Ensuring the longevity and safety of structures requires a comprehensive understanding of the necessary protocols for addressing various forms of damage. This section delves into essential procedures and methodologies aimed at maintaining and enhancing the overall strength of frameworks, highlighting best practices for practitioners in the field.
With an emphasis on systematic approaches, this resource serves as a vital reference for professionals seeking to navigate the complexities involved in assessing and addressing deficiencies. Through detailed guidance and practical insights, it aims to equip readers with the knowledge needed to effectively restore and uphold structural integrity.
Whether you are a seasoned expert or a newcomer to the discipline, understanding these foundational concepts is crucial for ensuring that every project meets safety standards and achieves optimal outcomes. The information presented here fosters a proactive mindset, encouraging thorough evaluations and informed decision-making in the restoration process.
This section delves into the essential principles governing the restoration and enhancement of various frameworks and constructions. It provides insights into common practices, methodologies, and considerations that are vital for effective restoration efforts.
Key Principles of Restoration
Understanding foundational concepts is crucial for successful rehabilitation projects. Here are the primary principles:
- Assessment of damage and integrity
- Selection of appropriate materials
- Ensuring compliance with safety regulations
- Adopting sustainable practices
Common Techniques Used
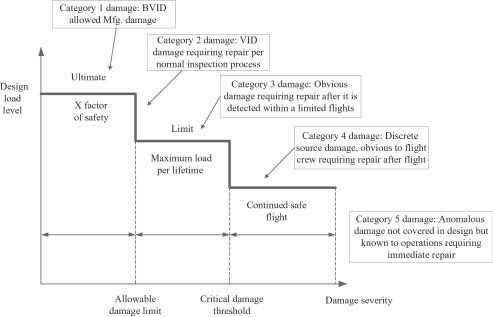
Various methods are employed to achieve effective outcomes in the restoration process:
- Reinforcement of existing structures
- Application of protective coatings
- Integration of new materials with old
- Monitoring and evaluation post-restoration
Common Issues in Structural Integrity
Maintaining the stability and longevity of various constructions is essential. Numerous challenges can arise, affecting the overall strength and durability of the framework. Identifying these concerns early on can prevent further damage and ensure safety.
| Issue | Description | Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Cracking | Fissures may develop due to stress, temperature changes, or settlement. | Compromised load-bearing capacity, potential collapse. |
| Corrosion | Metal components can rust, leading to weakened connections. | Increased risk of failure, reduced lifespan. |
| Deflection | Excessive bending or displacement of beams and supports. | Distortion of elements, discomfort for occupants. |
| Water Damage | Moisture infiltration can weaken materials and cause decay. | Structural deterioration, mold growth. |
| Pest Infestation | Insects or rodents may compromise wood and insulation. | Weakening of critical components, safety hazards. |
Key Components of the SRM

This section focuses on essential elements that play a critical role in the documentation process for enhancing structural integrity. Understanding these components is vital for effectively utilizing the guide and ensuring the longevity and safety of various constructions.
- Assessment Procedures: Detailed protocols for evaluating the condition of materials and structures.
- Material Specifications: Guidelines on the types of materials recommended for various applications, including strengths and weaknesses.
- Repair Techniques: Step-by-step instructions for applying different methods to restore integrity, including techniques for reinforcement and replacement.
- Safety Standards: Important regulations and safety measures to follow during restoration processes to protect personnel and structures.
- Documentation Requirements: Essentials for maintaining records of evaluations, repairs, and materials used, ensuring traceability and accountability.
Familiarity with these components allows users to navigate the guidance effectively, leading to informed decision-making and improved structural outcomes.
Steps for Effective Damage Assessment
Assessing damage requires a systematic approach to ensure all affected areas are thoroughly evaluated. This process helps in understanding the extent of the issue and guides further actions.
- Initial Inspection: Begin with a visual examination to identify visible signs of harm.
- Documentation: Take detailed notes and photographs of the affected areas to maintain a record.
- Prioritize Areas: Determine which sections need immediate attention based on severity.
- Evaluate Structural Integrity: Check for any compromises that may affect stability and safety.
- Consult Experts: Involve professionals for advanced analysis if necessary.
- Report Findings: Compile a comprehensive report summarizing all observations and recommendations.
Following these steps can help ensure a thorough evaluation and facilitate appropriate action for resolution.
Repair Techniques and Best Practices
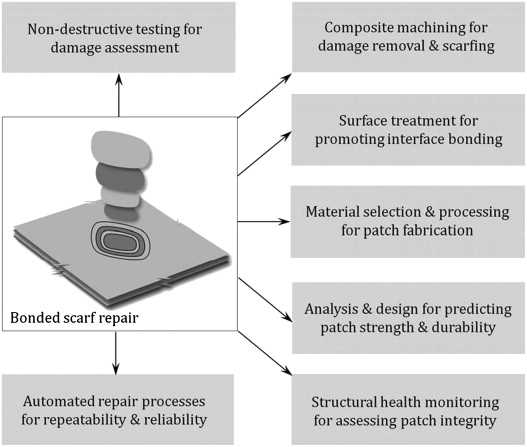
Effective methodologies play a crucial role in maintaining and restoring integrity to various structures. Implementing the right strategies can significantly enhance durability and performance while ensuring safety and compliance with industry standards.
