This section serves as a valuable resource for individuals seeking to enhance their understanding of compact loader upkeep. It aims to provide practical insights into the essential practices and troubleshooting methods necessary for optimal performance and longevity of the machinery.
By familiarizing oneself with the intricacies of this equipment, operators can ensure not only its efficient operation but also its safety. This guide will cover a variety of topics, including routine inspections, common issues, and effective solutions, equipping users with the knowledge to maintain their machinery effectively.
Understanding the importance of regular maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of the equipment. Whether you are a seasoned professional or a novice, this guide will offer you the tools and techniques needed to address potential challenges, thereby maximizing productivity and minimizing downtime.
This section provides a comprehensive introduction to a well-known compact construction vehicle. It highlights its design, functionality, and versatility, making it a valuable asset in various tasks, from landscaping to heavy lifting. The aim is to equip operators with essential knowledge for efficient usage and troubleshooting.
Key Features and Specifications
This subsection outlines the main attributes and technical details that define this robust machinery.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Engine Type | Diesel |
| Operating Weight | Approximately 1,500 lbs |
| Horsepower | 20 HP |
| Hydraulic Flow | 10 GPM |
Applications and Uses
Understanding the various scenarios in which this machine excels is crucial for maximizing its potential. It is suitable for a wide range of operations, ensuring efficiency in construction, agricultural tasks, and landscape management.
Common Issues and Symptoms
Understanding the typical problems and their corresponding signs is essential for effective troubleshooting of compact machinery. Recognizing these indicators can facilitate timely interventions and prevent more extensive damage. This section highlights prevalent complications and the symptoms that may arise, allowing operators to address issues promptly.
Engine Performance Problems
One of the most frequent concerns is related to engine efficiency. Operators may notice unusual noises or vibrations, indicating potential mechanical failures. Additionally, if the machine struggles to start or shows a significant drop in power, it may be a sign of underlying issues with fuel delivery or ignition systems.
Hydraulic System Malfunctions
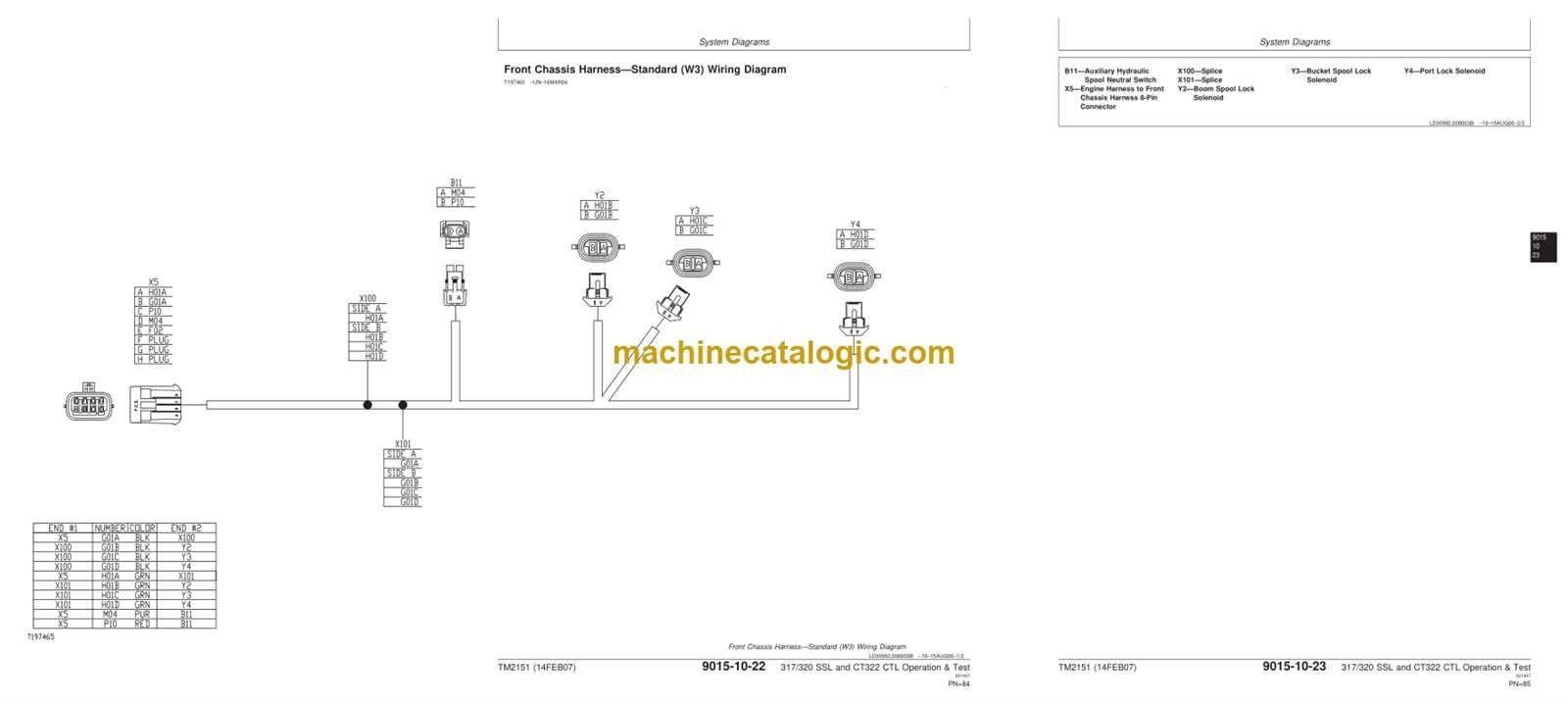
Hydraulic functionality is crucial for optimal operation. Symptoms such as slow or unresponsive movements of the attachments can signal issues with hydraulic fluid levels or pump integrity. Moreover, leaks or visible damage to hoses can lead to compromised performance, necessitating immediate attention to ensure safety and efficiency.
