
When it comes to keeping outdoor power equipment in optimal condition, understanding the intricacies of engine care is paramount. This guide delves into the various aspects of maintaining and troubleshooting small engines, ensuring longevity and efficiency. Whether you are a seasoned mechanic or a novice enthusiast, having access to comprehensive information can significantly enhance your skills and confidence.
Regular upkeep is crucial for preventing common issues that can arise with engine operation. Knowing how to address minor complications can save time and reduce the risk of major repairs. This resource is designed to equip you with the necessary knowledge, enabling you to tackle maintenance tasks with ease and precision.
In this exploration, we will cover essential topics such as identifying common symptoms of engine trouble, performing routine checks, and understanding the significance of various components. By familiarizing yourself with these elements, you will be better prepared to ensure the reliability of your equipment and maximize its performance.
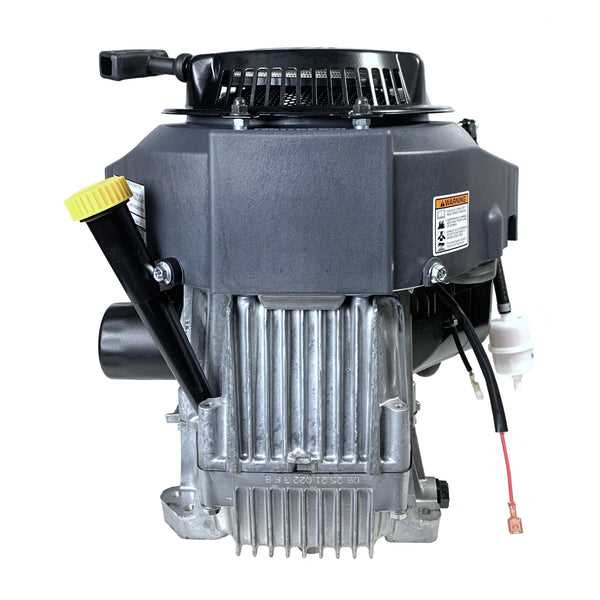
Kawasaki FH580V Overview

This section provides an insightful look into a versatile engine designed for various applications, particularly in outdoor power equipment. It showcases features that enhance performance, reliability, and efficiency, making it a popular choice among users seeking robust solutions for their gardening and landscaping needs.
Key Features
- Powerful performance with a robust output.
- Designed for easy maintenance and accessibility.
- Durable construction for extended lifespan.
- Optimized fuel efficiency, reducing operational costs.
Applications

- Lawn mowers
- Garden tractors
- Utility vehicles
- Commercial landscaping equipment
With these attributes, this engine stands out in the market, meeting the demands of both homeowners and professionals alike. Its design philosophy emphasizes ease of use and dependability, ensuring it can handle a variety of tasks efficiently.
Common Issues with FH580V Engines
Engines of this type are known for their reliability, but like any mechanical system, they can encounter various problems over time. Understanding these common issues can help in maintaining optimal performance and extending the lifespan of the equipment. Addressing these concerns early can prevent more significant damage and costly repairs.
One frequent issue is starting difficulties, often caused by fuel system problems, electrical failures, or issues with the ignition components. Regular checks of the battery, spark plugs, and fuel filters can mitigate this problem. Additionally, operators may notice a decrease in power or performance, which can stem from clogged air filters or worn-out internal components.
Overheating is another significant concern that can lead to severe damage if not addressed promptly. This can result from inadequate cooling system maintenance, such as low coolant levels or a malfunctioning radiator. Ensuring that the cooling system is in good condition is crucial for preventing overheating.
Finally, abnormal vibrations or noises can indicate underlying mechanical issues. These symptoms may arise from loose or damaged parts, and it’s essential to conduct regular inspections to identify and resolve these issues early. By being proactive and addressing these common problems, operators can ensure their engines run smoothly and efficiently.
Tools Required for Repairs

