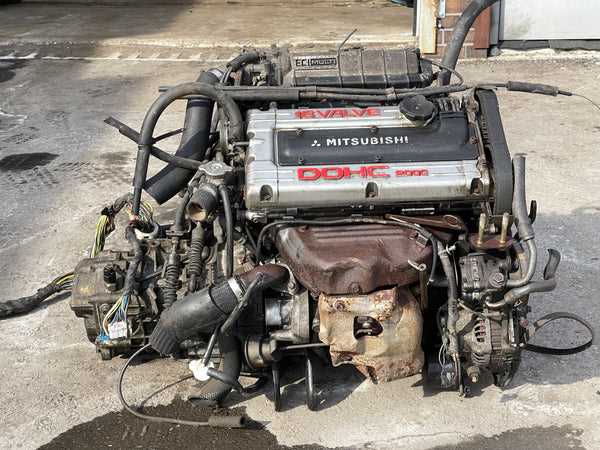

The heart of any vehicle lies within its mechanical system, a complex assembly that requires both understanding and maintenance. This section aims to provide valuable insights into the intricacies of overhauling a specific power unit known for its performance and reliability. By delving into essential techniques and tips, enthusiasts and professionals alike can ensure optimal functionality.
In this guide, you will discover various methodologies for disassembling, assessing, and reassembling critical components. With a focus on practical steps and troubleshooting strategies, readers will gain the knowledge necessary to address common issues and enhance the longevity of their automotive machinery. Whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a passionate DIYer, this resource is designed to support your journey in revitalizing your vehicle’s core.
Understanding the underlying principles of mechanical systems not only boosts performance but also fosters a deeper appreciation for automotive engineering. Armed with this information, you will be well-prepared to tackle challenges that arise, ensuring that your vehicle remains in peak condition for years to come. Embrace the challenge of restoring your power unit and unlock the full potential of your ride.
Mitsubishi 4G63 Engine Overview
This section provides a comprehensive examination of a well-regarded power unit known for its robust performance and versatility. Renowned for its application in various vehicles, this setup combines advanced engineering with efficiency, making it a popular choice among automotive enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Key Features
The highlighted power source is characterized by several significant attributes that contribute to its widespread acclaim:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Cylinders | Four-cylinder configuration for balanced power output and fuel efficiency. |
| Displacement | Typically around 2.0 liters, optimizing performance across a variety of applications. |
| Turbocharging | Available in turbocharged variants, enhancing power delivery and responsiveness. |
| Durability | Engineered for longevity, capable of withstanding high-performance demands. |
Applications
This power unit has found its way into numerous platforms, from sporty compacts to versatile sedans. Its adaptability allows for modifications that cater to both daily driving and competitive racing, solidifying its reputation as a dependable choice in the automotive community.
Common Issues with 4G63 Engines
This section outlines prevalent problems encountered with a specific automotive power unit known for its performance and reliability. Understanding these common issues can aid in diagnosis and maintenance, ensuring optimal functionality over time.
Overheating Problems
One frequent concern involves excessive heat, which can stem from various sources such as faulty cooling systems, blocked radiators, or worn-out water pumps. This overheating can lead to severe damage if not addressed promptly, including warped cylinder heads or blown gaskets.
Oil Leaks and Consumption
Another common issue is the presence of oil leaks, often originating from deteriorated seals or gaskets. Additionally, excessive oil consumption can occur, indicating potential internal wear or damage. Regular monitoring and timely interventions are crucial to prevent further complications and maintain performance.
Essential Tools for Engine Repair
When it comes to maintaining and restoring a power unit, having the right instruments at your disposal is crucial. The proper tools not only streamline the process but also enhance precision, ensuring that every task is executed efficiently and effectively.
Basic Toolkit Essentials
- Socket Set: A variety of sizes for different bolts.
- Wrenches: Both open-end and box-end for flexibility.
- Torque Wrench: To apply specific torque settings accurately.
- Screwdrivers: Flathead and Phillips for various fasteners.
- Pliers: For gripping and manipulating components.
Advanced Instruments
- Diagnostic Scanner: To read error codes and monitor performance.
- Compression Tester: To assess cylinder pressure.
