
Efficient performance and durability are vital for heavy-duty vehicle components, especially in complex drive systems. This guide provides insights into refreshing and maintaining the ZF 16 system, ensuring that each component operates at its peak, even under challenging conditions. From basic upkeep to advanced refurbishment techniques, the following sections cover the key aspects for optimal functionality.
Regular adjustments and system analysis can greatly extend the life of such a critical mechanism. This guide will walk through the steps for inspecting, cleaning, and replacing essential parts, while offering tips on diagnosing common issues and enhancing overall efficiency. Whether you’re an experienced mechanic or new to transmission systems, the advice here is structured to be straightforward and effective.
Careful attention to each part of the process, from precise alignment to lubrication practices, will lead to a reliable and smoother operation. By following the outlined methods, you’ll gain the skills and knowledge necessary to keep the ZF 16 transmission system running reliably for years to come.
ZF 16-Speed Gearbox Repair Insights
The following section explores effective approaches for handling and maintaining intricate multi-stage transmission systems. By understanding the essential components and working principles, technicians can streamline servicing processes, addressing common issues in a timely manner.
One of the core considerations is the internal synchronization between the shifting phases, which ensures optimal performance and longevity. Paying attention to wear signs in synchronizers and clutch assemblies can prevent further complications. Detailed inspection techniques play a crucial role in identifying underlying issues, facilitating the preservation of smooth operational flow.
Regular maintenance, including checks on lubrication quality and component alignment, enhances the resilience of these systems. Adopting proactive service strategies is essential for minimizing downtime and extending the life of each part within the complex transmission assembly.
Understanding the ZF Gearbox Structure
The intricate design of the ZF transmission system embodies a combination of precision engineering and durability, tailored for handling substantial operational demands. This section will explore the essential elements within the mechanism, highlighting the interconnected parts that contribute to smooth and efficient power transfer.
Main Components and Their Functions
The core of the ZF transmission system includes multiple sections, each with a distinct role in managing and distributing force. At the heart of the mechanism lies an arrangement of shifting elements, synchronizers, and control units, all working in unison to ensure fluid movement and adjustability under various conditions.
Internal Mechanism and Energy Flow
The energy transfer within the ZF system is facilitated by a series of linkages and shafts, meticulously aligned to convert rotational power effectively. By controlling the input and output through synchronized adjustments, the transmission maintains a seamless flow of energy, enhancing vehicle performance and response. Understanding this internal architecture is key to appreciating the ZF’s robustness and adaptability.
Identifying Common Gearbox Issues
In heavy-duty machinery, transmission components play a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Recognizing early signs of wear or malfunction can prevent severe mechanical failures and costly downtime. This section covers frequent indicators of mechanical inconsistencies and how to approach initial diagnostics effectively.
Unusual Noises and Vibrations
One of the most common symptoms of internal component issues is the presence of abnormal sounds, such as grinding or whining. These noises often point to misalignment, improper lubrication, or potential wear of internal parts. Likewise, unusual vibrations during operation can signal imbalanced mechanisms or weakened mounts, which require prompt assessment to avoid further complications.
Inconsistent Shifting and Reduced Responsiveness
When experiencing delayed response or inconsistent shifting, it may indicate internal deterioration, fluid-related issues, or a compromised synchronization system. Regular inspection of control components and lubrication levels can often identify underlying concerns before they escalate. Addressing these signs early supports smoother operation and prolongs the life of the system.
