
Regular maintenance and occasional adjustments are essential to ensure that your ZF transmission remains in optimal working order. Without consistent care, performance issues can emerge, impacting both efficiency and longevity. This section offers a comprehensive look at best practices to maintain smooth operation, allowing for a reliable driving experience.
Understanding the core functions and components is vital for anyone aiming to preserve transmission performance over time. Here, we’ll explore essential methods and tips that help prevent unexpected wear and extend the lifespan of your system. By following these steps, you can avoid common pitfalls and enhance the overall resilience of your equipment.
Key adjustments and routine inspections also play a crucial role in sustaining peak performance. This guide will walk you through specific methods, offering insights into recognizing early signs of potential issues. With the right approach, you can keep your transmission running seamlessly, reducing the need for extensive overhauls in the future.
Zf Gearbox Repair Manual
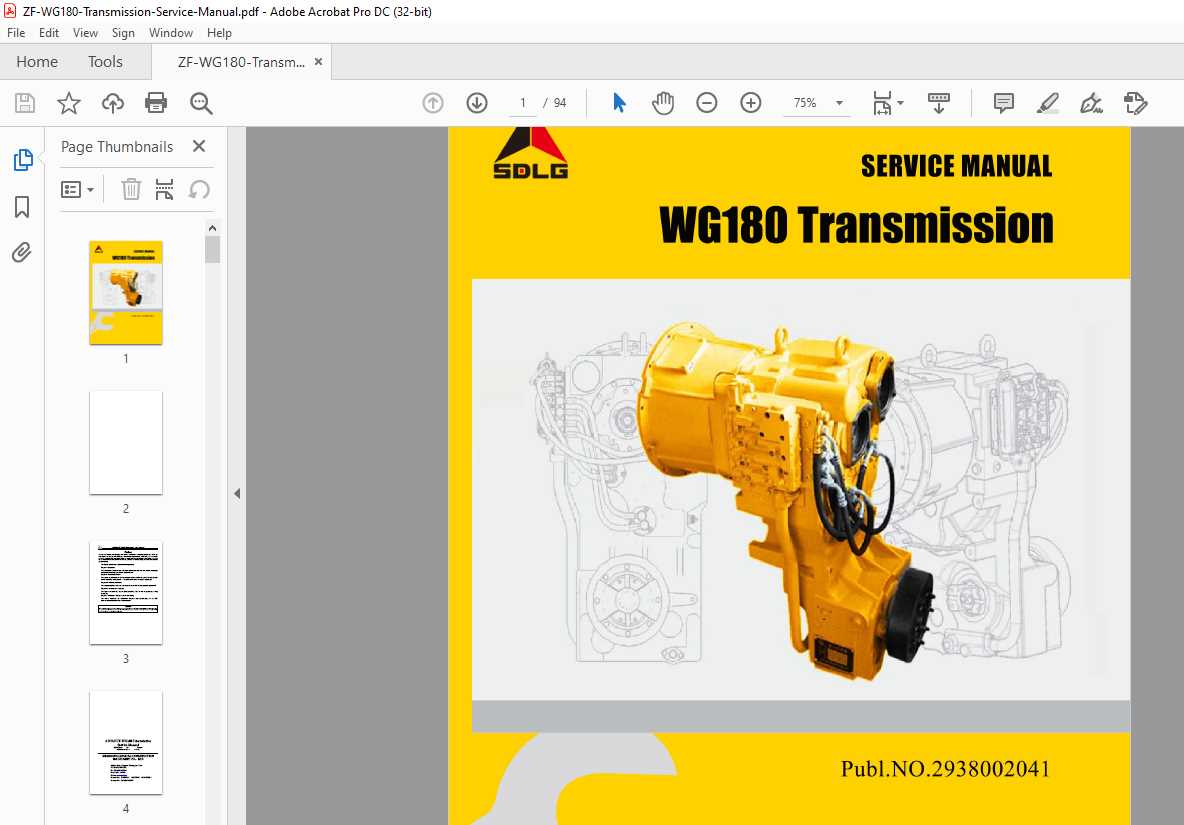
Understanding the maintenance and functionality of certain mechanical systems requires a detailed approach. This section provides essential insights and methods to help you navigate through various aspects, ensuring long-term efficiency and reliability.
- Inspection Techniques: Regular evaluation is crucial. Identifying early signs of wear can prevent more significant issues, ensuring optimal performance over time.
- Component Analysis: Each part plays a specific role in the overall operation. Knowing how these elements work together aids in a more comprehensive approach to upkeep and troubleshooting.
- System Adjustments: Periodic calibrations keep the setup functioning smoothly. Adjustments should be made according to the specifications to maintain operational integrity.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: Ensuring components are free of debris and properly lubricated reduces friction and extends the life of the machinery. This step is vital in routine servicing.
Following these structured guidelines allows for a more sustainable and effective upkeep process, minimizing downtime and improving the overall service lifespan of the system.
Common Gearbox Issues

