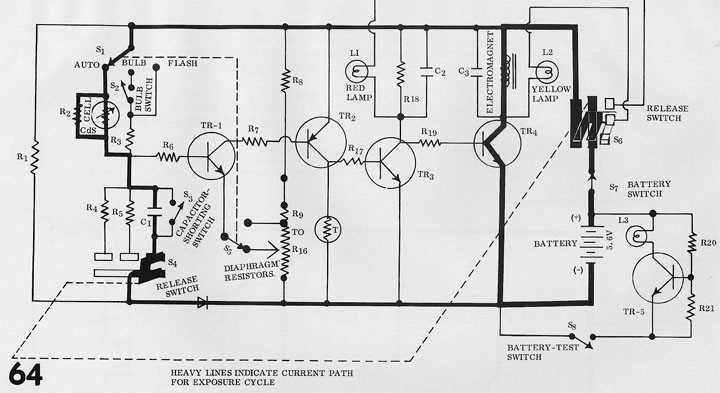
Maintaining vintage photographic devices can be a rewarding endeavor for enthusiasts and collectors alike. This section delves into the intricacies of preserving and restoring iconic models, emphasizing the significance of proper care and troubleshooting techniques. By familiarizing oneself with the essential components and functionalities, users can enhance their shooting experience and prolong the lifespan of these cherished artifacts.
The journey of reviving an old photographic instrument often begins with a comprehensive examination of its structure. Understanding how each part interacts with others is crucial for effective servicing. This knowledge not only aids in identifying potential issues but also empowers individuals to perform basic adjustments and improvements independently.
Furthermore, acquiring familiarity with the various tools and materials required for maintenance can streamline the process. With the right approach, even the most intricate problems can be addressed, ensuring that these mechanical masterpieces continue to capture moments as they were intended. Through careful handling and informed interventions, one can breathe new life into classic imaging devices, preserving their legacy for future generations.
Yashica Electro 35 Overview
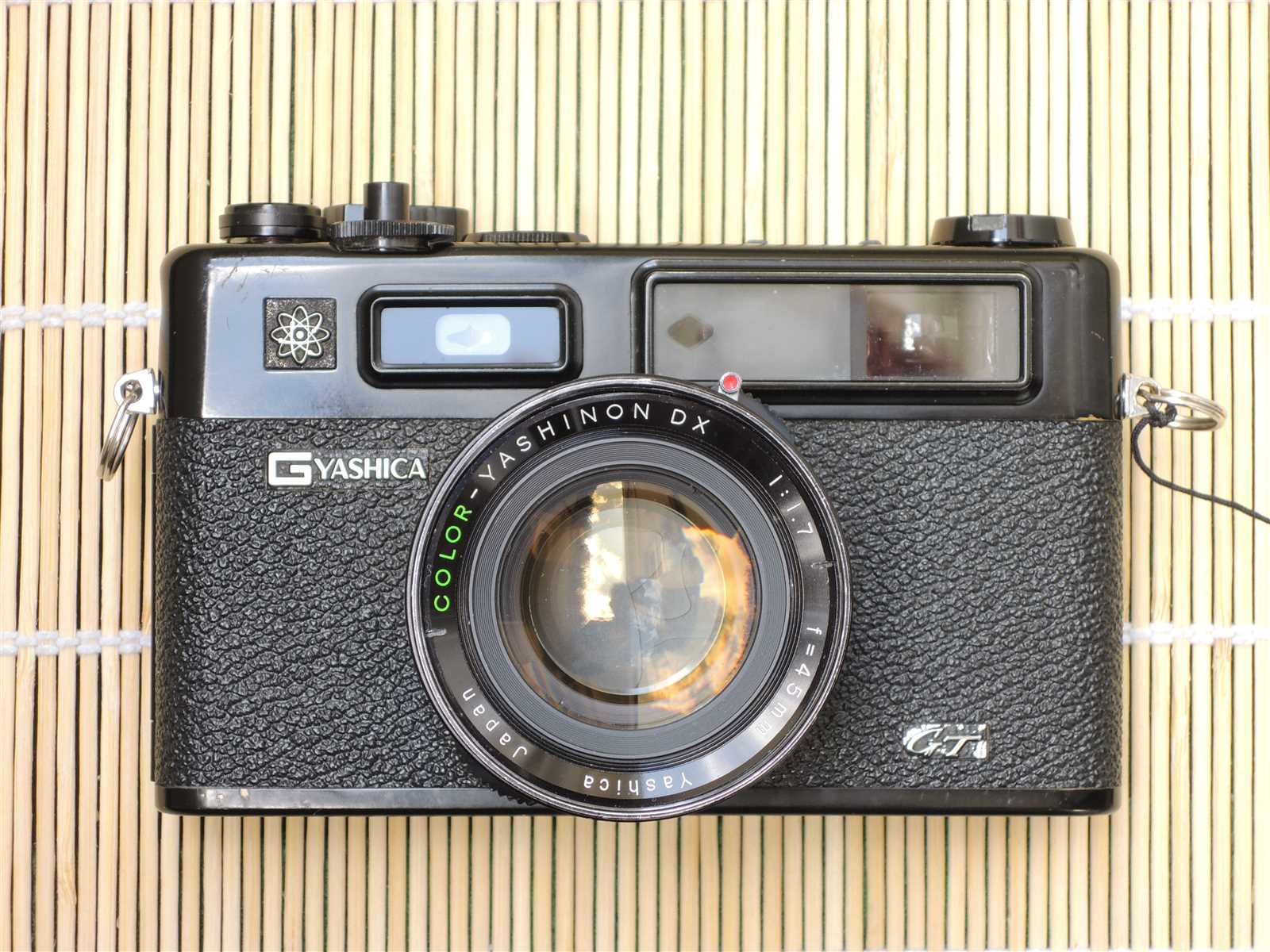