Essential Tools for Gearbox Repair
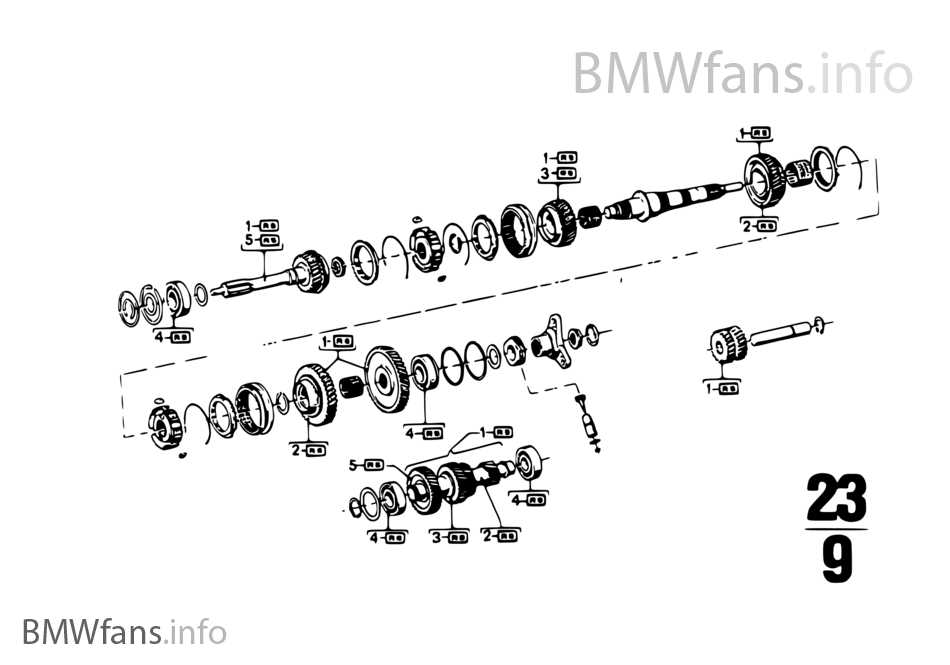
Working on complex transmission systems requires a specific set of tools to ensure efficiency and precision. The right equipment not only speeds up the process but also minimizes the risk of damage to intricate components. Below is a guide to the core instruments that are indispensable for this type of mechanical work.
Basic Hand Tools
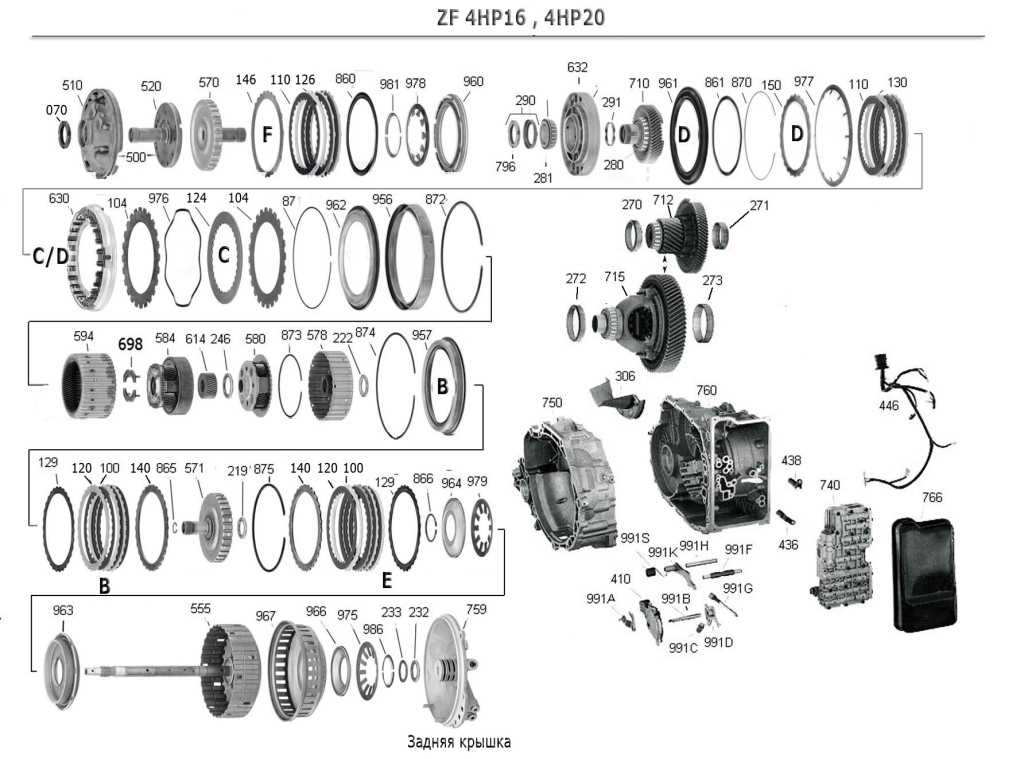
Hand tools are fundamental for most tasks. A selection of durable wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers is essential for adjusting and securing parts. Each of these tools allows for precise movements, which is critical when handling sensitive assemblies.
- Torque Wrench: Ensures bolts and screws are fastened to the required specifications, preventing both over-tightening and loosening.
- Socket Set: A variety of socket sizes allows for easy handling of different bolt dimensions.
- Snap Ring Pliers: Useful for removing and installing snap rings in tight areas without damaging components.
