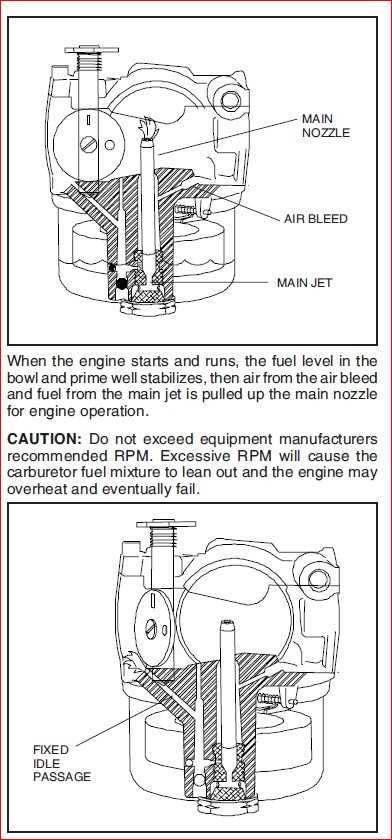
Understanding how to bring a two-stroke mechanism back to its optimal state can feel like unlocking a unique set of skills. The simplicity of the mechanism, combined with its efficient design, often makes it a popular choice for various machinery. However, when it begins to show signs of wear or decreased functionality, knowing the best steps to address these issues is essential for anyone looking to keep such systems running smoothly.
In this guide, we explore the fundamental techniques for diagnosing and addressing common issues that can arise within these compact systems. From examining essential components to ensuring proper function through routine upkeep, each section aims to equip you with practical insights. Whether you’re just starting or looking to deepen your knowledge, you’ll find approaches here tailored to meet various levels of experience.
With the right tools, a bit of patience, and a systematic approach, these straightforward mechanisms can be maintained and restored to their prime state. Here, you’ll uncover step-by-step strategies designed to give you a deeper understanding and mastery over every part of the process, ensuring that each aspect of care is clear and accessible.
Understanding the Basics of 2-Cycle Engines
In small machinery, there are mechanisms specially designed for simplicity and efficiency. These systems operate through a streamlined, continuous process that powers various equipment, from handheld tools to compact outdoor machines. Recognizing the foundational workings of these machines helps in grasping how they convert energy with remarkable ease, all while maintaining lightweight and robust functionality.
Key Components and Their Roles: At the core of this type of machinery lies a unique combination of parts, each contributing to a smooth transformation of power. The main sections include a combustion chamber, crankshaft, and essential ports, all working in unison to complete a power cycle within a minimal number of actions. Together, they enable fuel intake, compression, and release in a rapid, repeated sequence.
Fuel and Lubrication Mix: Unlike other motor types, these machines rely on a mixture that serves both as fuel and lubricant. This blend is vital, as it circulates throughout the system, ensuring each component moves with minimal friction. Without a separate lubrication mechanism, the blend must be precisely balanced to prevent wear, ensuring long-lasting operation and optimal performance.
Understanding how these mechanisms work not only helps in handling them more efficiently
Common Issues in Two-Stroke Engines
In small power systems that use rapid combustion cycles, maintaining peak performance can be challenging. A variety of issues can arise, often stemming from the high-speed dynamics and unique fuel mixtures these systems require. Understanding these common problems is essential for optimal functionality.
Poor Compression can lead to significant performance drops, often resulting from worn-out seals or rings. Reduced compression impacts overall efficiency and makes it harder for the system to maintain consistent power.
Excessive Smoke is another frequent issue, usually caused by improper fuel or oil ratios. If the fuel mix contains too much oil, or if lower-grade fuel is used, this can lead to dense exhaust smoke and carbon buildup.
Hard Starting often frustrates users, especially after extended use. This problem may be due to carburetor issues or spark plug fouling, both of which make it difficult to ignite the fuel mix effectively.
Overheating can result from clogged air intakes, insufficient lubrication, or prolonged operation at high speeds. Heat can damage internal parts, reducing both performance and lifespan if not addressed quickly.
Vibration and Noise increase as components wear down over time. Loose or degraded parts can contribute to in
Tools Needed for Effective Engine Repair
For a successful and efficient restoration process, having the right set of tools is essential. Proper tools not only ensure precision but also improve safety and save time. From basic hand implements to specialized measuring instruments, each item plays a crucial role in achieving professional-grade results.