This section provides a comprehensive insight into a renowned range of compact film cameras that gained popularity in the 1970s. Characterized by their innovative features and user-friendly design, these devices are celebrated for their blend of style and functionality.
The highlighted model showcases a robust construction, making it a favorite among both enthusiasts and professionals. Its automatic exposure system, combined with a quality lens, allows users to capture stunning images with ease. The incorporation of a light meter enhances the shooting experience by ensuring accurate exposures in various lighting conditions.
Moreover, the aesthetic appeal of this camera is undeniable, with a classic design that resonates with vintage photography lovers. Its portability and simplicity make it an ideal choice for street photography and everyday use, solidifying its place in the hearts of many.
In summary, this camera represents a harmonious fusion of technology and design, making it a timeless piece in the world of photography.
Common Issues and Symptoms
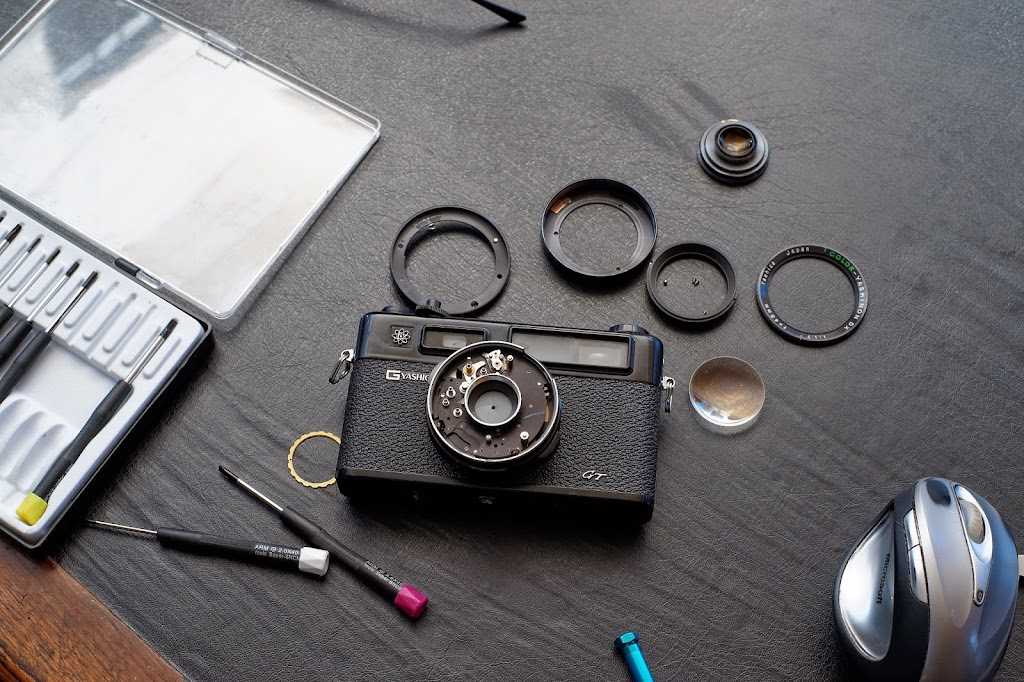

This section outlines frequent problems encountered with a specific vintage camera model, detailing the typical signs that users may observe when the device is not functioning optimally. Recognizing these symptoms can assist in diagnosing the underlying issues effectively.
