
In the world of temperature-sensitive storage solutions, ensuring optimal functionality is crucial for preserving quality and extending the lifespan of your assets. This section delves into essential techniques and insights for maintaining these vital systems, enabling users to confidently address common issues and enhance operational efficiency.
Understanding the intricacies of these systems can greatly reduce downtime and minimize financial losses. By familiarizing yourself with various components and their roles, you can quickly identify symptoms of malfunction and implement effective strategies to resolve them. Knowledge in this area empowers you to tackle challenges head-on, ensuring seamless operations in any environment.
Additionally, this guide provides a wealth of practical tips and systematic approaches to troubleshooting. Whether you are a seasoned professional or a novice, the information presented here will equip you with the skills needed to maintain peak performance and avoid potential pitfalls. Embrace the opportunity to deepen your understanding and improve your expertise in this essential field.
Understanding Commercial Refrigeration Systems
This section delves into the intricacies of temperature control mechanisms used in various businesses, emphasizing their importance for preserving products and ensuring operational efficiency.
These systems are essential in numerous industries, providing reliable solutions for maintaining optimal conditions. They utilize advanced technology to manage temperature and humidity levels effectively.
Key components include:
- Compressors: Responsible for circulating refrigerant through the system.
- Evaporators: Allow heat absorption from the environment.
- Condensers: Release absorbed heat, converting refrigerant back to a liquid state.
- Expansion Valves: Control the flow of refrigerant within the system.
Understanding the function of each component is crucial for efficient operation. Regular maintenance can enhance performance and prolong the lifespan of these systems. Here are some common maintenance practices:
- Regularly cleaning coils to ensure efficient heat exchange.
- Checking refrigerant levels to prevent leaks.
- Inspecting electrical connections for safety and performance.
- Testing thermostat settings for accuracy.
Familiarity with these elements and maintenance practices allows for better management of the systems, ensuring they operate effectively and reliably throughout their lifespan.
Common Issues in Refrigeration Units
Understanding the typical challenges faced by cooling systems is essential for maintaining efficiency and longevity. Various factors can lead to malfunctions, resulting in compromised performance and increased energy costs. Identifying these issues early can prevent further damage and ensure optimal operation.
Temperature Fluctuations
One frequent problem is inconsistent temperature levels. This can be caused by faulty thermostats, blocked air vents, or malfunctioning compressors. Such fluctuations not only affect the quality of stored items but can also lead to increased energy consumption as the system works harder to maintain desired conditions.
Unusual Noises
Another common concern is the presence of strange sounds coming from the unit. Noises like grinding, hissing, or buzzing may indicate issues with components such as fans, motors, or the compressor itself. These sounds can signal that a part may need maintenance or replacement to avoid more serious failures.
Tools Needed for Effective Repairs

To achieve successful outcomes in maintaining and restoring cooling systems, having the right instruments at your disposal is crucial. Proper tools not only enhance efficiency but also ensure safety and precision during the maintenance process.
Essential Instruments
Among the basic instruments, a reliable multimeter is indispensable for diagnosing electrical issues. Additionally, a good set of wrenches and screwdrivers is necessary for assembling and disassembling components effectively. These tools allow for quick adjustments and facilitate access to various parts.
Advanced Equipment
For more complex challenges, consider investing in specialized gauges that monitor pressure and temperature. A vacuum pump is also essential for removing moisture and contaminants from the system. Ensuring you have a complete toolkit will significantly enhance your ability to address various issues efficiently and effectively.
Safety Precautions During Repair Work
Ensuring safety during maintenance tasks is paramount. Adhering to specific guidelines helps mitigate risks and fosters a secure environment for both technicians and equipment. This section outlines essential measures to take when engaging in service activities.
Personal Protective Equipment
Utilizing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial. Safety glasses should always be worn to shield eyes from debris and chemical splashes. Gloves are essential to protect hands from sharp objects and hazardous substances. In addition, steel-toed boots can prevent foot injuries from falling materials.
