
Maintaining the functionality and longevity of machinery requires a thorough understanding of its inner workings. This guide aims to provide detailed insights into the processes involved in servicing and troubleshooting complex systems. By following the outlined steps, users can ensure optimal performance and reduce the likelihood of costly breakdowns.
Within this resource, you will find a wealth of information tailored for individuals looking to enhance their technical skills. Each section is designed to simplify the intricacies of system upkeep, offering practical tips and guidance. Whether you are a novice or an experienced technician, this compilation serves as a valuable reference.
By mastering the art of maintenance, you not only extend the life of your machinery but also improve its efficiency. Understanding common issues and their solutions can save time and resources, making it essential for anyone involved in the operation of heavy equipment. Dive into this comprehensive guide to empower yourself with the knowledge necessary for effective management and care.
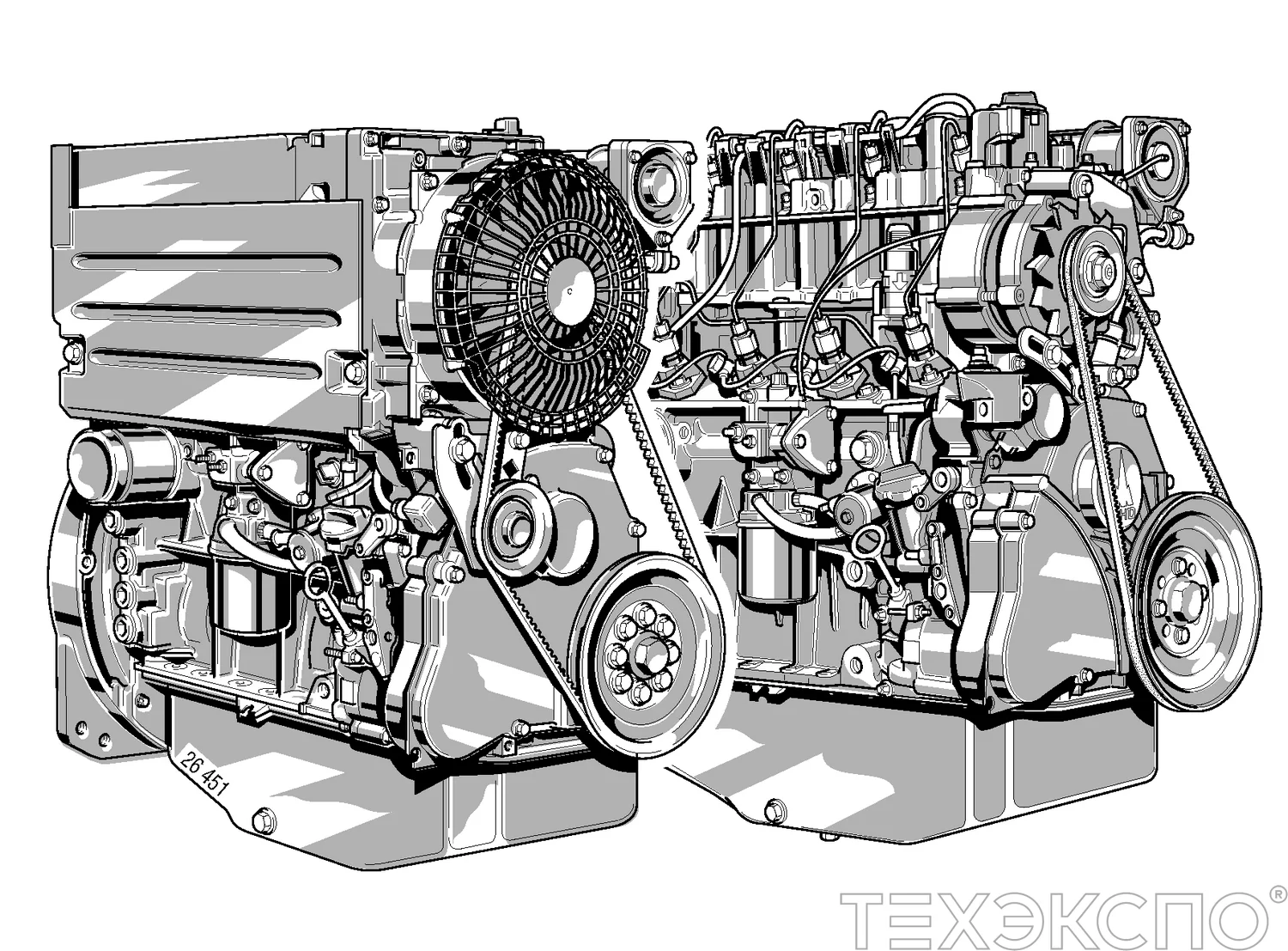
Understanding the Deutz F3L1011 Engine
This section delves into the intricacies of a specific power unit, highlighting its design, functionality, and maintenance aspects. Recognizing the significance of such machinery in various applications allows for better performance and longevity, ensuring that users can operate their equipment efficiently.