To effectively address maintenance and troubleshooting tasks, having the right equipment is essential. A well-equipped workspace can significantly enhance the efficiency and quality of the work being performed. Proper tools not only facilitate smoother operations but also contribute to safety and accuracy.
Basic hand tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers are fundamental for most procedures. Additionally, specialized instruments like torque wrenches and multimeters can be vital for more intricate tasks. It’s also advisable to have cleaning supplies and lubricants on hand to ensure optimal functioning of the components.
Safety gear, including gloves and goggles, should not be overlooked, as they protect against potential hazards during maintenance activities. Organizing tools in a dedicated area can streamline the process, allowing for quick access and preventing misplaced items. Overall, being well-prepared with the necessary instruments is key to achieving successful outcomes in any mechanical endeavor.
Step-by-Step Repair Instructions
This section provides detailed guidance for addressing common issues with small engines, ensuring effective restoration and optimal performance. Follow these systematic steps to enhance your understanding and skills in engine maintenance.
Preparation
- Gather necessary tools: wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers.
- Ensure you have replacement parts on hand, if needed.
- Work in a well-ventilated area to ensure safety.
Diagnostic Process
- Inspect the engine for visible damage or wear.
- Check the fuel system for clogs or leaks.
- Examine the ignition components, ensuring they are functioning properly.
- Test the oil level and quality; change if necessary.
- Document any irregularities for reference during repairs.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
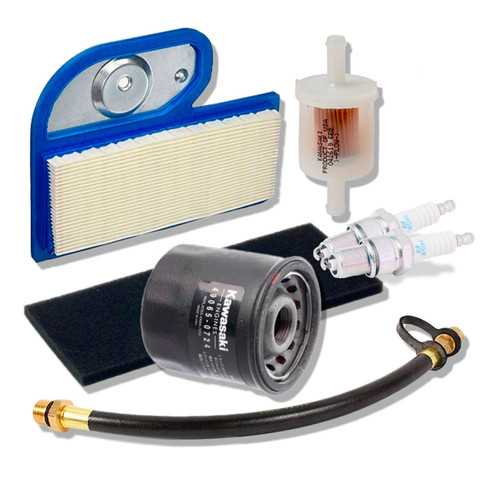

Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your equipment. By implementing a systematic approach to maintenance, you can prevent unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs. This section offers valuable suggestions to help keep your machinery in optimal condition.
1. Regular Inspection: Schedule routine checks to identify wear and tear before it leads to significant issues. Look for signs of damage, such as frayed belts or leaks, and address them promptly.
2. Cleanliness Matters: Maintain a clean working environment by removing debris and dirt that can hinder performance. Regularly clean filters, air intakes, and external surfaces to enhance airflow and cooling.
3. Lubrication: Ensure all moving parts are adequately lubricated to minimize friction and prevent premature wear. Use the recommended lubricants and follow guidelines for frequency of application.
4. Check Fluid Levels: Monitor oil, fuel, and coolant levels regularly. Keeping these fluids at appropriate levels not only promotes efficient operation but also protects critical components from damage.
5. Battery Maintenance: Inspect battery terminals for corrosion and ensure a secure connection. Regularly check the battery’s charge and replace it when necessary to avoid starting issues.
6. Follow Operating Guidelines: Adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions for operation and maintenance. This includes recommended schedules for service tasks and part replacements.
By following these preventive measures, you can significantly extend the life of your equipment and enhance its overall performance.
Understanding Engine Specifications
When it comes to the performance and longevity of small engines, a comprehensive grasp of their specifications is crucial. These details not only dictate how an engine operates but also influence maintenance practices and potential upgrades. Knowledge of these parameters helps users make informed decisions regarding repairs and enhancements.
Power Output: The power produced by an engine is often measured in horsepower or kilowatts. This figure indicates the engine’s capability to perform work, making it a key aspect for users looking for efficiency and effectiveness in their equipment.
Displacement: Engine displacement, usually expressed in cubic centimeters (cc) or liters, refers to the total volume of all the cylinders. It serves as a fundamental factor in determining the engine’s power potential and fuel consumption rates.
Torque: Torque represents the rotational force generated by the engine, essential for understanding how well the engine can handle various loads. Higher torque values are particularly important for applications requiring significant power at low speeds.
Fuel Type: The type of fuel an engine requires significantly impacts its performance and efficiency. Different engines are designed to operate with specific fuel grades, which can affect combustion quality and overall functionality.
Cooling System: An effective cooling system is vital for maintaining optimal operating temperatures. Understanding the cooling method, whether air-cooled or liquid-cooled, can help users recognize maintenance needs and prevent overheating issues.
By familiarizing oneself with these specifications, operators can ensure their equipment runs smoothly and efficiently, ultimately enhancing performance and extending the lifespan of the engine.
Fuel System Troubleshooting
The fuel system is a critical component that ensures the proper operation of small engines. Identifying and resolving issues within this system can enhance performance and prolong the lifespan of the engine. Common problems often stem from fuel delivery, contamination, or component malfunctions, making it essential to understand how to diagnose these issues effectively.
When troubleshooting fuel system concerns, consider the following key areas:
| Issue | Possible Causes | Suggested Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Engine won’t start | Empty fuel tank, clogged filter, faulty pump | Refill fuel, replace filter, test and replace pump |
| Engine runs poorly | Contaminated fuel, incorrect mixture, air leaks | Drain and replace fuel, adjust mixture, check gaskets |
| Fuel leaking | Damaged lines, loose connections, failed seals | Inspect and replace lines, tighten connections, change seals |
| Poor acceleration | Blocked jets, insufficient fuel pressure, air filter issues | Clean or replace jets, check fuel pressure, service air filter |
Regular maintenance and timely troubleshooting can prevent minor issues from escalating into major problems, ensuring optimal functionality of the engine.
Electrical System Diagnostics

