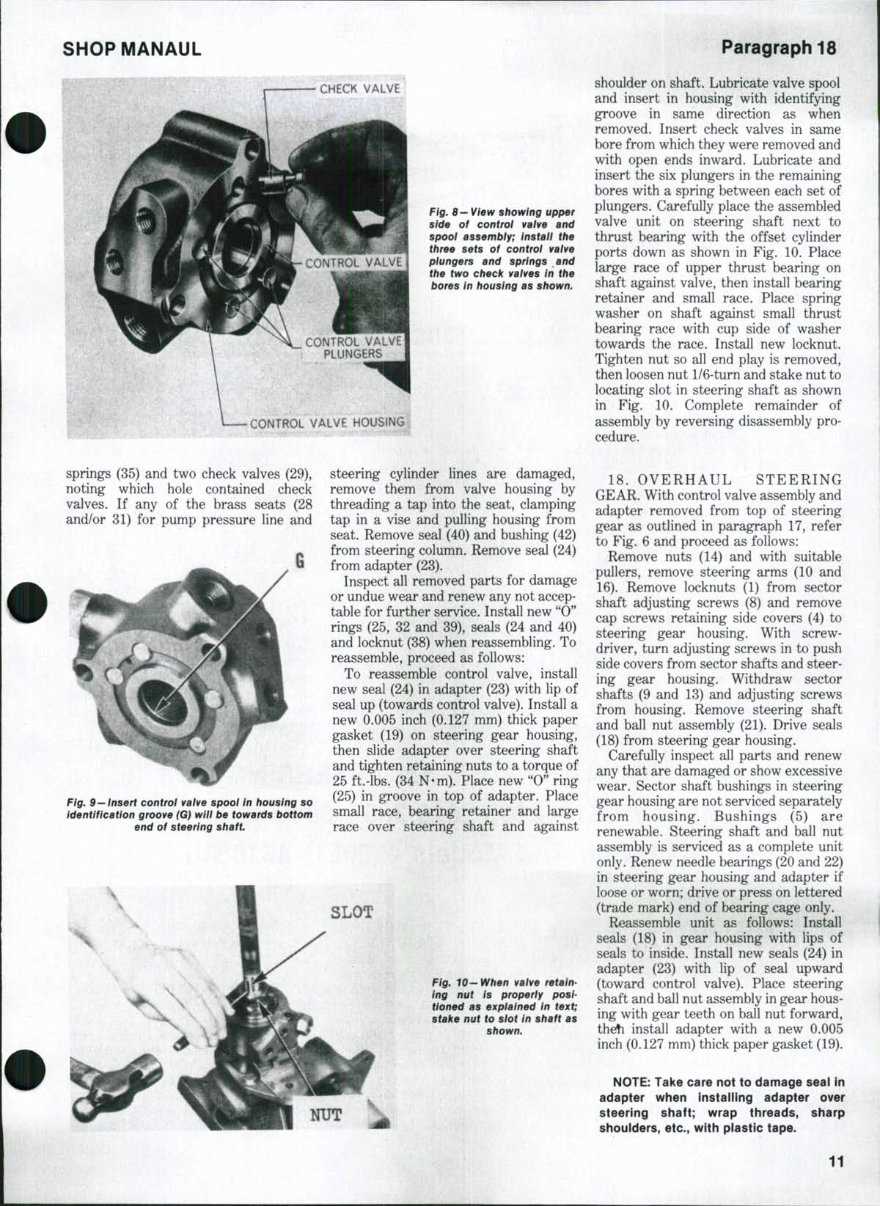
In the realm of machinery, understanding the intricacies of your equipment is vital for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This section provides essential insights into the upkeep of specific models, focusing on key components that require attention and care. With the right knowledge, users can enhance functionality and prevent potential issues.
Regular servicing is crucial for sustaining efficiency and avoiding unexpected malfunctions. By following systematic procedures and employing proper techniques, owners can address common challenges that may arise during operation. This guidance empowers users to take charge of their machinery and ensure it runs smoothly over time.
Additionally, awareness of specific parts and their functions enables proactive maintenance. Familiarizing oneself with the equipment’s structure and common pitfalls can lead to more effective problem-solving strategies. This section aims to equip users with the necessary tools and knowledge to navigate any difficulties encountered, ultimately fostering a more reliable and efficient experience.
To ensure your machine operates smoothly and efficiently, regular upkeep is essential. Proper maintenance not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of the equipment. By following a few key practices, you can keep your device in top condition and avoid unexpected issues.
Routine Checks

Conducting frequent inspections is vital. Pay attention to fluid levels, filters, and overall cleanliness. Ensure all components are functioning correctly, and replace any worn parts promptly.
Lubrication and Cleaning