Work Area Safety
Maintaining a tidy workspace is vital for preventing accidents. Ensure that all tools are organized and easily accessible. Keep pathways clear to avoid tripping hazards. It is also important to properly ventilate the area to reduce the risk of inhaling harmful fumes or gases, especially when handling chemicals or working with appliances that may emit hazardous substances.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
This section provides a systematic approach to identifying and resolving issues that may arise in cooling systems. By following these organized steps, technicians can efficiently diagnose problems and implement solutions, ensuring optimal performance.
- Identify the Symptoms:
- Check for unusual noises.
- Monitor temperature inconsistencies.
- Observe any error codes displayed.
- Gather Necessary Tools:
- Multimeter
- Thermometer
- Wrenches and screwdrivers
- Perform Visual Inspection:
- Look for leaks or damaged components.
- Ensure that all connections are secure.
- Examine the airflow for blockages.
- Check Power Supply:
- Verify that the unit is plugged in.
- Inspect circuit breakers and fuses.
- Confirm voltage levels are appropriate.
- Test Major Components:
- Examine the compressor for functionality.
- Assess the condenser and evaporator coils.
- Evaluate the thermostat settings and functionality.
- Consult Documentation:
- Refer to system specifications.
- Check troubleshooting charts for specific models.
- Look for any service bulletins related to known issues.
- Implement Solutions:
- Repair or replace faulty components.
- Clear any blockages affecting airflow.
- Adjust settings as necessary.
- Test the System:
- Run the unit to check for proper operation.
- Monitor performance for a specified period.
- Confirm that the issue has been resolved.
By adhering to this guide, technicians can systematically tackle issues and restore functionality, ensuring efficient operation of the cooling system.
Understanding Refrigerant Types and Uses
Refrigerants play a crucial role in the cooling process, enabling systems to effectively transfer heat and maintain desired temperatures. Different types of these substances are designed for various applications, each with unique properties that affect performance, efficiency, and environmental impact. Gaining insight into the various categories can enhance system functionality and longevity.
Common Types of Refrigerants
There are several primary categories of these cooling agents, including chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). CFCs, once widely used, are now largely phased out due to their adverse effects on the ozone layer. HCFCs were introduced as transitional substitutes but are also being limited for similar reasons. HFCs emerged as alternatives that are less harmful to the environment, though they still pose some challenges in terms of global warming potential.
Applications and Considerations
When selecting the appropriate cooling agent, factors such as efficiency, temperature range, and environmental impact must be considered. Some substances are better suited for low-temperature applications, while others excel in high-temperature scenarios. Understanding these distinctions is vital for optimizing performance and ensuring compliance with current regulations. Ultimately, choosing the right type contributes to both operational efficiency and sustainability efforts.
Maintaining Your Refrigeration Equipment
Proper upkeep of cooling devices is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Regular attention can prevent costly breakdowns and ensure that your systems operate efficiently, providing the necessary conditions for your products.
Key Maintenance Practices
- Regular Inspections: Check for any signs of wear, leaks, or unusual noises.
- Clean Coils: Ensure that the condenser and evaporator coils are free of dirt and debris to enhance heat exchange.
- Check Seals: Inspect door seals for integrity to maintain temperature and reduce energy consumption.
- Monitor Temperature: Regularly verify that internal temperatures remain within recommended ranges.
- Drain Maintenance: Ensure that drain lines are clear to prevent water buildup and possible damage.
Tips for Efficient Operation
- Keep the area around the equipment clear to allow proper airflow.
- Avoid overloading the unit, as this can strain the system.
- Use energy-efficient practices to reduce operational costs.
- Schedule professional service regularly to address any complex issues.
- Stay informed about manufacturer recommendations for specific models.
By following these guidelines, you can help ensure that your cooling systems remain in peak condition, providing reliable service and saving on repair costs in the long run.
How to Diagnose Temperature Problems
Identifying issues related to temperature control in cooling systems can significantly enhance their efficiency and lifespan. This section focuses on systematic approaches to pinpointing temperature anomalies, ensuring optimal performance and preventing further complications.