- Oil Pressure Gauge: For monitoring lubrication efficiency.
- Feeler Gauge: To measure gaps with precision.
- Magnetic Tool Holder: To keep small parts organized and accessible.
Step-by-Step Disassembly Process
Understanding the procedure for dismantling a mechanical unit is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. This section outlines a systematic approach to disassemble the assembly, ensuring that each stage is clear and manageable. Following these steps will help in identifying potential issues and facilitate a smoother reassembly.
1. Preparation: Gather necessary tools and create a clean workspace. Ensure all components are labeled to avoid confusion during reassembly.
2. Removal of Accessories: Start by detaching any external parts, such as belts and pulleys. Take care to keep all fasteners organized for easy access.
3. Drain Fluids: Before proceeding, drain all fluids from the unit to prevent spills and ensure safety.
4. Disengaging the Housing: Carefully remove the outer casing, making note of any seals or gaskets that may need replacing later.
5. Extracting Internal Components: Begin to take out internal parts, such as the piston assembly and crankshaft. Document each step, including the orientation of components.
6. Inspection: Once disassembled, inspect each part for wear or damage. This will inform necessary replacements or repairs.
7. Cleaning: Clean all components thoroughly before reassembly, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Following these structured steps will simplify the disassembly process, enabling a thorough understanding of the unit’s inner workings.
Inspecting Engine Components for Damage
Thorough examination of key parts is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Identifying any signs of wear, cracks, or deformation helps in assessing the overall health of the system. Regular inspections can prevent minor issues from escalating into major failures.
Begin by visually assessing each component for visible damage. Look for oil leaks, unusual noises, or abnormal vibrations during operation. Use tools like calipers and micrometers to measure critical dimensions, ensuring they meet specified tolerances.
Additionally, check for signs of overheating, such as discoloration or warping. Pay close attention to the surface finish and integrity of components, as these can indicate underlying problems. Document any findings to track changes over time and guide future maintenance efforts.
Rebuilding the 4G63 Engine Block
Reconstructing a power unit core involves meticulous attention to detail and a clear understanding of the components. This process not only revitalizes performance but also extends the lifespan of the machinery. A systematic approach ensures that every aspect, from assessment to reassembly, is addressed thoroughly.
Disassembly and Inspection
Begin with careful disassembly of the core unit, noting the position and condition of each component. Inspect for wear, cracks, and distortions. Cleaning parts thoroughly is essential for effective evaluation and future assembly. Identifying areas needing replacement or refurbishment will guide the rebuilding process.
Reassembly and Final Checks
After preparing the components, proceed to reassemble them in the correct sequence. Utilize new gaskets and seals to prevent leaks. Once assembled, conduct final checks for alignment and torque specifications. This ensures optimal functionality and durability in the restored core.
Replacing Gaskets and Seals
Maintaining the integrity of various components is crucial for optimal performance. Over time, gaskets and seals can deteriorate, leading to leaks and compromised functionality. This section outlines the essential steps for effectively replacing these critical elements to ensure longevity and reliability.
Preparation for Replacement

Before starting the replacement process, gather all necessary tools and components. Clean the surfaces where the new gaskets and seals will be installed to remove any debris or old material. Proper preparation prevents future issues and ensures a tight fit, reducing the risk of leaks.
Installation Steps
Begin by carefully removing the old gaskets and seals without damaging the mating surfaces. Apply a suitable sealant if required, and position the new components accurately. Follow the manufacturer’s specifications regarding torque settings and tightening sequences to achieve an even seal. After installation, check for any leaks during operation to confirm a successful replacement.