Frequent Malfunctions
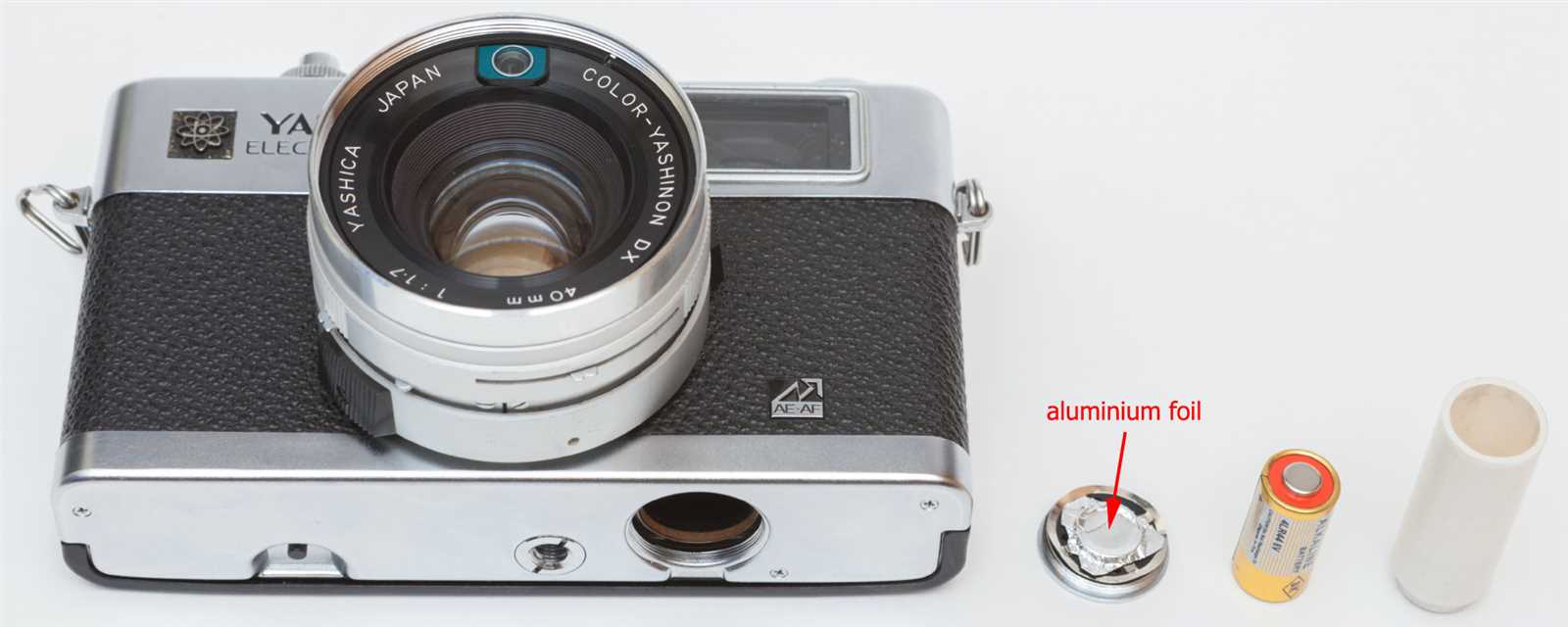

- Shutter Failure: Inability to open or close the shutter can lead to blank images.
- Meter Inaccuracy: Erratic exposure readings resulting in overexposed or underexposed photographs.
- Film Advance Issues: Difficulty in advancing the film can cause multiple exposures or film jams.
Visual Symptoms
- Blurred Images: Soft focus or lack of sharpness in photographs.
- Light Leaks: Unwanted streaks of light appearing in images, indicating potential seals or body issues.
- Corrosion Signs: Visible rust or deterioration on metal components, which can affect performance.
Tools Needed for Repair

When embarking on the journey of restoring a vintage camera, having the right equipment is crucial for a successful outcome. This section outlines the essential instruments required to efficiently handle various issues that may arise during the restoration process.
Essential Tools
- Precision screwdriver set: Ideal for accessing small screws without causing damage.
- Tweezers: Useful for handling tiny components with care.
- Lens cleaning solution: Necessary for maintaining optical clarity.
- Microfiber cloth: Effective for safely cleaning delicate surfaces.
- Multimeter: Essential for checking electrical connections and voltages.
Additional Equipment
- Desoldering pump: Helpful for removing solder from circuit boards.
- Spudger: A non-conductive tool for prying open casings without scratching.