Common Symptoms of Temperature Issues
Before diving into diagnostics, it’s essential to recognize typical signs that indicate temperature inconsistencies. Familiarizing yourself with these symptoms can streamline the troubleshooting process.
| Symptom | Possible Causes |
|---|---|
| Inadequate cooling | Blocked airflow, malfunctioning thermostat |
| Excessive cooling | Thermostat miscalibration, refrigerant overcharge |
| Temperature fluctuations | Faulty sensors, improper door sealing |
Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process
To accurately determine the underlying cause of temperature problems, follow a structured diagnostic procedure:
- Observe the unit’s operation and note any irregular sounds or behaviors.
- Check the settings on the control panel for accuracy.
- Inspect airflow pathways for obstructions.
- Evaluate the performance of key components such as compressors and fans.
- Utilize testing tools to measure temperature and pressure at critical points.
By employing these methods, you can effectively isolate the source of temperature-related issues and take appropriate corrective actions.
Electrical Components and Their Functions
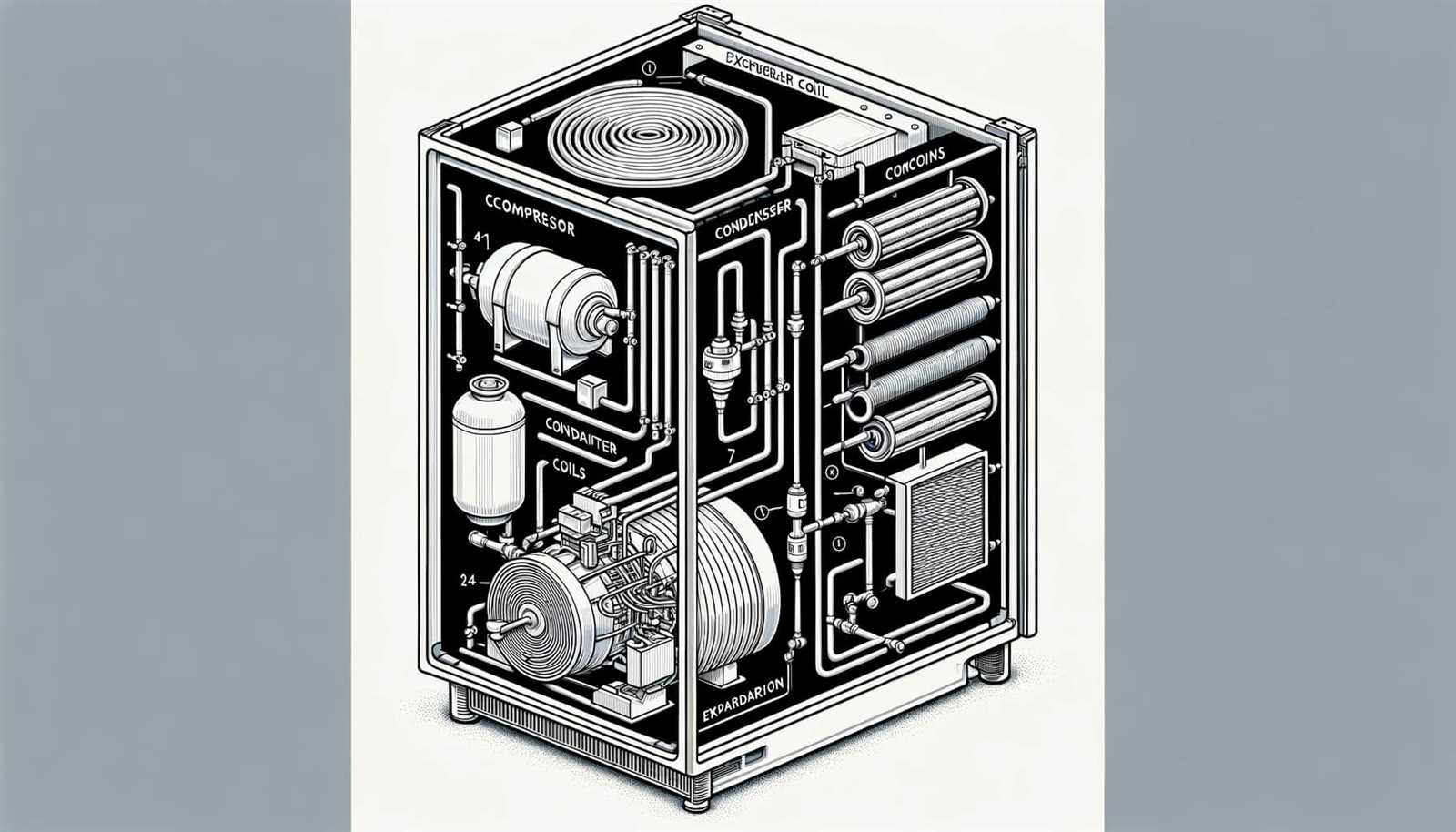
Understanding the various electrical parts in cooling systems is essential for effective operation and maintenance. Each component plays a critical role in ensuring that the system runs smoothly, delivering optimal performance while maintaining energy efficiency. This section will explore the key elements and their specific functions, providing insight into their importance in the overall functionality of these systems.