Specialized Instruments
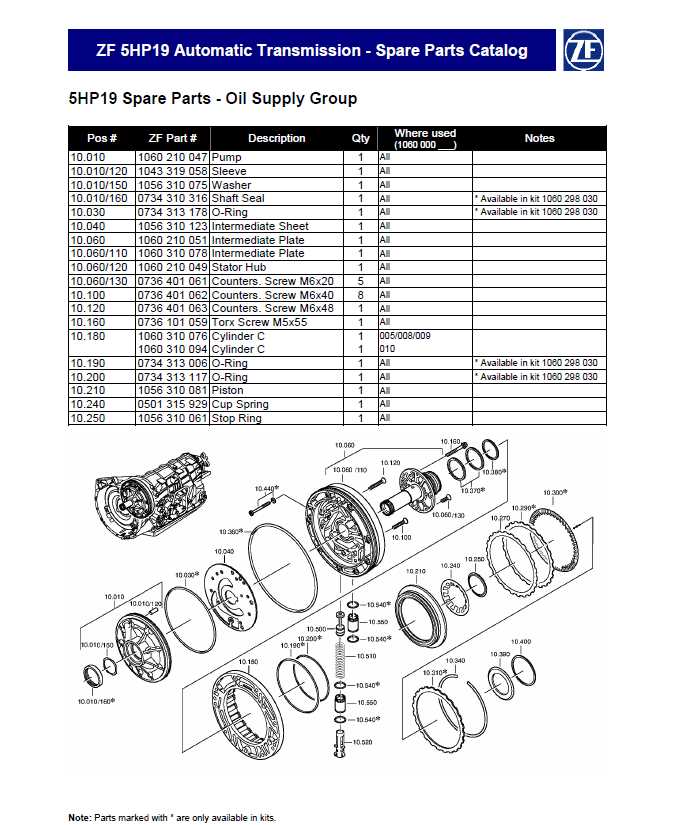
Beyond basic tools, specialized equipment helps in managing intricate adjustments and inspections. These instruments enable precise calibration and alignment, vital for high-performance outcomes.
- Dial Indicator: Measures small movements and is essential for verifying alignment and calibration accuracy.
- Bearing Puller: Removes and installs bearings without harming adjacent parts, which is crucial for component longevity.
- Press Machine: Facilitates the pressing
Disassembly Techniques for Efficiency
Achieving effective dismantling processes requires a focus on systematic approaches and mindful preparation. An organized method, with each step carefully planned, helps to avoid unnecessary delays and ensures each part is accessible for further inspection or maintenance. The goal is a seamless workflow that optimizes time and minimizes the chance of errors.
Preparation is essential before starting. Ensure the work area is clean and tools are organized for easy access. Identifying necessary components and creating a checklist can streamline the process, helping to maintain order as parts are removed.
Strategic sequencing of component removal reduces risk and enhances the reassembly process. Begin with outer components, moving inward methodically. Label each part as it’s detached, and document the order for a smooth reassembly later.
Finally, maintaining a careful approach throughout each step helps prevent damage to intricate elements. Avoid using excessive force, and employ the correct tools for each part, keeping precision and accuracy as priorities to ensure each element remains in optimal condition.
Diagnosing Synchronizer Failures
Identifying issues with synchronizers is crucial for maintaining the optimal functioning of transmission systems. Synchronizers play a vital role in ensuring smooth engagement between different elements during operation. When they malfunction, it can lead to various performance problems, making it essential to understand how to detect these failures effectively.
The symptoms of synchronizer issues can manifest in several ways, including difficulty in shifting, unusual noises, or grinding sensations during gear changes. Recognizing these signs early can prevent further damage and costly repairs. Below is a table outlining common symptoms and their possible causes.
Symptom Possible Cause Difficulty shifting gears Worn or damaged synchronizer rings Grinding noise during engagement Insufficient lubrication or misalignment Inability to engage certain gears Failed synchronizer mechanism Excessive resistance during shifts Contaminated or degraded transmission fluid By systematically analyzing these symptoms, technicians can pinpoint the root causes and implement the necessary corrective actions to restore proper functionality.
Proper Cleaning and Maintenance Tips
Maintaining optimal functionality of complex mechanical systems requires diligent attention to cleaning and regular upkeep. Proper procedures not only extend the lifespan of components but also enhance performance efficiency. This section outlines essential practices that should be followed to ensure longevity and reliability.
Cleaning Techniques
Effective cleaning methods help remove dirt, debris, and contaminants that can impede the functioning of intricate mechanisms. Regularly scheduled cleaning sessions are vital, particularly after extensive use or exposure to harsh environments.