Many mechanical systems face a variety of operational challenges over time, often due to wear and environmental conditions. These challenges can affect performance, leading to irregularities in function that may require attention. Understanding these issues can help in identifying and addressing them effectively.
One of the frequent concerns involves noise during operation. Unusual sounds, such as grinding or clunking, may signal that certain components are no longer working smoothly together, possibly indicating the need for lubrication or part replacement.
Another prevalent issue is difficulty in shifting smoothly. This may occur when internal parts have excessive friction or have shifted out of alignment. Addressing this can help prevent further complications and restore efficient functioning.
Finally, leaks are a common problem that can stem from worn seals or connections. Even a small leak can impact overall performance, as it can lead to reduced fluid levels, which in turn can affect the entire system’s efficiency.
Identifying Early Signs of Wear

Recognizing early indicators of wear in mechanical systems is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing costly breakdowns. Monitoring specific symptoms can help in detecting issues before they escalate, ensuring the smooth functioning of the machinery.
Common Warning Signs

- Unusual noises: Squeaking, grinding, or other atypical sounds during operation can signal internal friction or misalignment.
- Temperature increase: A rise in temperature may indicate increased friction within components, which can lead to further damage if untreated.
- Performance fluctuations: Noticeable decreases in efficiency, such as sluggish response or intermittent functionality, often point to underlying wear.
Inspecting Components Regularly
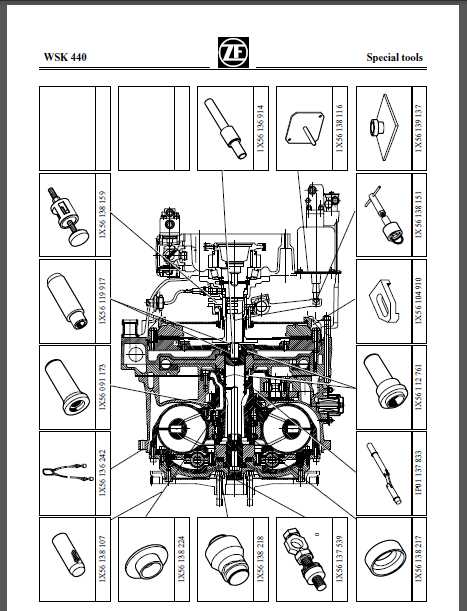
Routine inspections are essential to catching signs of wear early. Pay particular attention to:
- Seals and connections: Look for any signs of leaks or damage around joints, which can signal potential wear and the need for maintenance.
- Fastenings and fittings: Loose bolts
Step-by-Step Dismantling Guide