Power Supply and Distribution
The power supply is the lifeline of any electrical system, providing the necessary energy to all components. It consists of circuits, wires, and connectors that distribute electricity throughout the unit. Transformers may also be included to adjust voltage levels, ensuring that other parts receive the correct amount of power. Proper maintenance of these components is vital to prevent disruptions in energy flow.
Control and Safety Devices
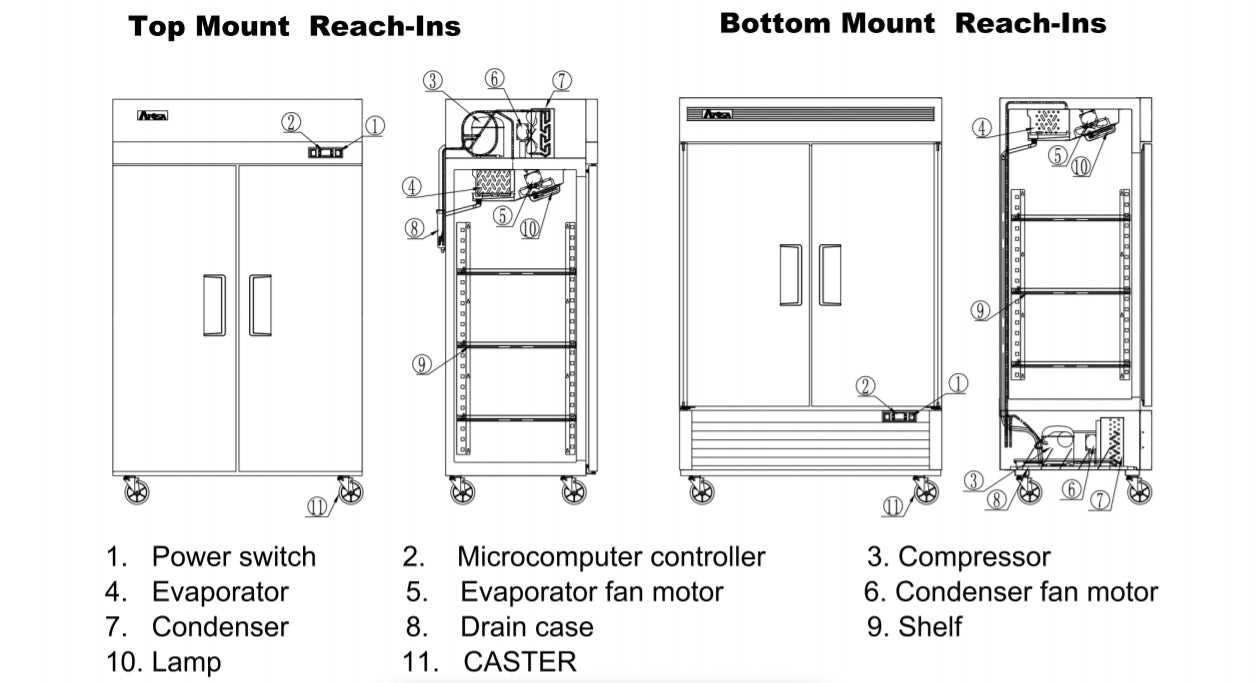
Control devices, such as thermostats and timers, regulate the temperature and operating cycles of the system. These elements allow for automated adjustments based on preset conditions. Safety devices, including fuses and circuit breakers, protect the system from electrical faults, preventing potential damage or hazards. Understanding how these devices work together ensures reliability and safety in operation.
