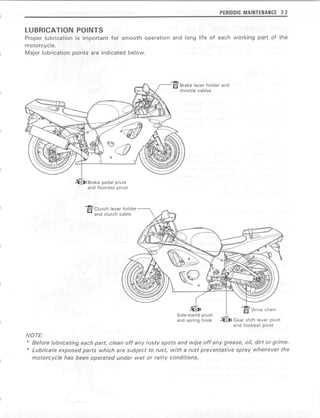
Maintaining high-performance two-wheelers is essential for enthusiasts who seek to prolong the life of their machines and enhance their riding experience. This resource serves as a valuable asset for both novice and experienced riders, providing insights into the intricate world of motorcycle upkeep. From routine checks to more complex interventions, understanding the fundamentals is crucial.
Within this guide, you will discover a wealth of information covering essential procedures, troubleshooting techniques, and best practices. Each section is designed to empower owners with the knowledge required to address common issues effectively. By familiarizing yourself with your vehicle’s intricacies, you can ensure its peak performance and reliability on the road.
Whether you’re preparing for a long journey or simply looking to optimize your ride, having a reliable reference can make all the difference. This resource not only demystifies maintenance tasks but also fosters a deeper connection between rider and machine. Prepare to dive into a world of mechanical understanding and enhance your ownership experience.
Suzuki GSX-R 750 Overview
This section provides a comprehensive insight into a renowned sport motorcycle that has captivated enthusiasts for decades. Known for its blend of performance, agility, and cutting-edge technology, this model has established itself as a staple in the world of high-performance biking. With a legacy of innovation, it continues to evolve while maintaining the core attributes that riders cherish.
Key Features

The motorcycle is designed with precision engineering and a commitment to excellence. Riders can expect a harmonious combination of power and control, making it suitable for both the racetrack and the open road. Below are some of the notable characteristics that set this machine apart:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Engine | High-performance engine that delivers exceptional power and responsiveness. |
| Chassis | Lightweight and durable frame designed for optimal handling and stability. |
| Technology | Advanced electronics including traction control and quick shifter for enhanced riding experience. |
| Design | Aerodynamic bodywork that not only looks striking but also improves performance. |
Performance and Handling
Engineered for those who seek thrill and excitement, the motorcycle delivers impressive acceleration and cornering capabilities. The meticulous balance between power and weight ensures a responsive ride, allowing enthusiasts to navigate curves with confidence. This model continues to set benchmarks in the sportbike category, appealing to both novice riders and seasoned veterans alike.
Common Issues with GSX-R 750
This section explores frequent challenges faced by owners of a certain high-performance motorcycle model. Understanding these issues can help riders take proactive steps to maintain their vehicles in optimal condition and enhance their riding experience.
1. Electrical Problems
- Battery drain: Many users report unexpected battery failures due to electrical system faults.
- Faulty wiring: Corroded or damaged wires can lead to intermittent issues, affecting performance.
- Indicator malfunctions: Problems with turn signals and dashboard lights can occur, impacting visibility and safety.
2. Engine Performance
- Fuel system issues: Clogs in fuel lines or filters can lead to poor engine performance.
- Overheating: Inadequate cooling can cause the engine to run hot, potentially leading to severe damage.
- Oil leaks: Regularly check for leaks, as they can affect lubrication and overall engine health.
Essential Tools for Repairs
When it comes to maintaining and fixing your vehicle, having the right equipment is crucial for efficiency and safety. The correct tools not only facilitate the repair process but also ensure that tasks are completed to a high standard. This section will outline the indispensable instruments you should have on hand for effective maintenance.
Wrenches and Sockets: A comprehensive set of wrenches and socket heads is vital for loosening and tightening various fasteners. Look for both metric and imperial sizes to accommodate different components.
Screwdrivers: A variety of screwdrivers, including flathead and Phillips types, is necessary for accessing screws in multiple locations. Consider investing in a magnetic tip to simplify handling small screws.
Torque Wrench: To apply precise torque to bolts, a torque wrench is essential. This tool helps prevent over-tightening, which can lead to damage.
Plier Set: Pliers are versatile tools that can assist in gripping, twisting, and cutting. A set with needle-nose and slip-joint options will cover most needs.
Jack and Stands: A reliable jack and set of stands are critical for lifting your vehicle safely. Always ensure your vehicle is securely supported before working underneath it.
Diagnostic Tools: Investing in a good diagnostic scanner can help you quickly identify issues by reading error codes. This tool is invaluable for troubleshooting problems efficiently.
Equipping yourself with these essential tools will prepare you for a variety of tasks, making your maintenance efforts more effective and enjoyable.
Step-by-Step Maintenance Guide
Regular upkeep of your motorcycle is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This guide provides a systematic approach to maintaining your bike, covering crucial aspects that every owner should address periodically. By following these steps, you can enhance your riding experience and prevent costly repairs in the future.
Essential Checks
Begin with a thorough inspection of your vehicle. Check the fluid levels, including oil, coolant, and brake fluid, ensuring they are within the recommended range. Examine the tires for wear and proper pressure, as well as the condition of the brakes. Keeping an eye on these fundamental components will help you identify potential issues early.
Routine Maintenance Tasks