Maintaining proper lubrication is crucial for reducing friction and wear. Regularly clean the machine to prevent dust and debris buildup, which can lead to overheating and damage.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Level Check | Weekly | Ensure all fluids are at recommended levels. |
| Filter Replacement | Monthly | Replace air and oil filters as needed. |
| Lubrication | Monthly | Use appropriate lubricant for each component. |
| General Cleaning | Bi-weekly | Remove dirt and debris from exterior and interior. |
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
This section provides a comprehensive approach to diagnosing and resolving common issues encountered with machinery. By following a systematic method, users can efficiently identify problems and implement appropriate solutions.
Initial Checks

- Ensure that the equipment is powered on and connected properly.
- Inspect for any visible signs of damage or wear on components.
- Verify fluid levels and ensure they are within acceptable limits.
Diagnostic Steps

- Begin by observing any unusual sounds or vibrations during operation.
- Check for error codes or warning lights on the control panel.
- Conduct tests on electrical connections and sensors for continuity.
- Inspect filters and air intakes for blockages that could impede performance.
- Review user feedback and performance logs for insights into recurring issues.
Engine Repair and Rebuild Procedures
Effective restoration and maintenance of an engine are crucial for optimal performance and longevity. This section outlines essential steps and techniques for overhauling and fixing various engine components.
Initial Assessment is the first step in the process. Begin by inspecting the engine for any visible signs of damage, such as leaks or unusual wear. A thorough evaluation helps identify specific issues that need addressing.
Next, dismantling the engine involves carefully removing components to access internal parts. Ensure that all pieces are organized to facilitate reassembly. Use proper tools to avoid damaging sensitive components during this stage.
Once dismantled, cleaning each part is essential. Remove carbon deposits and other contaminants using suitable cleaning solutions. Pay special attention to areas that affect the engine’s efficiency, such as valves and pistons.
The next phase is inspecting components for wear and tear. Utilize precise measuring instruments to assess tolerances. Replace any damaged parts to ensure reliable operation upon reassembly.
After inspection, reassembly requires careful attention to detail. Follow the manufacturer’s specifications regarding torque settings and sequence. Proper alignment of all components is vital for smooth functionality.
Finally, conducting a test run after reassembly allows for monitoring engine performance. Listen for unusual noises and check for leaks to ensure that the overhaul was successful.
Electrical System Diagnostics and Fixes