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
Ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your equipment requires consistent attention and care. Proper upkeep not only enhances functionality but also prevents unexpected breakdowns. This section provides essential guidelines to maintain peak performance and extend the life of your machinery.
Regular Inspection

- Check fluid levels regularly, including oil, coolant, and hydraulic fluids.
- Inspect filters and replace them as necessary to ensure clean operation.
- Examine belts and hoses for wear, cracking, or leaks.
Cleaning and Lubrication
- Clean the exterior to remove dirt and debris that can cause overheating.
- Lubricate moving parts according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Ensure that all pivot points and joints are properly greased to reduce friction.
By following these maintenance tips, you can achieve optimal performance and reliability from your equipment, minimizing the risk of costly repairs and maximizing productivity.
Essential Tools for Repairs
Having the right equipment is crucial for maintaining and fixing compact machinery. Proper tools not only facilitate efficient work but also ensure safety during tasks. This section outlines the indispensable implements that every technician should have on hand.
Basic Hand Tools

- Wrenches: Various sizes for different fasteners.
- Screwdrivers: Both flathead and Phillips types.
- Socket Set: For loosening and tightening bolts.
- Pliers: Useful for gripping, twisting, and cutting wires.
- Utility Knife: Essential for cutting through various materials.
Specialized Equipment

- Torque Wrench: Ensures fasteners are tightened to the correct specifications.
- Diagnostic Tools: Electronic devices for troubleshooting performance issues.
- Hydraulic Jack: Necessary for lifting heavy components safely.
- Grease Gun: For applying lubrication to moving parts.
- Cleaning Supplies: Such as brushes and solvents for maintenance.
Equipping yourself with these fundamental and specialized tools will greatly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of any maintenance tasks.
Engine Troubleshooting Guide
This section provides essential insights into diagnosing common issues related to engine performance. Understanding these problems can lead to effective solutions and ensure optimal functioning of the equipment.
1. Start-Up Issues: If the engine fails to start, check the battery voltage and connections. Ensure the fuel system is functioning correctly and there is adequate fuel supply.
2. Overheating: Monitor the temperature gauge. Overheating may indicate low coolant levels, a malfunctioning thermostat, or a blocked radiator. Regularly inspect these components to prevent severe damage.