Core Features: The power unit is characterized by its robust construction and reliability. With a multi-cylinder configuration, it offers a balanced power output, making it suitable for heavy-duty tasks. Its compact design enables easy integration into various types of machinery, providing versatility across different industries.
Operating Principles: Understanding how this machinery functions is essential for optimal use. The core operation involves the transformation of fuel into mechanical energy through a series of controlled explosions. This process is enhanced by advanced timing mechanisms and efficient fuel injection systems, contributing to its effectiveness and reduced emissions.
Maintenance Importance: Regular upkeep is crucial for sustaining performance. Routine checks and timely servicing can prevent potential issues, extending the lifespan of the unit. Users should familiarize themselves with common maintenance practices, such as fluid level monitoring, filter replacements, and overall system inspections.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of this specific power unit not only improves operational efficiency but also empowers users to make informed decisions regarding its use and care. By investing time in learning about its features and functions, operators can enhance their productivity and ensure reliability in their equipment.
Common Issues with Deutz F3L1011
When operating machinery powered by a particular model, several problems may arise that can hinder performance and efficiency. Identifying these common complications early can prevent more extensive damage and costly repairs. Below are some frequently encountered issues and their potential causes.
- Overheating: This can be caused by inadequate coolant levels, a malfunctioning thermostat, or a blocked radiator.
- Starting difficulties: Issues such as weak batteries, faulty starter motors, or fuel delivery problems can lead to failure to start.
- Excessive smoke: Black, blue, or white smoke can indicate issues ranging from improper fuel mixture to oil burning.
- Noisy operation: Unusual sounds may signal worn bearings, loose components, or issues with the exhaust system.
Regular maintenance and timely diagnostics are crucial in mitigating these issues. Keeping a close eye on performance metrics can also aid in identifying early signs of trouble.
- Monitor fluid levels regularly.
- Conduct routine inspections of the cooling system.
- Check electrical connections and components.
- Maintain proper fuel quality and delivery.
Addressing these concerns promptly can enhance longevity and reliability, ensuring optimal functionality for your equipment.
Essential Tools for Engine Repair
Having the right instruments at your disposal is crucial for tackling any mechanical project effectively. Properly chosen tools not only enhance your efficiency but also ensure that every task is performed with precision and safety. Understanding which items are essential can make a significant difference in the outcome of your work.
Basic Hand Tools

At the foundation of any mechanical endeavor are hand tools. A comprehensive toolkit should include a variety of wrenches, sockets, and screwdrivers. Ratchet wrenches and combination wrenches are indispensable for loosening and tightening fasteners. Additionally, having a selection of Phillips and flathead screwdrivers will prepare you for various tasks. Don’t forget pliers and a dependable hammer, which can assist in numerous situations.
Specialized Equipment
Beyond basic tools, certain specialized equipment is necessary for more intricate tasks. A torque wrench ensures that fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications, while a compression tester can diagnose potential issues with cylinders. An oil filter wrench is also vital for maintaining proper fluid levels. Investing in these tools can significantly streamline your work process and lead to better results.
Step-by-Step Maintenance Guide
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive approach to maintaining your machinery, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. By following these systematic steps, you can identify potential issues early and keep your equipment in top condition.