The effectiveness of any machinery largely depends on the reliability of its electrical components. This section focuses on identifying common issues within the electrical framework and providing solutions to ensure optimal performance.
Common Issues in Electrical Systems
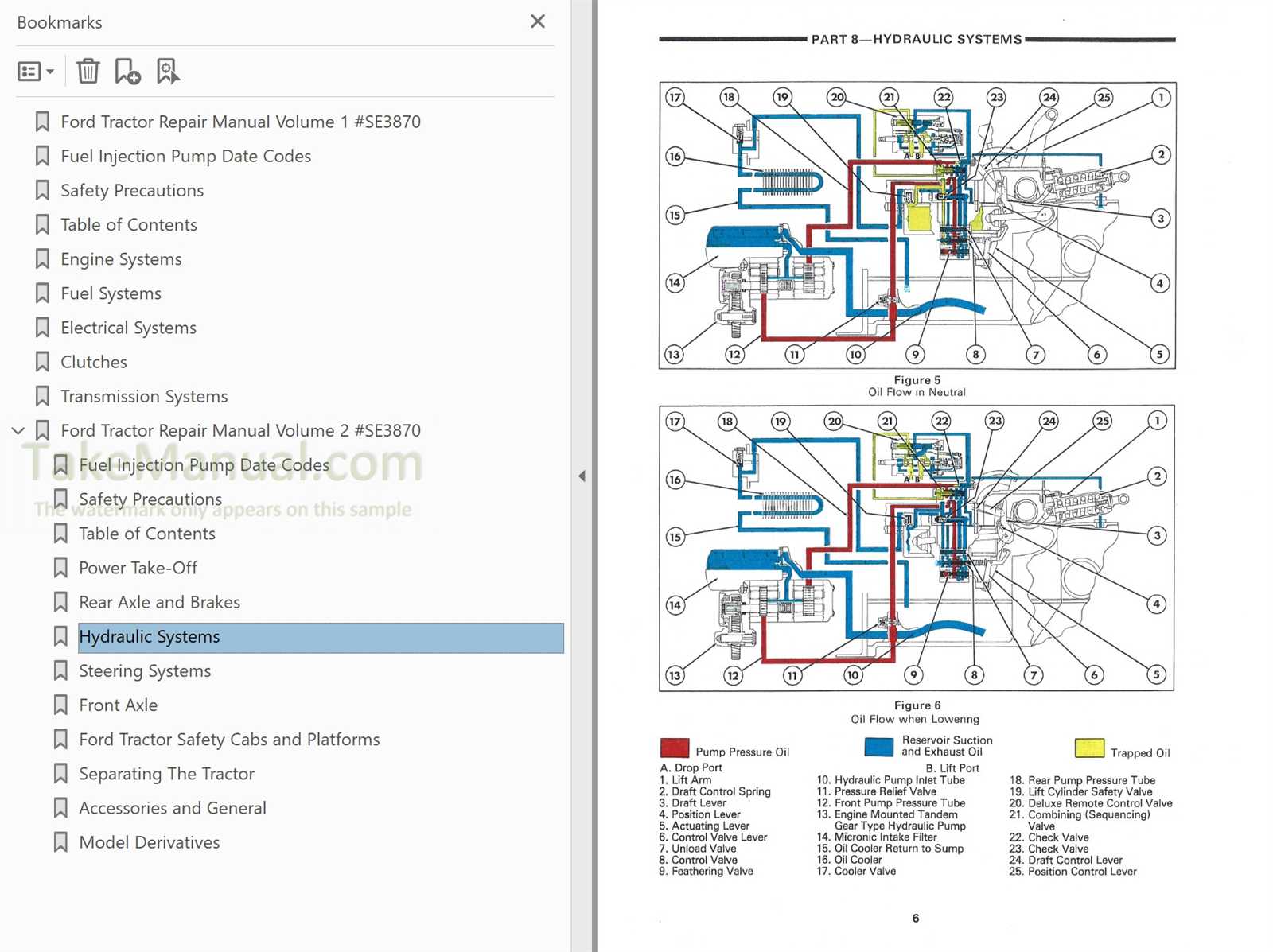
- Battery problems, including insufficient charge and corrosion.
- Wiring faults, such as frayed or damaged cables.
- Malfunctioning switches that may fail to make proper contact.
- Faulty sensors that provide inaccurate readings.
- Issues with connectors, which may be loose or corroded.
Diagnostic Procedures
- Check the battery voltage using a multimeter. Ensure it meets the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Inspect all wiring for signs of wear or damage. Replace any compromised sections.
- Test switches for continuity to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Use diagnostic tools to assess sensor functionality and replace as necessary.
- Examine connectors for proper fit and clean any corrosion present.
By systematically diagnosing these common electrical issues, operators can enhance the longevity and reliability of their machinery.
Hydraulic System Maintenance Essentials