- Assessment and Inspection: Conduct thorough evaluations to identify damage and assess the extent of required intervention. Regular monitoring can help in early detection of potential issues.
- Material Selection: Choose appropriate materials that match the existing components in terms of strength and compatibility. This ensures cohesive performance and longevity.
- Techniques of Reinforcement: Employ various methods to bolster weak areas, such as using additional supports or applying composites that improve overall strength without adding excessive weight.
- Adhesive Bonding: Utilize high-quality adhesives for joints and connections to enhance load-bearing capacity and provide a seamless finish. This method can also reduce stress concentrations.
- Quality Control: Implement strict quality assurance processes during all stages of restoration. This includes verifying material specifications and ensuring adherence to best practices.
By adhering to these approaches, one can achieve not only a successful outcome but also prolong the life of the structure, ultimately leading to greater satisfaction for all stakeholders involved.
Tools and Materials for Repairs
Successful restoration projects rely heavily on the right equipment and supplies. Ensuring that the appropriate instruments and components are at hand can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the work. This section delves into essential items that facilitate various tasks, promoting optimal outcomes.
Basic instruments such as hammers, screwdrivers, and pliers are indispensable for most tasks. Specialized tools like chisels and saws may also be necessary depending on the nature of the work. Additionally, power tools, including drills and grinders, can greatly speed up processes and improve precision.
In terms of materials, adhesives, sealants, and fasteners are critical for achieving strong and lasting connections. Depending on the specific requirements, various types of wood, metal, and composites may be utilized to ensure compatibility and durability. Selecting high-quality materials is vital to the success of any undertaking.
Lastly, proper safety gear such as gloves, goggles, and masks should not be overlooked. Protecting oneself while working is essential to prevent injuries and ensure a safe environment for all involved in the project.
Safety Considerations During Repairs
When undertaking maintenance tasks, it is crucial to prioritize safety to protect both personnel and equipment. Awareness of potential hazards and implementing precautionary measures can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.
Proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is essential. Always wear appropriate gear such as helmets, gloves, and safety goggles to shield against falling debris and sharp objects. Additionally, ensure that all participants are familiar with the equipment and tools being used to minimize operational risks.
Site assessment plays a vital role in ensuring a safe working environment. Before starting any task, evaluate the area for potential dangers such as unstable surfaces, exposure to hazardous materials, or inadequate lighting. Identifying these issues in advance allows for the implementation of corrective measures.
Lastly, clear communication among team members is imperative. Establishing a protocol for reporting hazards and coordinating efforts can help maintain a safe atmosphere throughout the entire process. By fostering a culture of safety, the likelihood of incidents can be greatly diminished.
Maintenance Tips for Long-Term Durability
Ensuring the longevity of your installations involves regular upkeep and mindful practices. Adopting a proactive approach can significantly enhance the lifespan of your structures, ultimately saving time and resources.
- Regular Inspections: Schedule periodic assessments to identify early signs of wear or damage.
- Clean Surfaces: Keep all surfaces free from debris and contaminants to prevent deterioration.
- Address Moisture Issues: Ensure proper drainage and ventilation to mitigate moisture-related problems.
- Use Quality Materials: Invest in high-quality components to withstand environmental stresses.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the recommendations provided for maintenance and operation.
By implementing these strategies, you can greatly enhance the resilience and performance of your structures, ensuring they remain effective for years to come.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Adhering to established guidelines is crucial for ensuring safety and reliability in construction and renovation projects. These standards provide a framework for quality assurance, helping to mitigate risks associated with structural integrity and overall performance. Compliance with these regulations not only safeguards public welfare but also enhances the credibility of the involved parties.
Various organizations and governing bodies develop and enforce these standards, encompassing a wide range of criteria, including design, materials, and workmanship. Regular audits and inspections are often conducted to verify adherence, ensuring that all projects meet the necessary requirements. This proactive approach fosters a culture of accountability and continuous improvement within the industry.
Incorporating these guidelines into project planning and execution is essential for maintaining industry best practices. By doing so, stakeholders can minimize potential liabilities and enhance operational efficiencies. Ultimately, a commitment to regulatory standards fosters trust among clients, regulators, and the general public, reinforcing the importance of compliance in all facets of the field.
Case Studies in Structural Repairs
This section explores various instances where restoration and reinforcement techniques have been successfully applied to enhance the integrity of different frameworks. By examining these scenarios, valuable insights can be gained regarding effective practices and methodologies in the field of construction and restoration.
-
Bridge Reinforcement Project:
A well-known project involved the assessment and subsequent enhancement of an aging bridge. Engineers utilized innovative materials to strengthen load-bearing elements, significantly improving safety and longevity.
-
Historical Building Preservation:
In this case, a century-old structure faced deterioration. Experts implemented modern techniques to restore its façade while preserving its historical significance, ensuring compliance with contemporary safety standards.
-
Industrial Facility Stabilization:
During routine inspections, signs of distress were identified in an industrial facility. The response included the introduction of additional support systems, effectively redistributing weight and preventing further damage.
These examples illustrate the diverse approaches and solutions that can be adopted to address challenges in maintaining and enhancing various types of frameworks, emphasizing the importance of tailored strategies in ensuring structural integrity.