Essential Hand Tools
Hand tools like wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers form the backbone of most restoration tasks. Socket sets of various sizes are also invaluable, allowing you to handle bolts and nuts of different diameters with ease. Using quality hand tools reduces the risk of damage to sensitive components and provides better grip and control during maintenance.
Diagnostic and Precision Instruments
Specialized diagnostic tools such as compression testers and torque wrenches are vital in assessing internal conditions and applying correct levels of force. Feeler gauges allow for accurate measurements of small gaps, ensuring that each part is correctly calibrated. These instruments contribute to a detailed inspection, helping identify issues that may not be visible to the naked eye.
Equipping yourself with these essential tools enhances both the speed and quality of your work, enabling you to tackle even complex tasks with confidence and precision.
Step-by-Step Engine Disassembly Guide
In this section, you’ll find detailed instructions on how to carefully take apart various parts of the mechanism, ensuring that each component is handled properly and set aside in an organized way. Following these steps will aid in a thorough assessment and facilitate accurate reassembly later.
1. Preparing the Workspace
Before starting, ensure you have a clean, well-lit area with all necessary tools nearby. Organize your workspace to avoid misplacing small parts or tools, and lay out a cloth or mat to catch any loose pieces. This preparation will make the task smoother and help prevent accidental damage to fragile parts.
2. Removing External Components
Begin by detaching any external parts, such as the cover and housing. Carefully unscrew and store these pieces in a labeled container. Make note of how each part connects, as this will be crucial during reassembly. Using a step-by-step approach will ensure that each piece is removed safely without undue force.
Next, continue by loosening the bolts and screws holding the main sections together. Gradual and even pressure will reduce the risk of damage. Pay special attention to smaller screws and washers, which can be easily misplaced. Keep each component grouped to avoid confusion later.
Inspecting Engine Components for Wear
Regular inspection of mechanical parts ensures longer service life and prevents unexpected breakdowns. Assessing wear allows for early detection of issues that might escalate if left unattended, maintaining reliable performance and efficiency over time.
To check for signs of wear, visually inspect each section, noting any unusual discoloration, deformation, or residue. A physical examination helps identify issues that may not be visible to the eye, such as looseness in connected areas.
| Component | Inspection Point | Signs of Wear | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piston | Surface and edge | Scratches, scoring, or heat marks | |
| Crankshaft | Journals and bearings | Metal flakes, pitting, or excessive movement | |
| Cylinder | Inner wall | Scoring, cracks, or worn surfaces | |
| Connecting Rod | Bolt and bearing areas | Bent structure or loose fit |
| Cleaning Method | Best For | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasonic Cleaning | Intricate parts | Thorough cleaning, reaches crevices | Equipment cost can be high |
| Solvent Cleaning | Greasy components | Effective on oil and grease | Potentially harmful fumes |
| Pressure Washing | External surfaces | Fast and efficient for large areas | Risk of damaging sensitive parts |
| Manual Scrubbing | Heavy deposits | Control over cleaning process | Labor-intensive and time-consuming |
| Steam Cleaning | General dirt and grime | Eco-friendly, sanitizes surfaces | Requires careful handling to avoid water damage |
Choosing the appropriate cleaning technique depends on the specific needs of the components being serviced. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each method will lead to better maintenance practices and improved overall performance.
Reassembly Tips for Two-Stroke Engines
Reassembling a two-stroke power unit requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Following systematic procedures can help avoid common pitfalls and enhance the efficiency of the assembly process. This section provides valuable insights into the essential steps and best practices for successful reassembly.
Preparation Steps

Before diving into the assembly, ensure that all components are clean and free from debris. Organize parts systematically to streamline the reassembly process. Here are some recommended preparatory actions:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Inspect all parts for wear and damage. |
| 2 | Clean components with appropriate solvents. |
| 3 | Gather necessary tools and lubricants. |
Assembly Techniques
During the assembly phase, precision is paramount. Implement the following techniques to enhance the quality of your work:
- Align parts accurately to avoid misfits.
- Use lubricants sparingly on moving components.
- Tighten fasteners to specified torque settings to prevent loosening.
Proper Lubrication for Smooth Engine Operation
Effective lubrication is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of any mechanical system. By maintaining proper fluid levels and selecting the right type of lubricant, one can significantly reduce friction and wear on critical components, allowing for seamless functionality.