3. Unusual Noises: Pay attention to any strange sounds during operation. A knocking noise may suggest a lack of lubrication, while a high-pitched squeal could indicate a worn belt or pulley.
4. Reduced Power: If the engine exhibits a lack of power, check for air filter blockages and ensure the fuel injectors are clean. Clogged filters can restrict airflow and fuel delivery, affecting performance.
5. Exhaust Smoke: Different colors of smoke can indicate various issues. Blue smoke often suggests oil burning, while black smoke can indicate an overly rich fuel mixture. Identifying the smoke color can help in pinpointing the problem.
By systematically addressing these common issues, operators can maintain peak engine performance and extend the lifespan of their machinery.
Hydraulic System Check Procedures
The hydraulic mechanism plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient operation of various machinery. Proper assessment of this system is essential to maintain functionality and prevent potential issues. This section outlines the essential steps to evaluate the hydraulic components effectively.
1. Visual Inspection: Begin with a thorough examination of the hydraulic lines, fittings, and connections. Look for any signs of wear, leaks, or damage. Pay attention to the condition of hoses and ensure that all connections are secure.
2. Fluid Level Check: Verify the hydraulic fluid level in the reservoir. Ensure it meets the manufacturer’s recommended specifications. If the fluid is low, refill it with the appropriate type to prevent air from entering the system.
3. Fluid Quality Assessment: Examine the hydraulic fluid for contamination. Check for discoloration, sediment, or a burnt smell. If the fluid appears dirty or degraded, consider replacing it to maintain optimal performance.
4. Pressure Testing: Use a gauge to measure the hydraulic pressure while the system is operating. Compare the readings with the specifications provided for the equipment. Any significant deviation may indicate underlying issues that require attention.
5. Functionality Test: Activate various hydraulic functions and observe their performance. Listen for unusual noises and check for responsiveness. Irregular operation can signal problems within the hydraulic system that need addressing.
By following these procedures, operators can ensure the hydraulic system remains in peak condition, promoting safety and efficiency in equipment operation.
Electrical Components Diagnostics
This section provides essential insights into the evaluation and troubleshooting of electrical elements within the equipment. Proper diagnosis of electrical issues is crucial for ensuring optimal functionality and preventing further complications.
Common Symptoms of Electrical Failures
Recognizing the signs of electrical malfunctions is the first step toward effective resolution. Below are typical indicators that may suggest issues with electrical components:
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Inconsistent operation | Faulty wiring or connectors |
| Non-responsive controls | Defective switches or relays |
| Dim or flickering lights | Weak battery or poor connections |
Diagnostic Procedures
Implementing systematic testing methods is essential for accurate diagnostics. Follow these steps to assess electrical components effectively:
- Check battery voltage and connections.
- Test circuit continuity using a multimeter.
- Inspect connectors for corrosion or damage.
- Verify the functionality of switches and relays.