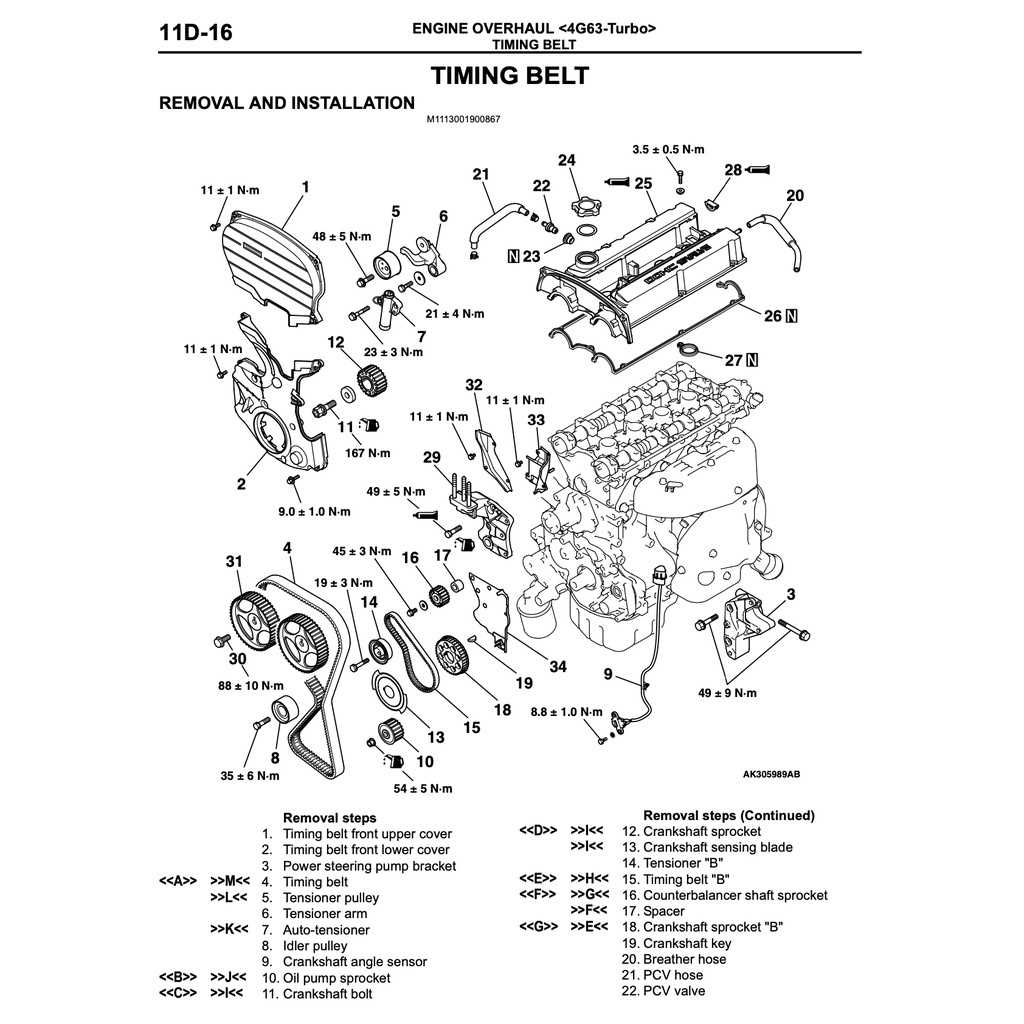
Timing Belt Replacement Guide
Replacing the timing belt is a crucial maintenance task that ensures the longevity and proper functioning of the vehicle’s internal components. A well-maintained belt prevents costly repairs and unexpected breakdowns. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the steps involved in the replacement process, ensuring that you can tackle this job with confidence.
Tools and Materials Needed
Before starting, gather the necessary tools and materials. You will need a socket set, wrenches, a torque wrench, a timing belt kit, and possibly a pulley removal tool. Additionally, have a clean work area and some rags for any spills.
Step-by-Step Procedure
1. Preparation: Begin by disconnecting the battery and removing any components obstructing access to the belt. This may include the radiator fan, serpentine belt, or timing cover. Always refer to specific guides for your vehicle to avoid missing any crucial steps.
2. Removing the Old Belt: Align the timing marks on the pulleys and carefully loosen the tensioner to relieve tension on the belt. Remove the old belt and inspect the tensioner and pulleys for wear, replacing them if necessary.
3. Installing the New Belt: Position the new timing belt according to the manufacturer’s specifications, ensuring that it aligns correctly with the timing marks. Adjust the tensioner to apply the proper tension to the new belt.
4. Reassembly: Reattach any components that were removed earlier. Double-check the alignment of the timing marks and ensure everything is securely fastened.
5. Final Checks: Reconnect the battery and start the vehicle, listening for any unusual noises. Monitor the performance for a short drive to ensure everything operates smoothly.