1. Preparation
- Gather necessary tools and materials, including wrenches, oil, filters, and cleaning supplies.
- Review the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines for your specific model.
- Ensure the working environment is clean and safe.
2. Routine Checks
- Inspect fluid levels regularly, including oil, coolant, and fuel.
- Check for leaks or signs of wear in hoses and connections.
- Examine air filters and replace them if necessary.
- Look for loose bolts and tighten them as needed.
By adhering to this structured maintenance schedule, you can significantly enhance the efficiency and reliability of your machinery, reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns.
Identifying Engine Components
Understanding the various parts of a power unit is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Each component plays a significant role in the overall functionality, and recognizing them can aid in diagnosing issues and ensuring optimal performance.
Below are the primary components typically found in such machinery:
- Block: The main structure housing the critical parts and providing support.
- Cylinder Head: Covers the cylinders and contains intake and exhaust valves.
- Piston: Moves within the cylinder to convert energy from combustion into mechanical work.
- Crankshaft: Transforms the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotational motion.
- Camshaft: Operates the opening and closing of the valves at the correct timing.
- Fuel Injector: Delivers fuel into the combustion chamber for efficient burning.
- Exhaust Manifold: Collects and directs exhaust gases away from the cylinders.
- Intake Manifold: Distributes the air-fuel mixture to the cylinders.
Each of these elements must be accurately identified and understood to facilitate successful maintenance efforts. Familiarity with their locations and functions will enhance your ability to diagnose and address performance issues efficiently.
Engine Disassembly Procedures Explained

The process of dismantling a power unit requires meticulous attention and a systematic approach. Understanding the key steps involved is essential for effective maintenance and ensuring that all components are handled correctly. This section outlines the necessary procedures for safely disassembling a unit, highlighting important considerations throughout the process.
Preparation for Dismantling
Before initiating the breakdown, it is crucial to prepare the workspace and gather the required tools. Ensure that the environment is clean and organized to avoid losing parts or causing damage. Documentation of the assembly and component locations can aid in reassembly later. Additionally, all safety precautions should be followed, including wearing appropriate protective gear.
Step-by-Step Disassembly Process
Start by disconnecting any electrical connections and fluid lines to prevent spills or shorts. Carefully remove outer covers and any accessories attached to the unit. Take note of the order of disassembly, as this will facilitate easier reassembly. Use the proper tools to avoid stripping bolts or damaging components. As each part is removed, inspect it for wear or damage, and place it in a designated area for further assessment.
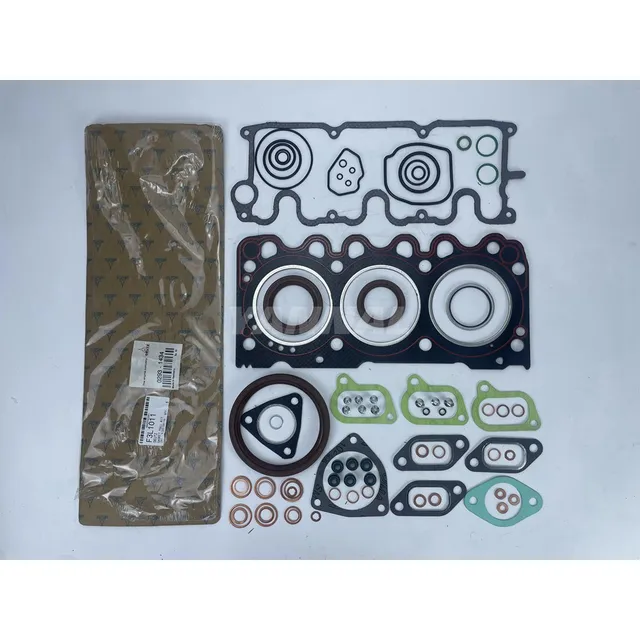
Common Replacement Parts Overview
Understanding the essential components that may require substitution during maintenance is crucial for optimal performance. This section highlights the frequently needed items that play a vital role in ensuring smooth operation and longevity of machinery.