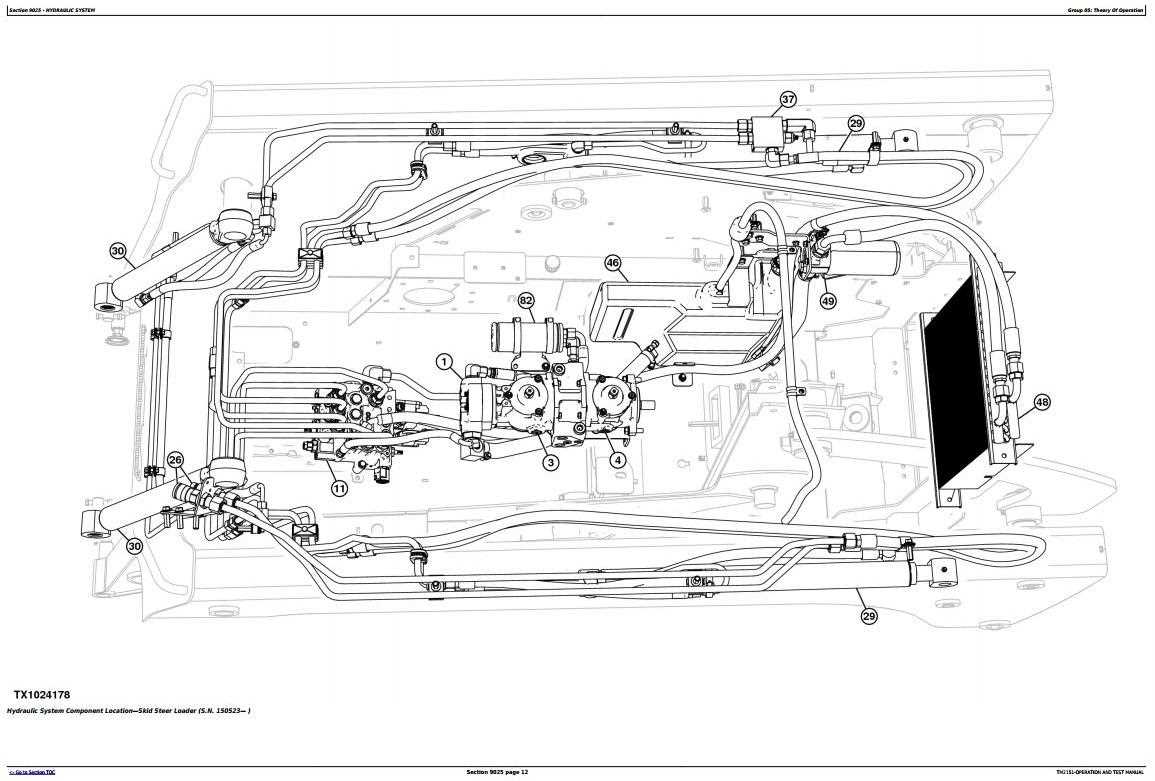
Transmission and Drive System Insights

The efficiency and reliability of any machinery largely depend on its propulsion and transmission systems. These components play a crucial role in converting engine power into effective movement, ensuring optimal performance under various operational conditions. Understanding their functionality can significantly enhance maintenance practices and operational longevity.
Transmission Systems are designed to manage the distribution of power from the engine to the wheels or tracks. This intricate mechanism involves various gears and hydraulic elements that work in harmony to provide smooth acceleration and deceleration. Regular checks and adjustments of these systems are essential to prevent wear and tear that could lead to costly breakdowns.
Drive Mechanisms are equally vital, as they determine the traction and maneuverability of the equipment. These systems often include components such as axles, bearings, and drive belts, which must be maintained meticulously to ensure seamless operation. Routine inspections can help identify potential issues early, allowing for timely interventions that keep the machinery running efficiently.
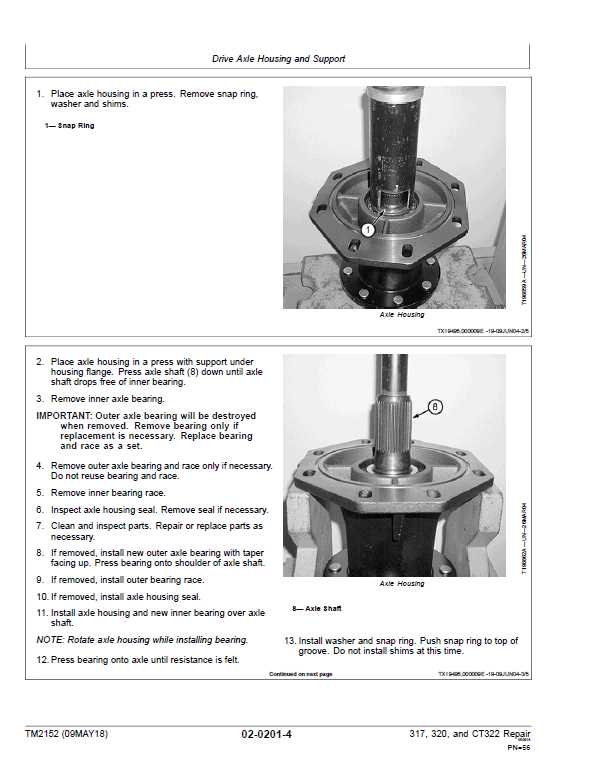
Replacing Wear Parts Efficiently
Maintaining optimal performance in machinery requires regular attention to components that experience wear over time. Efficiently replacing these parts not only enhances the equipment’s longevity but also minimizes downtime. This section explores strategies to streamline the process of substituting worn components, ensuring your machinery operates at peak efficiency.