In this section, we will go through each stage of disassembly to help you understand how to carefully take apart the assembly components. Follow these steps to ensure a precise and smooth process.
- Preparation: Set up a clean, organized workspace with all necessary tools at hand, such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and containers for small parts. Label each part and make notes if necessary.
- Initial Components: Start by removing any accessible covers or panels to gain a better view of the internal structure. These outer sections often shield the primary parts, so take time to unscrew and carefully lift them off.
- Securing Mechanisms: Identify bolts or screws securing the main components. Loosen these in a balanced, gradual manner to avoid any imbalance or damage. Place all fasteners in labeled containers for easy reassembly.
- Internal Connections: With the outer layers removed, locate internal couplings, connections, or clips. Carefully detach these, ensuring no cables or hoses are pulled abruptly.
- Core Section: Gently extract the core assembly, taking care to avoid contact with sensitive or delicate parts. This may require a slow, balanced pull to ensure safe removal without any force.
- Inspection: As each part is removed, inspect it for wear or damage. This step is essential to assess which parts may need replacement or spec
Essential Tools for Gearbox Repair
When working on transmission maintenance, having the right set of instruments can simplify the process and improve the quality of results. Carefully chosen tools not only make each step more efficient but also help to avoid potential mistakes during disassembly and reassembly.
- Socket and Wrench Sets: These are fundamental for loosening and tightening various parts, ensuring all bolts and fasteners are properly secured during reassembly.
- Pry Bars and Pullers: Ideal for separating tightly fitted components, reducing the risk of accidental damage and making the process smoother.
- Torque Wrench: Helps maintain the correct force on each fastener, which is crucial for ensuring stability and longevity of the entire system.
- Cleaning Supplies: Degreasers and brushes help remove accumulated oil and dirt from components, allowing for a clear view of any signs of wear or damage.
- Measuring Tools: Precision tools like calipers and feeler gauges are essential for checking tolerances, which ensures each component fits together accurately.
Cleaning Techniques for Internal Parts
Maintaining the cleanliness of internal components is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Proper techniques ensure that residues and contaminants do not impair functionality, allowing for smoother operation and reducing wear. Various methods can be employed to effectively clean these intricate parts, each suited to specific types of contaminants.
Cleaning Method Description Recommended For Solvent Cleaning Using chemical solvents to dissolve grease and dirt. Heavy oil and grime build-up Ultrasonic Cleaning Employing high-frequency sound waves in a liquid to agitate particles. Delicate or intricate parts Steam Cleaning Using high-temperature steam to remove contaminants. General cleaning without chemical residues Brushing Manual scrubbing with brushes to remove loose dirt. Accessible areas with stubborn debris Compressed Air Blowing away dirt and dust using high-pressure air. Tight spaces and electronic components Inspecting and Replacing Worn Components

Regular examination and substitution of damaged parts are crucial for ensuring the efficient operation of machinery. Identifying signs of wear early can prevent further complications and maintain optimal functionality. This section outlines essential procedures to assess components and implement necessary replacements effectively.
Begin by visually inspecting the parts for any noticeable deterioration, such as cracks, excessive wear, or corrosion. Utilize appropriate tools to measure dimensions and tolerances, ensuring they remain within specified limits. If any component appears compromised, it is advisable to replace it promptly to avoid further damage.
When selecting replacement parts, ensure they are of high quality and compatible with the existing assembly. Follow proper installation techniques to secure the components effectively. After installation, conduct a thorough test to verify that the machinery operates smoothly and efficiently, confirming that all parts are functioning as intended.
Reassembling the Gearbox Correctly
Reassembling complex machinery components requires precision and attention to detail. Proper alignment and secure fitting of each part are crucial to ensure optimal functionality. This section outlines the essential steps to effectively bring the assembly back together, ensuring longevity and performance.
Steps for Successful Assembly

Begin by organizing all components systematically. Clean each piece thoroughly to remove any debris or residue. Follow the manufacturer’s specifications closely, referring to any provided diagrams. Start with the foundation elements, ensuring each part is seated correctly before proceeding to the subsequent layers. Tightening bolts should be done in a specific sequence to prevent distortion.
Final Checks
Once the assembly is complete, conduct a thorough inspection. Check for any signs of misalignment or improper fitting. Ensure that all securing mechanisms are tightened to the recommended torque settings. A final test run should be performed to verify smooth operation before the assembly is fully operational.
Testing Gearbox Functionality After Repair

After completing the necessary maintenance on the transmission system, it is crucial to ensure that it operates efficiently. This involves a series of tests to verify its performance and detect any issues that may have arisen during the service. Proper evaluation will help confirm that the unit functions correctly and meets the required standards.
The following steps outline a systematic approach to assess the functionality of the transmission system:
Test Description Expected Outcome Visual Inspection Examine for leaks or damage in components. No visible leaks or damages. Fluid Level Check Ensure the fluid levels are within specified ranges. Fluid levels at the correct capacity. Functionality Test Engage and disengage the system under various conditions. System engages and operates smoothly. Noise Assessment Listen for unusual sounds during operation. No abnormal noises detected. Performance Evaluation Test under load to observe power transfer efficiency. Efficient power transfer with minimal loss. Following these assessments will help ensure the transmission system is ready for reliable performance. Addressing any detected issues promptly will prevent future complications.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring the longevity and smooth operation of any mechanical system. By implementing proactive measures, potential issues can be identified and addressed before they escalate into significant problems. This approach not only enhances performance but also minimizes unexpected downtime.
Routine Inspections
Conducting periodic assessments can help in detecting wear and tear early. Consider the following practices:
- Examine fluid levels and conditions regularly.
- Check for signs of leaks or unusual noises.
- Inspect mounting points and connections for integrity.
Lubrication Practices
Proper lubrication is vital for reducing friction and prolonging the life of components. Follow these guidelines:
- Use the recommended lubricant for your system.
- Apply lubricant at regular intervals to ensure adequate coverage.
- Monitor lubrication points for any blockages or contamination.
Recommended Lubricants for Optimal Performance