Diagnosing the electrical system of outdoor power equipment is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. By understanding the components involved and employing systematic testing methods, one can effectively identify issues and restore functionality.
Key Components to Check
- Batteries: Inspect for corrosion and ensure proper voltage.
- Wiring: Look for frayed or damaged wires that could cause shorts.
- Connectors: Ensure all connections are tight and free from rust.
- Fuses: Check for blown fuses that may interrupt the circuit.
Diagnostic Steps
- Begin with a visual inspection of the entire electrical system.
- Use a multimeter to test battery voltage and continuity of wires.
- Examine switches and relays for proper operation.
- Document any abnormalities and replace faulty components as needed.
By following these steps and focusing on the critical parts of the electrical system, users can effectively troubleshoot and maintain their equipment.
Replacing Spark Plugs
Maintaining optimal engine performance requires regular attention to various components, including the ignition system. One crucial aspect of this system is the spark plug, which ignites the fuel-air mixture, ensuring smooth operation. Over time, spark plugs can wear out or become fouled, leading to misfires, reduced power, and increased fuel consumption. This section outlines the process of replacing these vital components to keep your engine running efficiently.
Tools and Materials Needed
- New spark plugs
- Socket wrench with the appropriate size socket
- Torque wrench
- Spark plug gap tool
- Anti-seize lubricant (optional)
Step-by-Step Replacement Process
- Ensure the engine is cool before starting the replacement.
- Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to avoid electrical issues.
- Remove the ignition wire from the first spark plug carefully.
- Use the socket wrench to unscrew the old spark plug from the engine.
- Inspect the old spark plug for signs of wear or damage.
- Set the gap on the new spark plug according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Apply a small amount of anti-seize lubricant to the threads of the new spark plug, if desired.
- Insert the new spark plug into the cylinder head and tighten it using the socket wrench.
- Reconnect the ignition wire securely.
- Repeat the process for the remaining spark plugs as needed.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your engine maintains peak performance and efficiency. Regularly checking and replacing spark plugs can prevent larger issues down the line, ultimately saving time and resources.
Oil Change Procedures
Regular maintenance of your engine’s lubrication system is essential for optimal performance and longevity. One critical aspect of this upkeep is the timely replacement of oil, which ensures that all moving parts are adequately lubricated and protected against wear and tear. This section outlines the steps to effectively perform an oil change, ensuring that your machinery continues to operate smoothly.
Preparation Steps
Before starting the oil change, gather the necessary tools and materials: a new oil filter, the correct type and amount of oil, an oil catch pan, a wrench, and a funnel. Ensure the engine is cool and parked on a flat surface to facilitate proper drainage. Safety equipment, such as gloves and goggles, is also recommended to protect against spills and splashes.
Oil Change Procedure
Begin by removing the drain plug located at the bottom of the oil pan. Allow the old oil to completely drain into the catch pan. Once drained, replace the drain plug securely. Next, remove the old oil filter using the wrench. Apply a small amount of new oil to the rubber gasket of the new filter before installing it, ensuring a proper seal. Finally, pour the new oil into the engine through the funnel, checking the dipstick to ensure the correct level is reached. Start the engine and let it run for a few minutes, then check for leaks around the filter and drain plug.
Maintaining a routine for oil changes is crucial for the health of your engine, promoting efficiency and reliability over time.
Safety Precautions During Repairs

Ensuring a safe working environment is crucial when performing maintenance tasks on machinery. Adhering to proper safety measures minimizes the risk of injury and equipment damage, promoting a smooth and effective workflow. This section outlines essential guidelines to follow while working on mechanical devices.
Essential Safety Guidelines
Before starting any maintenance activity, it’s important to familiarize yourself with safety protocols. Here are key practices to consider:
| Precaution | Description |
|---|---|
| Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) | Always wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, goggles, and hearing protection, to safeguard against potential hazards. |
| Work Area Organization | Keep your workspace tidy and free of obstacles to prevent trips and falls while working. |
| Proper Tools | Use the correct tools for the job to avoid accidents and ensure efficiency during tasks. |
| Electrical Safety | Disconnect power sources before starting any electrical work to prevent shocks or short circuits. |
| Follow Manufacturer Guidelines | Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and recommendations to ensure safe handling and operation. |
Emergency Preparedness
Being prepared for emergencies can significantly reduce risks. Familiarize yourself with the location of first aid kits and fire extinguishers. Knowing how to respond quickly to accidents or equipment malfunctions can save lives and minimize damage.
Where to Find Replacement Parts
Locating suitable components for machinery maintenance is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Various sources are available for enthusiasts and professionals alike to obtain high-quality parts, whether for routine upkeep or necessary repairs.
Authorized Dealers
One of the most reliable options is to visit authorized dealerships. These establishments often stock genuine components, guaranteeing compatibility and quality. Engaging with knowledgeable staff can also provide valuable insights into the best parts for your specific needs.
Online Retailers
Another convenient choice is to explore online marketplaces. Numerous websites specialize in aftermarket and original equipment parts, often featuring user reviews and ratings. When purchasing online, ensure that the retailer is reputable and offers a return policy to safeguard your investment.