Identifying Worn Components

The first step in the replacement process is recognizing which parts need attention. Regular inspections can help identify signs of wear, such as cracks, deformities, or decreased functionality. Keeping a maintenance log can also aid in tracking the lifespan of various components.
Steps for Efficient Replacement

Following a systematic approach when replacing components can save time and effort. Here are essential steps to consider:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Gather necessary tools and parts before starting to ensure a smooth workflow. |
| 2 | Carefully remove the worn part, following safety protocols to avoid accidents. |
| 3 | Install the new component, ensuring it is correctly aligned and secured. |
| 4 | Test the machinery to verify that the new part is functioning as intended. |
By adhering to these practices, operators can ensure a more efficient and effective replacement process, ultimately contributing to the overall performance and reliability of their equipment.
Safety Precautions During Repairs
When engaging in maintenance tasks on machinery, it is crucial to prioritize safety to prevent accidents and ensure a secure working environment. Adhering to proper safety measures can significantly reduce the risk of injury and enhance the effectiveness of the work being performed.
Essential Safety Gear
Always wear appropriate protective equipment, such as gloves, safety goggles, and sturdy footwear. This gear serves as a barrier against potential hazards, including sharp components and flying debris. Regularly inspect your safety gear for wear and tear to guarantee optimal protection.
Work Area Preparation

Before starting any task, ensure that the workspace is clean and free of obstacles. Maintain good ventilation to prevent the accumulation of harmful fumes. Keep all tools organized and within reach to minimize distractions during the process. Remember, a tidy environment contributes to a safer and more efficient workflow.
Finding Replacement Parts Easily
Locating suitable components for machinery maintenance can often seem daunting. However, with the right approach and resources, the process can be streamlined significantly, ensuring that your equipment remains operational with minimal downtime.
Utilizing Online Resources
The internet offers a plethora of options for sourcing parts. Here are some effective strategies:
- Official Websites: Check the manufacturer’s official site for parts catalogs and online ordering systems.
- Third-Party Retailers: Many specialized online retailers provide a wide range of components, often at competitive prices.
- Forums and Community Groups: Engaging with online forums can lead to valuable insights and recommendations from experienced users.
Local Suppliers and Dealerships

In addition to online sources, local options can be very beneficial:
- Authorized Dealers: These outlets often have a comprehensive inventory of parts specific to your equipment.
- Local Auto Parts Stores: Some stores may carry compatible components or be able to order them for you.
- Networking with Technicians: Building relationships with local service professionals can provide access to reliable suppliers and advice on the best parts to use.
Service Schedule Recommendations
Maintaining optimal performance and longevity of your machinery requires adherence to a structured service timetable. Regular inspections and maintenance activities not only enhance functionality but also prevent unexpected breakdowns, ensuring reliability during operation.
Below are key recommendations for scheduling maintenance tasks:
- Daily Checks:
- Inspect fluid levels (engine oil, hydraulic fluid, coolant).
- Check for leaks and overall machine cleanliness.
- Examine tires for proper inflation and wear.
- Weekly Maintenance:
- Clean or replace air filters as necessary.
- Tighten all loose bolts and fasteners.
- Lubricate moving parts to ensure smooth operation.
- Monthly Service:
- Inspect hydraulic hoses and connections for signs of wear.
- Change engine oil and oil filters.
- Check battery terminals for corrosion and clean as needed.
- Annual Maintenance:
- Conduct a thorough inspection of the entire system.
- Replace worn components to prevent future issues.
- Review safety features and ensure they are functioning properly.
Following these recommendations will help maintain the efficiency and safety of your equipment, ultimately extending its operational lifespan.