Choosing the right lubricants is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of mechanical systems. Proper lubrication reduces friction, minimizes wear, and ensures smooth operation under various conditions. This section highlights the types of lubricants best suited for achieving optimal functionality.
Type of Lubricant Recommended Brand Application Notes Synthetic Oil Brand A Provides excellent protection and performance at high temperatures. Mineral Oil Brand B Good for moderate temperature applications, cost-effective. Grease Brand C Ideal for areas needing a thicker lubricant that stays in place. Biodegradable Oil Brand D Environmentally friendly option, suitable for various applications. When selecting a lubricant, consider the operating conditions, including temperature, load, and environmental factors. Using the appropriate type enhances performance and reduces maintenance needs.
Troubleshooting Unresolved Gearbox Problems
Addressing persistent issues within transmission systems can be challenging. Often, these problems require a systematic approach to identify the root causes and implement effective solutions. Understanding common signs of malfunction can greatly aid in resolving ongoing complications.
Identifying Symptoms
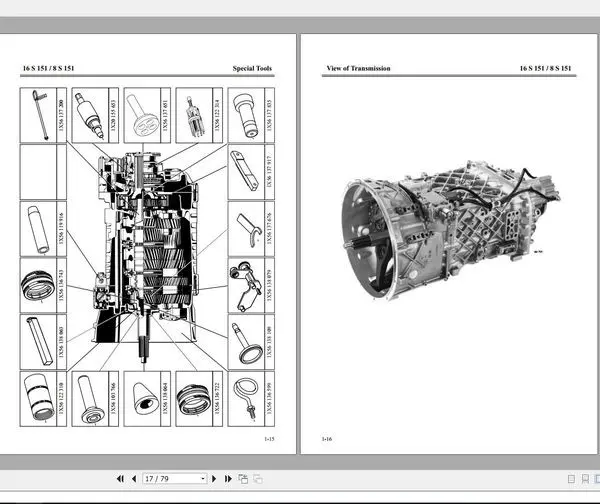
Recognizing the signs of distress is the first step in diagnosing issues. Common indicators include:
- Unusual noises during operation
- Slipping or delayed engagement of gears
- Fluid leaks around the system
- Overheating during use
- Erratic shifting patterns
Systematic Approach to Diagnosis
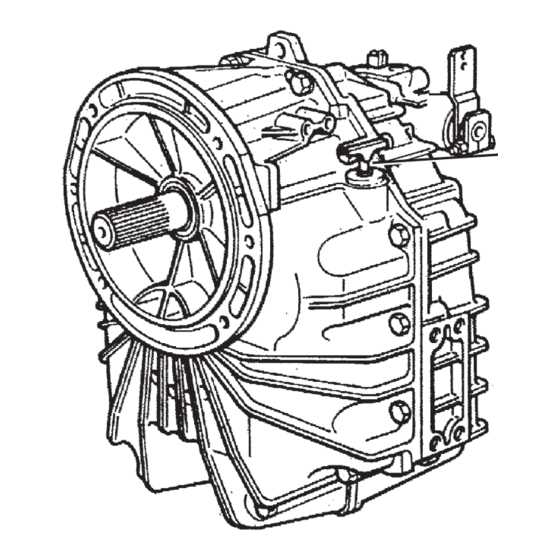
To effectively troubleshoot unresolved issues, follow these steps:
- Conduct a visual inspection for leaks and damage.
- Check fluid levels and quality.
- Test for error codes using diagnostic tools.
- Inspect linkage and electronic components for wear.
- Evaluate the overall performance under various conditions.
By following these methods, one can systematically narrow down the potential sources of trouble and work towards resolving them effectively.