Engage in regular maintenance tasks such as changing the oil and replacing the oil filter at intervals specified in the owner’s guide. Clean or replace the air filter to maintain optimal airflow and engine efficiency. Additionally, inspect the chain and adjust its tension as needed, lubricating it to ensure smooth operation. These simple yet vital actions can significantly extend the life of your motorcycle.
Understanding the Engine Components
The engine of a motorcycle is a complex assembly of parts that work in harmony to convert fuel into motion. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and reliability. A comprehensive understanding of these elements is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key components of a motorcycle engine include:
- Engine Block: The main structure that houses the cylinders and supports other components.
- Cylinders: The chambers where fuel combustion occurs, driving the pistons.
- Pistons: Moving parts that convert the energy from combustion into mechanical work.
- Crankshaft: A rotating shaft that translates the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion.
- Valves: Mechanisms that control the intake of air and fuel and the exhaust of gases.
- Camshaft: A shaft that operates the valves, ensuring they open and close at the right times.
- Ignition System: Composed of components that ignite the fuel-air mixture, leading to combustion.
By familiarizing oneself with these parts, riders can better understand their vehicle’s operation and enhance their ability to diagnose issues when they arise.
Transmission Troubleshooting Tips
Addressing issues within the transmission system can be crucial for maintaining optimal performance. Identifying symptoms early can prevent further complications and ensure smooth operation. Below are essential tips to assist in diagnosing and resolving common transmission problems.
Common Symptoms to Look For
- Unusual noises during shifting
- Difficulty in engaging gears
- Slipping out of gear while in motion
- Delayed response when accelerating
- Fluid leaks beneath the vehicle
Troubleshooting Steps
- Check fluid levels: Ensure that the transmission fluid is at the correct level, as low fluid can cause various issues.
- Inspect for leaks: Look for any signs of leakage around seals and gaskets.
- Examine the clutch: If applicable, test the clutch for proper engagement and disengagement.
- Test shift linkage: Ensure that the shift linkage is correctly adjusted and not damaged.
- Scan for error codes: Utilize diagnostic tools to check for any electronic issues.
Braking System Insights
The braking mechanism is a critical component of any motorcycle, ensuring safety and control during operation. Understanding its intricacies can enhance performance and longevity, as well as improve rider confidence. This section delves into various aspects of the braking assembly, highlighting essential features, maintenance tips, and troubleshooting methods.
| Component | Function | Maintenance Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Brake Pads | Friction material that slows down the wheel | Check for wear regularly and replace when necessary |
| Brake Discs | Surface that brake pads clamp onto to stop the bike | Inspect for warping and scoring; clean to maintain effectiveness |
| Brake Fluid | Transfers force from the lever to the calipers | Replace fluid as recommended; check for contamination |
| Master Cylinder | Generates hydraulic pressure for braking | Ensure no leaks; inspect seals for damage |
| Calipers | Holds brake pads and applies them to the disc | Check for fluid leaks and proper alignment |
Electrical System Diagnostics
The evaluation of an electrical system is crucial for identifying issues that may hinder performance and reliability. Proper diagnosis involves systematic checks and analysis of components to ensure they operate effectively. Understanding the various elements and their interactions can greatly aid in troubleshooting common electrical faults.
Initial Inspection
Begin with a visual inspection of the wiring and connectors. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or loose connections that could disrupt the flow of electricity. Pay special attention to any damaged insulation that may lead to short circuits.
Battery Assessment
The battery serves as the power source for the entire system. Use a multimeter to check the voltage levels; a healthy battery should typically read around 12.6 volts when fully charged. If the voltage is low, consider testing the charging system to ensure it’s functioning properly.
Component Testing
Next, evaluate individual components such as the alternator, fuses, and relays. Each part should be tested according to specifications provided by the manufacturer. This includes checking resistance and continuity to confirm they are in optimal working condition.
Troubleshooting Procedures
If an issue is identified, follow a structured approach to troubleshoot. Start by isolating the problem area, using diagnostic tools as necessary to pinpoint failures. Document findings to assist in determining whether a repair or replacement is required.
Final Verification
After repairs are made, conduct a final verification to ensure everything operates as intended. Recheck voltage levels and component functionality to confirm that the electrical system is fully restored. This comprehensive approach ensures reliability and longevity of the system.
Cooling System Maintenance Techniques
Proper upkeep of the cooling mechanism is essential for optimal performance and longevity of any high-performance machine. Regular checks and maintenance not only prevent overheating but also ensure efficient operation under various conditions. This section outlines effective strategies to maintain and enhance the functionality of the cooling system.
Routine Inspection

Conducting frequent inspections is a key step in ensuring the cooling system operates effectively. Here are some critical aspects to check:
- Coolant Level: Regularly monitor the coolant reservoir to maintain appropriate levels.
- Leaks: Inspect hoses and connections for any signs of leakage that could compromise efficiency.
- Debris: Keep the radiator and other components free from dirt and obstructions that can hinder airflow.
Coolant Replacement