Regularly monitoring and changing the lubricant is crucial in preventing the buildup of contaminants that can hinder performance. The choice of lubricant should be based on the specific requirements of the system, including temperature range and operating conditions. High-quality fluids can enhance efficiency and minimize the risk of overheating.
It is also important to ensure that all moving parts receive adequate coverage. Implementing a routine maintenance schedule that includes checking levels and replacing fluids will contribute to the overall health of the system. Attention to these details can lead to improved performance and a reduction in costly failures.
Testing the Engine After Repairs
Once the necessary modifications have been completed, it is crucial to evaluate the performance of the unit to ensure that everything operates smoothly. This assessment helps identify any lingering issues that may need attention and confirms the successful restoration of functionality.
Initial Start-Up
Begin by starting the unit in a controlled environment. Listen for any unusual sounds that may indicate improper functioning. Pay close attention to vibrations and emissions, as these can provide insights into the overall health of the mechanism. It is advisable to allow the machine to idle for a short period to observe how it behaves without any load.
Performance Evaluation
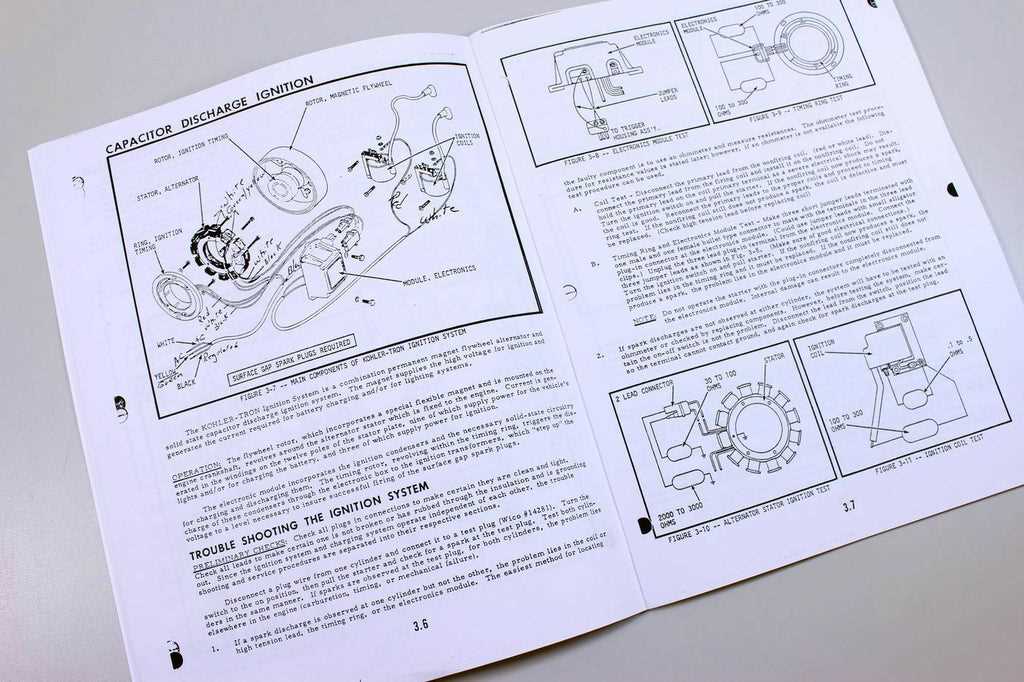
After the initial start-up, gradually increase the load to assess performance under operational conditions. Monitor key parameters such as temperature and pressure to ensure they remain within acceptable ranges. Conducting this evaluation allows for early detection of any issues that could compromise efficiency or safety.
In summary, thorough testing following modifications is essential for ensuring optimal functionality and longevity of the unit. Proper assessment techniques can significantly enhance reliability and performance.
Maintenance Tips for Long-Lasting Engine Health
Proper upkeep is essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of any power unit. Implementing regular maintenance practices not only enhances efficiency but also prevents potential issues from escalating into significant problems. Below are key strategies to maintain optimal functionality.
Regular Inspection and Cleaning

Frequent examination and cleaning are crucial in identifying wear and tear before they become serious concerns. Consider the following:
- Check all fluid levels and replace fluids as needed.
- Inspect and clean filters to ensure optimal air and fuel flow.
- Look for signs of leakage or corrosion in components.
Proper Fuel Usage
The quality of fuel directly impacts performance. Adhere to these guidelines:
- Use high-quality fuel to prevent residue buildup.
- Store fuel properly to avoid contamination.
- Be mindful of the recommended octane rating for your specific model.