By following this guide, you can successfully replace the timing belt, contributing to the reliable operation of your vehicle for years to come.
Installing a New Cylinder Head
Replacing the cylinder head is a crucial step in ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your vehicle’s power unit. This task requires careful preparation and attention to detail to prevent future issues. Proper installation is essential for maintaining compression and efficient operation.
Preparation Steps
- Gather necessary tools and materials, including a torque wrench, gaskets, and sealants.
- Ensure the work area is clean and free of debris to avoid contamination.
- Remove any old components and clean the surface of the block thoroughly.
Installation Procedure
- Position the new cylinder head onto the block, aligning it with the dowel pins.
- Install the gasket, ensuring it fits snugly and correctly.
- Carefully place the bolts in their designated holes, following the manufacturer’s specified order.
- Tighten the bolts incrementally using a torque wrench to achieve the correct specifications.
- Double-check all connections and ensure no debris is present before proceeding with reassembly.
Adjusting Valves and Lifters
Ensuring optimal performance of your vehicle requires periodic adjustments of the components responsible for air and fuel flow within the combustion chamber. Proper calibration of these parts enhances efficiency, reduces noise, and prolongs the lifespan of the system. This section outlines the essential steps to achieve precise settings for these crucial elements.
Tools and Preparation

Before beginning the adjustment process, gather the necessary tools: a feeler gauge, a wrench set, and a screwdriver. Make sure the vehicle is on a level surface and the ignition is turned off. It’s advisable to allow the system to cool if it has been running recently. Familiarize yourself with the specifications for clearance settings, as variations can impact overall functionality.
Adjustment Procedure
Start by removing any components obstructing access to the adjusters. Then, rotate the crankshaft to align the timing marks, ensuring that the valves are in the closed position for the specific cylinder being adjusted. Using the feeler gauge, measure the clearance between the lifter and the valve stem. If the clearance deviates from the specified range, loosen the adjuster nut and turn the screw until the correct gap is achieved. Once adjusted, tighten the nut securely while holding the screw in place. Repeat this process for each valve, following the manufacturer’s specifications for all measurements.
Regular adjustments not only maintain performance but also prevent premature wear. A well-maintained system contributes significantly to the overall driving experience.
Fuel System Maintenance Tips
Regular upkeep of the fuel delivery system is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Proper maintenance ensures that the components function efficiently, preventing issues that could lead to decreased power and increased emissions. By following a few straightforward practices, you can enhance the reliability of your vehicle’s fuel system.
1. Regular Fuel Filter Replacement
The fuel filter plays a crucial role in keeping impurities out of the fuel system. Over time, it can become clogged, affecting fuel flow and performance. It is advisable to replace the fuel filter at regular intervals, as recommended in the vehicle’s specifications. This simple task can significantly improve fuel efficiency and engine responsiveness.
2. Inspect Fuel Lines and Connections
Check for any signs of wear, cracks, or leaks in the fuel lines and connections. Damaged components can lead to fuel leaks, which are hazardous and can impair engine performance. Ensure all fittings are tight and secure. If any issues are detected, replace the damaged parts promptly to maintain safety and functionality.
Regular maintenance of the fuel system is key to ensuring that your vehicle operates smoothly and efficiently. By incorporating these tips into your routine, you can prevent potential problems and enjoy a reliable driving experience.
Testing Engine Performance After Repair
Assessing the functionality of a vehicle’s power unit following maintenance is crucial to ensure optimal operation. This process involves a series of evaluations that provide insights into how effectively the system performs under various conditions.
Initial Diagnostics
Begin with a thorough diagnostics check. Utilize specialized tools to measure parameters such as compression levels, fuel efficiency, and exhaust emissions. This initial assessment helps identify any lingering issues that may affect performance.
Road Testing
Conduct a practical evaluation through road tests. Pay attention to acceleration, stability, and responsiveness. Observing the behavior of the vehicle under different driving scenarios will ultimately reveal the success of the undertaken tasks.
Regular monitoring of performance metrics is essential for long-term reliability. Documenting findings aids in future assessments and highlights areas needing attention, ensuring the unit remains in peak condition.