Maintenance Practices

In addition to cleaning, implementing proper maintenance practices is crucial. These practices include regular inspections, lubrication, and timely replacements of worn parts. Keeping a maintenance schedule can prevent unexpected failures and prolong service life.
Task Frequency Notes Clean external surfaces Weekly Use a soft cloth and suitable cleaning agents. Inspect for leaks Monthly Check seals and connections for integrity. Lubricate moving parts Every 3 months Apply recommended lubricants to prevent wear. Replace worn components As needed Monitor performance to determine replacement times. Reassembly Steps for Optimal Performance
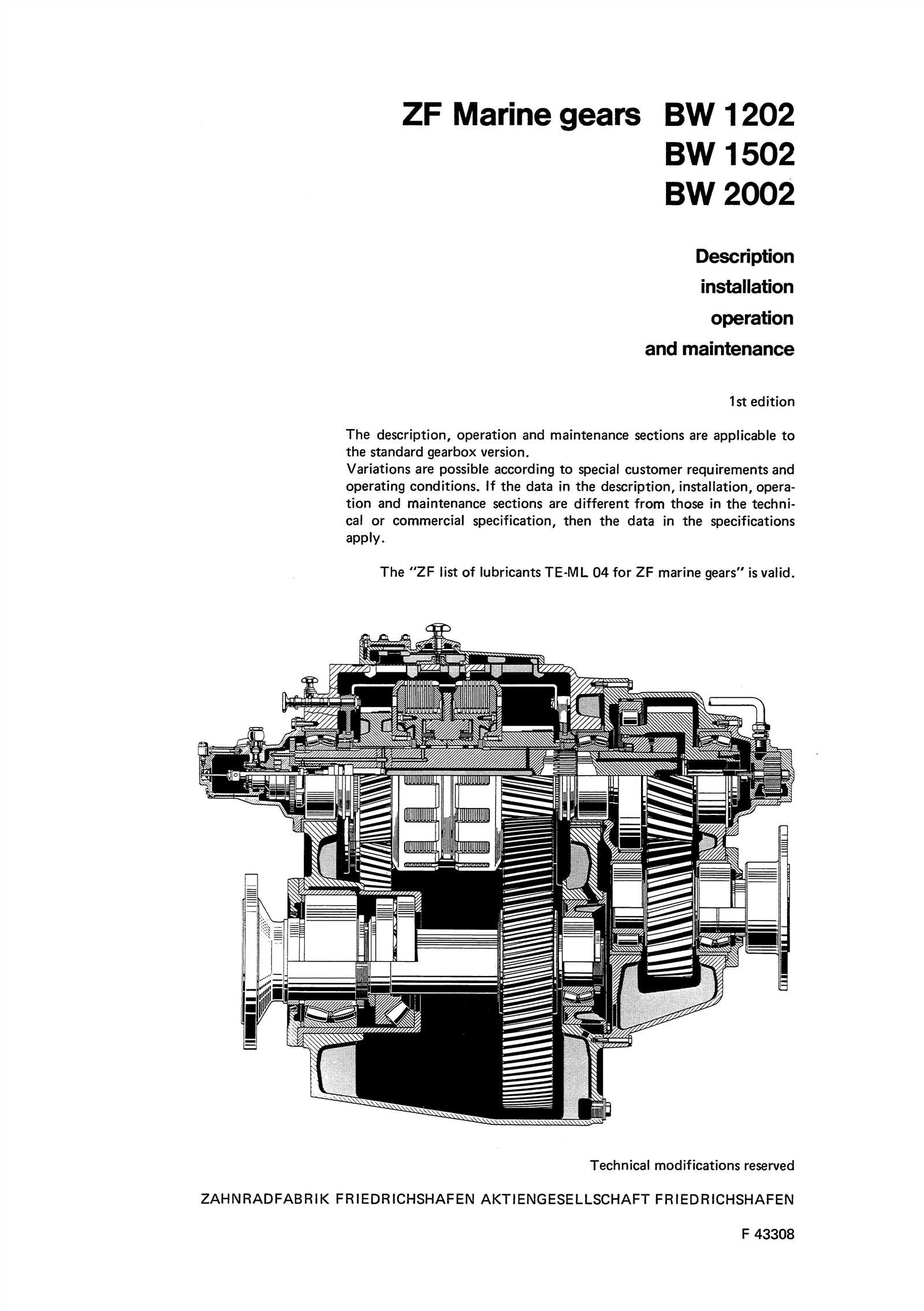
Ensuring the best functionality after disassembling a transmission system requires careful attention to detail during the reassembly process. Each component must be positioned accurately and secured properly to guarantee smooth operation and longevity.