Proper upkeep of the hydraulic system is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of machinery. Regular checks and maintenance can prevent costly breakdowns and enhance operational efficiency. This section outlines key practices for maintaining hydraulic components, focusing on fluid quality, system cleanliness, and component inspection.
To effectively maintain the hydraulic system, consider the following essential practices:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Inspection | Monthly | Check hydraulic fluid levels and quality, ensuring it is clean and free from contaminants. |
| Filter Replacement | Every 200 hours | Replace filters to prevent dirt and debris from affecting system performance. |
| Leak Checks | Weekly | Inspect all hoses and connections for signs of leaks or wear, addressing any issues promptly. |
| Fluid Change | Every 1000 hours | Replace hydraulic fluid according to manufacturer recommendations to maintain system efficiency. |
| Component Inspection | Quarterly | Conduct a thorough inspection of pumps, cylinders, and valves for proper function and any signs of damage. |
Implementing these maintenance tasks will help ensure the hydraulic system operates smoothly and effectively, reducing downtime and extending the life of the equipment.
Transmission Troubleshooting and Solutions
This section focuses on identifying and resolving common issues associated with the gear shifting mechanism in agricultural machinery. By understanding the typical problems and their potential causes, operators can maintain optimal performance and extend the lifespan of their equipment.
Common Issues and Symptoms
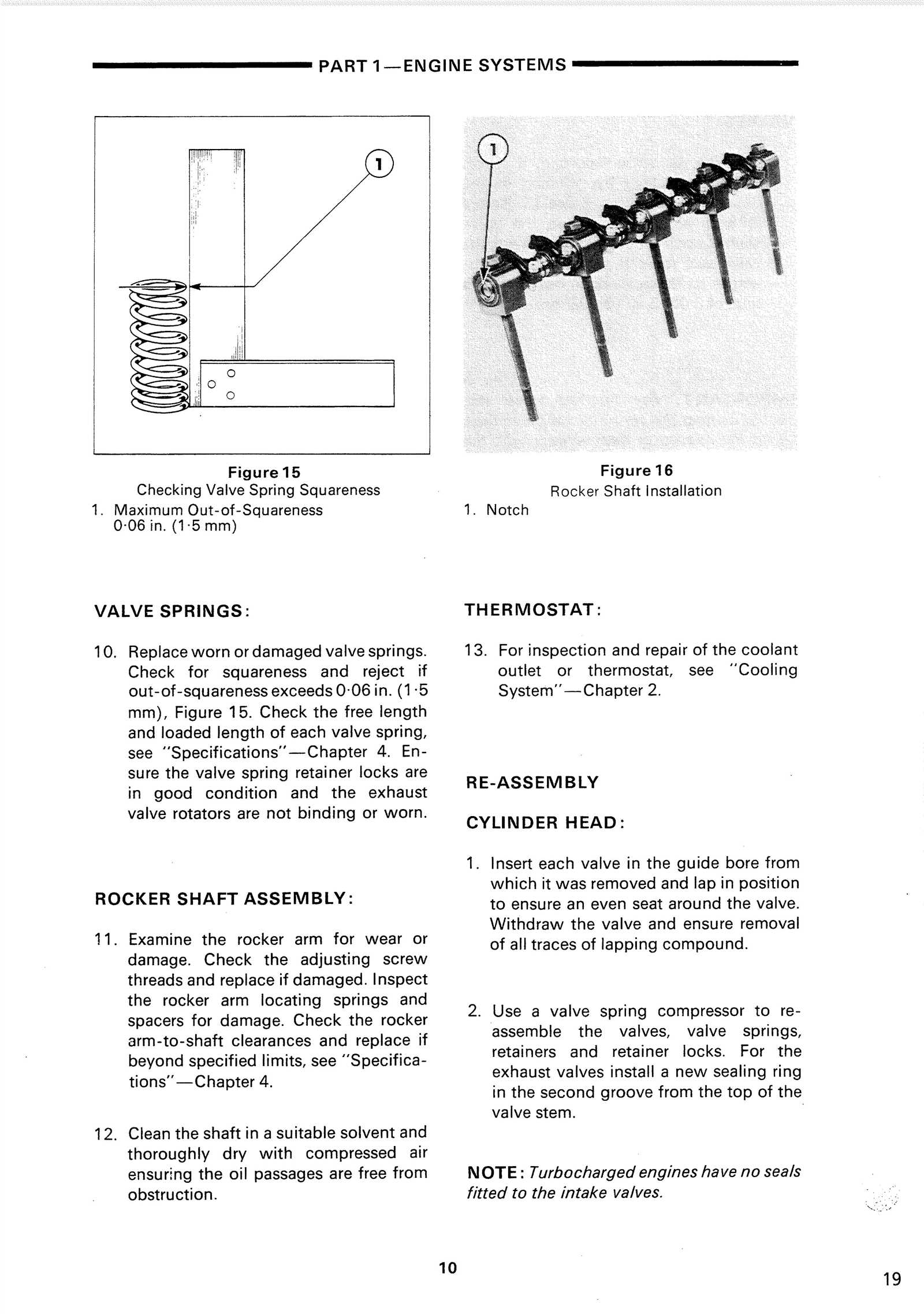
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Difficulty in shifting gears | Low transmission fluid or contamination |
| Unusual noises during operation | Worn gears or bearings |
| Slipping gears | Faulty clutch or incorrect fluid levels |
| Overheating | Insufficient cooling or fluid circulation |
Troubleshooting Steps
To effectively address the issues outlined, follow these systematic troubleshooting steps:
- Check fluid levels and condition. Replace or top up if necessary.
- Inspect for leaks or signs of damage in the transmission system.
- Test the clutch operation and ensure proper adjustment.
- Listen for abnormal sounds, indicating potential mechanical failure.
Implementing Safety Practices During Repairs

Ensuring a secure environment while conducting maintenance is paramount. Adopting safety protocols not only protects the individual performing the task but also safeguards the equipment and surrounding areas. A structured approach to safety can mitigate risks associated with mechanical work.
Essential Safety Gear

Using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is critical for preventing injuries. This gear includes items such as gloves, goggles, and sturdy footwear, each serving a specific purpose in enhancing safety during mechanical tasks.
Work Area Organization

Maintaining an orderly workspace contributes significantly to safety. Keeping tools and parts neatly arranged helps prevent accidents and promotes efficiency. A clutter-free environment allows for easier movement and reduces the likelihood of mishaps.
| Safety Gear | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Gloves | Protect hands from cuts and abrasions |
| Goggles | Shield eyes from debris and harmful substances |
| Sturdy Footwear | Prevent foot injuries from heavy objects |
| Ear Protection | Reduce exposure to loud noise |