Filters are among the most commonly replaced components. These elements are essential for keeping the system free from contaminants, thus prolonging the lifespan of various parts. Regularly changing the oil, fuel, and air filters can significantly enhance overall efficiency.
Gaskets also deserve attention, as they are critical for maintaining proper seals within the unit. Over time, these materials can degrade due to heat and pressure, leading to leaks and reduced functionality. Ensuring that gaskets are in good condition can prevent costly damage.
Belt and chain assemblies are another key category. These components are responsible for transferring power and motion. Wear and tear can lead to slippage or failure, so regular inspections and timely replacements are essential for uninterrupted operation.
Water pumps and thermostats play significant roles in temperature regulation. If either component fails, it can lead to overheating, causing serious damage. Proactive replacement of these parts is critical to maintaining the correct operating temperature.
In summary, staying informed about these commonly needed components can greatly assist in maintaining the efficiency and reliability of your machinery. Regular checks and timely substitutions will help prevent more extensive issues in the future.
Reassembling the Engine: Best Practices
Putting components back together after disassembly is a critical phase in the restoration process. This stage requires careful attention to detail to ensure optimal functionality and longevity. Adhering to best practices can significantly enhance the overall performance and reliability of the machinery.
Here are some essential tips for effective reassembly:
- Cleanliness: Maintain a clean workspace to prevent contaminants from entering critical areas. Use lint-free cloths and designated cleaning solutions.
- Follow Manufacturer Specifications: Refer to any available documentation for torque settings and assembly sequences to avoid mistakes.
- Inspect Components: Before reassembly, check all parts for wear or damage. Replace any compromised components to ensure a proper fit.
- Use Proper Tools: Utilize the correct tools for the job. This not only speeds up the process but also reduces the risk of damaging components.
- Apply Lubrication: Use the recommended lubricants on moving parts during assembly. This helps reduce friction and wear during initial operation.
By following these practices, you can enhance the durability and functionality of your machinery, ensuring it operates smoothly for years to come.
Fuel System Maintenance Techniques
Ensuring the optimal performance of a combustion unit requires careful attention to the fuel delivery mechanism. Regular upkeep of this system not only enhances efficiency but also prolongs the lifespan of the entire assembly. Implementing proper maintenance techniques is essential for preventing common issues that may arise due to neglect or poor fuel quality.
Key strategies for maintaining the fuel system include routine inspections, timely replacements of filters, and the use of high-quality fuel. Additionally, monitoring for leaks and ensuring proper seals can prevent contamination and other complications. Below is a summary of effective maintenance practices:
| Technique | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Filter Replacement | Replace fuel filters to prevent clogging and ensure clean fuel flow. | Every 500 hours |
| Leak Checks | Inspect connections and lines for any signs of leaks. | Monthly |
| Fuel Quality Monitoring | Use only recommended fuel types to avoid deposits and degradation. | Ongoing |
| System Flush | Periodically flush the fuel system to remove accumulated debris. | Annually |
By adhering to these techniques, operators can ensure reliable performance and minimize the risk of unexpected failures within the fuel delivery system.
Cooling System Troubleshooting Tips
Maintaining optimal performance in a power unit requires a well-functioning cooling system. Issues can lead to overheating and other complications, so it’s essential to identify and address any potential problems promptly. Here are some effective strategies to diagnose and resolve common cooling system issues.
Check Fluid Levels: Ensure that the coolant is at the appropriate level. Low fluid can lead to inadequate heat dissipation. Regularly inspect for any signs of leaks around hoses, the radiator, and connections.
Inspect for Blockages: Accumulation of debris or corrosion can impede coolant flow. Examine the radiator and associated components for any obstructions that could affect cooling efficiency. Cleaning these areas can enhance performance.
Thermostat Functionality: A malfunctioning thermostat can prevent proper coolant circulation. Test the thermostat to ensure it opens and closes at the designated temperatures. If it’s stuck, replacement may be necessary.
Radiator Condition: Inspect the radiator for any damage, such as dents or rust. A compromised radiator can reduce cooling capacity. Flushing the system periodically can help remove accumulated deposits and improve function.