Preparation for Reassembly
Before commencing the reassembly, follow these essential steps:
- Gather all necessary tools and components.
- Thoroughly clean all parts to remove debris and old lubricant.
- Inspect each component for wear or damage.
Reassembly Procedure
Adhering to a systematic approach will help achieve optimal results:
- Begin by placing the main casing in a secure position.
- Install the primary components in the correct order, following the specifications.
- Utilize appropriate seals and gaskets to prevent leaks.
- Tighten all fasteners to the specified torque settings, ensuring even pressure distribution.
- Check the alignment of moving parts to avoid friction or binding.
- Finally, apply the recommended lubricant to ensure smooth operation.
By following these steps diligently, you can enhance the performance and reliability of the assembly, ensuring it operates at its best for an extended period.
Testing Procedures After Repair
After completing the maintenance work on the transmission system, it is crucial to conduct thorough assessments to ensure optimal functionality. This stage involves a series of tests designed to confirm that all components are operating efficiently and that any potential issues have been addressed effectively.
Initial Assessment

The first step involves a visual inspection of the assembly, looking for any signs of leaks or misalignment. Once this is completed, the system should be run at idle to verify that it engages smoothly and without unusual noises. Observing the fluid levels and condition is also essential at this stage.
Functional Testing
Following the initial assessment, the next phase includes functional tests under load conditions. Gradually increase the operational demands while monitoring for any irregularities. It is important to assess the response times and overall performance during various operational scenarios to ensure reliability.
Lubrication Guidelines for Longevity
Proper maintenance of the internal components in any mechanical system is crucial for ensuring their durability and performance. Regular attention to lubrication practices can significantly extend the lifespan of the equipment, reducing wear and tear and preventing costly failures. This section outlines essential principles for maintaining optimal lubrication.
Choosing the Right Lubricant

Selecting an appropriate lubricant is fundamental to the effectiveness of the maintenance process. Different environments and operational conditions may require specific types of lubricants. Consider the following factors when choosing a lubricant:
Factor Description Viscosity Ensure the lubricant has the correct viscosity for the operating temperature and conditions. Compatibility Verify that the lubricant is compatible with the materials used in the system to prevent degradation. Performance Additives Look for additives that enhance protection against wear, corrosion, and oxidation. Lubrication Frequency
Regularly scheduled lubrication is vital to maintaining optimal performance. The frequency will depend on several factors, including operational load, environmental conditions, and the type of lubricant used. Establish a routine that includes:
- Checking lubricant levels frequently.
- Replenishing or replacing the lubricant as needed.
- Monitoring for signs of contamination or degradation.
Addressing Unusual Noise Problems
Unusual sounds emanating from mechanical systems can indicate underlying issues that require prompt attention. Identifying the source of these noises is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and preventing further damage. This section provides insights into common types of noises and possible solutions.
Common Types of Noises
- Grinding: A harsh sound often associated with worn components.
- Clunking: A thumping noise that may signal loose or damaged parts.
- Squeaking: A high-pitched sound indicating friction or lack of lubrication.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Conduct a visual inspection to identify any loose connections or damaged components.
- Listen carefully to pinpoint the location of the noise during operation.
- Check fluid levels and quality to ensure proper lubrication.
- Consider consulting a professional if the source remains elusive or if repairs are beyond your expertise.
Addressing these unusual noises early can help extend the lifespan of the equipment and ensure smooth operation.
Gearbox Care for Prolonged Use
Maintaining the functionality of a transmission system is crucial for ensuring its longevity and optimal performance. Proper care involves regular monitoring, timely maintenance, and understanding the operational needs of the unit. Following best practices can significantly extend the life of the mechanism and prevent costly breakdowns.
Regular Inspection
Conducting frequent assessments is essential. Look for the following:
- Signs of fluid leakage
- Unusual noises during operation
- Temperature variations
- Worn-out seals or gaskets
Fluid Management
Maintaining the right fluid levels and quality is vital. Here are key points to consider:
- Check fluid levels regularly.
- Replace fluids according to manufacturer recommendations.
- Use the appropriate type of fluid for your system.
- Monitor for contamination and change the fluid if necessary.