Replacing the coolant at specified intervals is vital for maintaining thermal efficiency. Follow these steps for proper coolant management:
- Drain the old coolant completely to avoid contamination.
- Flush the system with clean water to remove any residue.
- Refill with the appropriate mixture of coolant and water, following manufacturer guidelines.
By adhering to these maintenance techniques, the cooling system can operate smoothly, ensuring the engine remains at the ideal temperature during operation.
Suspension Adjustments and Repairs

Proper tuning and maintenance of the suspension system are crucial for optimal performance and rider comfort. This section focuses on the essential adjustments and necessary fixes to ensure the suspension works efficiently, providing a smooth and stable ride. Understanding the various components and their functionalities can significantly enhance handling and overall safety.
Adjustment Basics
Suspension systems typically feature multiple settings that can be modified based on rider preferences and road conditions. Adjusting preload, compression, and rebound damping allows for fine-tuning the bike’s response. Preload affects the initial sag of the suspension, influencing ride height and comfort, while compression settings control how quickly the forks or shock compress under load. Rebound adjustments ensure that the suspension returns to its original position smoothly after compression, preventing bounce and maintaining stability.
Common Repairs
Wear and tear can lead to various issues within the suspension setup. Leaking seals, worn-out bushings, and damaged springs are common problems that may require attention. Regular inspections can help identify these issues early, preventing further damage and ensuring safety. Replacing seals and bushings can restore functionality, while spring replacement may be necessary to match the rider’s weight and intended use.
Regular Maintenance
Routine maintenance is vital for extending the lifespan of the suspension components. This includes cleaning and lubricating moving parts, checking fluid levels, and ensuring all connections are secure. Keeping an eye on the performance and making adjustments as needed will contribute to a more enjoyable riding experience.
Bodywork and Fairing Replacement
Replacing the exterior panels and protective covers of a motorcycle is a vital aspect of maintaining its aesthetics and performance. This process not only enhances the bike’s appearance but also protects critical components from environmental damage. Understanding the steps involved ensures a smooth and efficient replacement, keeping your ride in optimal condition.
Assessing Damage

Before beginning the replacement process, it’s essential to thoroughly inspect the bodywork for any signs of wear, cracks, or dents. Look for structural integrity, as compromised panels can affect aerodynamics and handling. Documenting the damage will help in determining whether a complete replacement or just minor repairs are needed.
Replacement Process

To start the replacement, gather the necessary tools, including screwdrivers, wrenches, and possibly a heat gun for stubborn fasteners. Carefully remove the damaged panels by loosening screws and bolts, taking care to note their locations for reassembly. Once the old parts are off, clean the surfaces to ensure a good fit for the new components.
When installing the new panels, align them properly before tightening any fasteners. This step is crucial for achieving a seamless look and maintaining proper airflow. Finally, check all connections and ensure that everything is secure. Regular maintenance and timely replacements will keep your motorcycle looking sharp and performing at its best.
Wiring Diagrams and Schematics

This section provides an overview of the electrical layouts and circuit designs crucial for understanding the intricate systems of your vehicle. These visual representations are essential for troubleshooting and ensuring proper connections throughout the machine.
Importance of Wiring Diagrams
Wiring diagrams serve several key purposes:
- Facilitate troubleshooting by highlighting the flow of electricity.
- Provide clear visual guidance for installation and repairs.
- Help identify component locations and their interconnections.
Types of Schematics

There are different types of electrical schematics, each serving specific needs:
- Block Diagrams: Simplified versions showing the major components and their relationships.
- Schematic Diagrams: Detailed representations that illustrate electrical paths and components.
- Wiring Diagrams: Focus on the physical connections between components, often including color codes.
Utilizing these diagrams effectively can greatly enhance your understanding and ability to work on the electrical systems of your machine.
Upgrading Your GSX-R 750
Enhancing the performance and aesthetics of your sportbike can significantly improve your riding experience. Whether you seek better handling, increased power, or simply a more aggressive look, there are numerous upgrades available to elevate your machine.
Here are some popular areas to consider for enhancement:
- Engine Modifications:
- High-performance air filters for improved airflow.
- Upgraded exhaust systems to reduce weight and increase horsepower.
- ECU remapping for optimized engine performance.
- Suspension Improvements:
- Adjustable forks to fine-tune handling characteristics.
- Upgraded rear shock absorbers for better stability.
- Preload adjustments for personalized riding comfort.
- Brake System Enhancements:
- Performance brake pads for improved stopping power.
- Upgraded rotors for better heat dissipation.
- Stainless steel brake lines for enhanced feel and responsiveness.
- Cosmetic Upgrades:
- Custom paint jobs or vinyl wraps for a unique appearance.
- LED lighting for improved visibility and style.
- Aerodynamic fairings to reduce drag.
Each modification can contribute to a more enjoyable ride, so carefully consider your priorities and budget when planning upgrades. Remember to consult with professionals or experienced enthusiasts to ensure compatibility and safety during the enhancement process.