Cleaning and Maintaining Condenser Coils
Proper upkeep of heat exchange components is crucial for optimal performance and energy efficiency. Regular cleaning ensures that these parts function effectively, preventing unnecessary strain on the entire system.
Here are essential steps to follow for cleaning and maintaining these vital components:
- Safety First:
- Disconnect the power supply to avoid accidents.
- Wear protective gear, including gloves and goggles.
- Initial Inspection:
- Check for visible dirt, debris, and damage.
- Look for signs of corrosion or wear on the coils.
- Cleaning the Coils:
- Use a soft brush or vacuum to remove loose dirt.
- For stubborn grime, apply a gentle coil cleaner and follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Flushing the Coils:
- Rinse the coils with water, ensuring all cleaner is removed.
- Use a hose with a spray nozzle for even distribution.
- Final Inspection:
- Check for proper alignment and secure any loose parts.
- Ensure that the area around the coils is clear of obstructions.
Routine maintenance will prolong the lifespan of these components and enhance overall system efficiency. Aim to perform these tasks at least twice a year for best results.
Replacing Broken Parts: A Guide
When equipment malfunctions, it often requires the replacement of faulty components to restore functionality. Understanding the process of substitution is essential for efficient maintenance. This section will guide you through the necessary steps to identify, remove, and install new elements effectively.
Follow these steps for a successful replacement:
- Identify the Faulty Component:
- Inspect the system for visible signs of damage.
- Listen for unusual sounds that may indicate a malfunction.
- Check performance metrics to isolate the issue.
- Gather Required Tools and Parts:
- Ensure you have all necessary tools, such as wrenches and screwdrivers.
- Obtain the correct replacement part compatible with your system.
- Power Down the Equipment:
- Always disconnect the power source before starting any work.
- Wait for any residual energy to dissipate.
- Remove the Damaged Part:
- Carefully unscrew or unclip the broken element.
- Take note of the arrangement for easier installation of the new part.
- Install the New Component:
- Position the new part accurately according to the original setup.
- Tighten screws or clips securely to ensure stability.
- Power Up and Test:
- Reconnect the power source and turn on the equipment.
- Monitor the system for proper operation and check for any leaks or unusual sounds.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively address issues with damaged components and ensure that your system operates smoothly and efficiently.
Recognizing Signs of Compressor Failure
Identifying the early indicators of a malfunctioning unit is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. Recognizing these signs can prevent further damage and costly replacements. Below are common symptoms to watch for when assessing functionality.
- Unusual Noises: Listen for any grinding, clicking, or buzzing sounds that are not typical during operation.
- Overheating: A unit that feels excessively hot may indicate internal issues, such as electrical faults or blocked airflow.
- Frequent Cycling: If the unit turns on and off more often than usual, this could suggest a failing component.
- Inadequate Cooling: A noticeable decrease in cooling efficiency may signal compressor problems.
- Increased Energy Bills: Higher electricity costs can indicate that the system is working harder than it should due to compressor strain.
By keeping an eye out for these signs, you can address potential failures promptly, ensuring longevity and reliability.
Professional Services vs. DIY Repairs
When facing issues with cooling systems, individuals often find themselves at a crossroads: to hire a specialist or attempt to fix the problem themselves. This decision hinges on various factors, including expertise, time constraints, and the complexity of the malfunction. Understanding the pros and cons of each approach can help in making an informed choice.
| Aspect | Professional Services | DIY Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Expertise | Highly skilled technicians with specialized knowledge. | Varied skill levels; may lack advanced understanding. |
| Time Efficiency | Quick diagnostics and solutions, saving time. | Can be time-consuming, especially for inexperienced individuals. |
| Cost | Higher upfront costs, but often more reliable results. | Potentially lower expenses, but risks of recurring issues. |
| Safety | Trained to handle hazardous components safely. | May encounter dangerous elements without proper training. |
| Warranty | Often includes service guarantees. | No warranty on personal work, leading to further costs. |
Ultimately, the choice between professional help and self-service hinges on individual circumstances, weighing both immediate needs and long-term implications.