Fan Operation: Verify that the cooling fan operates as intended. A faulty fan can lead to overheating, especially at low speeds. Listen for unusual noises or check for physical obstructions that may hinder movement.
Temperature Gauge Monitoring: Regularly monitor the temperature readings during operation. If the gauge shows excessive heat, investigate immediately. This could indicate a deeper issue that requires attention.
By following these troubleshooting tips, you can ensure that the cooling system operates effectively, maintaining optimal temperature levels and enhancing overall performance.
Electrical System Diagnostics and Repair
Understanding the functionality and troubleshooting of the electrical components is essential for maintaining optimal performance in machinery. This section focuses on the key diagnostic procedures and solutions necessary to address electrical issues effectively. Proper identification of faults can lead to timely interventions, preventing more extensive complications.
Begin with a thorough inspection of the wiring harness for signs of wear or damage. Check for frayed wires, loose connections, and corrosion at terminals, as these issues can significantly hinder electrical flow. Utilizing a multimeter, measure voltage levels at various points to ensure proper operation of sensors and actuators.
If irregularities are detected, refer to the circuit diagrams to trace back the source of the problem. Testing individual components such as relays and switches is crucial. Verify their functionality and replace any defective parts. Additionally, assess grounding points to confirm that all connections are secure and free from rust or dirt, which can impede electrical performance.
Finally, implement preventive measures by regularly maintaining the electrical system. Cleaning terminals, securing connections, and routinely checking for signs of wear can extend the lifespan of the components and enhance reliability in performance.
Upgrading Performance of F3L1011
Enhancing the efficiency and output of a power unit can lead to significant improvements in overall functionality and longevity. By implementing specific modifications and optimizations, users can achieve better performance, lower fuel consumption, and increased reliability. This section outlines several effective strategies for boosting the capabilities of your machinery.
1. Air Intake Enhancements: Improving the air intake system can result in better combustion efficiency. Consider upgrading to a high-performance air filter or adding an intake manifold that promotes smoother airflow. This modification allows for more oxygen to enter the combustion chamber, leading to increased power and responsiveness.
2. Fuel System Optimization: Ensuring the fuel delivery system operates at peak efficiency is crucial. Upgrading to higher-quality fuel injectors can improve atomization, enhancing combustion. Regular maintenance of fuel lines and filters also plays a vital role in maintaining optimal performance.
3. Exhaust System Upgrades: A more efficient exhaust system can reduce back pressure and improve exhaust flow. Installing a performance exhaust manifold or a high-flow muffler can enhance the engine’s ability to expel gases, contributing to improved power output and efficiency.
4. Tuning the Control Unit: Adjusting the electronic control unit can optimize fuel maps and ignition timing, allowing for better performance characteristics. A professional remap can unlock additional power and torque, tailoring the output to specific operational needs.
5. Regular Maintenance: Consistent upkeep cannot be overlooked. Routine checks on oil levels, coolant conditions, and component wear can prevent performance drops and extend the lifespan of your unit. Consider implementing a maintenance schedule that addresses these aspects proactively.
By following these strategies, users can maximize the potential of their machinery, achieving a balance between performance and efficiency while ensuring reliability over time.
Safety Precautions During Repairs
When undertaking maintenance tasks, ensuring a safe working environment is paramount. Adhering to proper guidelines not only protects the individual performing the work but also safeguards the equipment and surrounding area. Awareness of potential hazards and implementing preventive measures can significantly reduce risks associated with mechanical tasks.
General Safety Guidelines

- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and steel-toed boots.
- Ensure the workspace is well-ventilated to avoid the accumulation of harmful fumes.
- Keep the area tidy and free from unnecessary tools and materials to prevent tripping hazards.
- Be familiar with emergency procedures, including the location of first aid kits and fire extinguishers.
Equipment Handling and Maintenance
- Before starting, disconnect all power sources to prevent accidental activation.
- Use proper lifting techniques and tools when handling heavy components.
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for tool usage to avoid injuries.
- Inspect tools regularly for wear and damage; replace as necessary.
By following these precautions, individuals can create a safer environment and contribute to the successful completion of maintenance activities.