- Magnifying glass: Aids in inspecting small parts and details.
- Heat gun: Useful for loosening adhesive materials.
- Work mat: Provides a clean and organized surface for assembly and disassembly.
Disassembly Process Explained
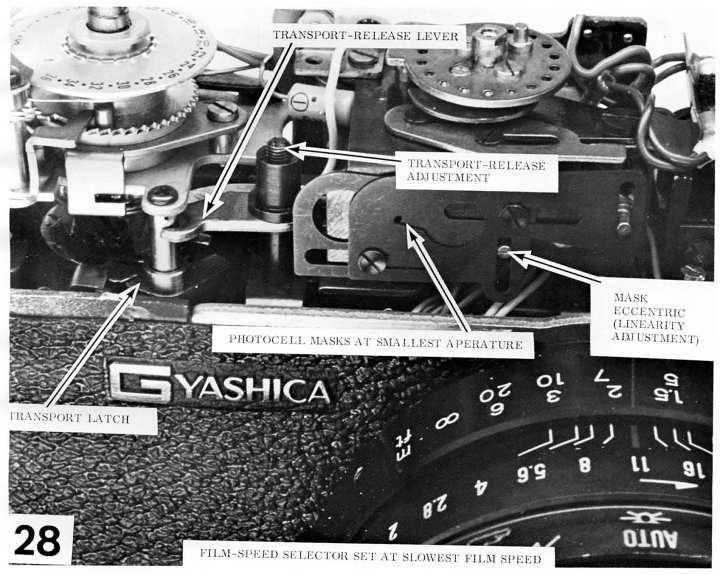
This section outlines the step-by-step method for dismantling a classic photographic device. Understanding the process is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. By following the outlined procedures, users can safely access the internal components without causing damage.
Before beginning the disassembly, ensure you have the necessary tools at hand. A clean, organized workspace will facilitate a smoother experience. It is advisable to document each step to assist with reassembly.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Remove the outer casing screws using a small screwdriver. |
| 2 | Carefully detach the front and back panels from the main body. |
| 3 | Disconnect any ribbon cables or connectors that may be attached. |
| 4 | Take out the lens assembly by unscrewing the securing elements. |
| 5 | Inspect the internal components for any signs of wear or damage. |
Following these steps will enable a thorough examination of the device, allowing for effective problem-solving and upkeep. Always handle parts with care to prevent any inadvertent harm.
Testing Electrical Components
When troubleshooting electronic devices, it is essential to evaluate the functionality of various electrical parts. This process ensures that each component operates within its intended parameters, which can help identify potential failures and improve overall performance.
1. Multimeter Usage: A multimeter is a crucial tool for measuring voltage, current, and resistance. Begin by setting the device to the appropriate measurement mode. For instance, to check voltage, connect the probes to the component terminals and read the display to confirm if the values align with expected specifications.
2. Continuity Testing: This test determines if a circuit is complete. With the multimeter set to the continuity mode, place the probes on either end of the pathway. A beep or a reading indicates a successful connection, while no response suggests a break in the circuit.
3. Resistance Measurement: Evaluating resistance helps ascertain if a component is functioning correctly. Set the multimeter to the resistance mode and connect the probes to the terminals. Compare the measured value with the component’s rated resistance to determine if it is operating as intended.
4. Capacitor Testing: For capacitors, use a dedicated capacitance meter if available. If using a multimeter, discharge the capacitor first, then connect it to the appropriate terminals. Measure the capacitance and compare it with the rated value to ensure proper functionality.
By systematically testing these electrical elements, one can pinpoint issues effectively, ensuring the device operates optimally and prolonging its lifespan.
Replacing Damaged Parts

When maintaining a vintage camera, addressing worn or broken components is essential for optimal functionality. This process ensures the device operates as intended and preserves its overall performance.
Before starting the replacement, it’s important to identify the specific parts that require attention. Common issues may include:
- Lens malfunction
- Shutter inconsistencies
- Viewfinder misalignment
- Corroded electrical contacts
Once the damaged components are identified, the following steps can guide the replacement process:
- Gather necessary tools, including screwdrivers, tweezers, and replacement parts.
- Carefully disassemble the camera body, taking care to document the placement of each component.
- Remove the faulty parts, ensuring not to damage surrounding elements.
- Install the new components, following the manufacturer’s specifications to guarantee compatibility.
- Reassemble the camera, double-checking that all screws and parts are securely fastened.
- Conduct a functional test to ensure proper operation of the newly installed components.
Regular maintenance and timely replacement of damaged parts contribute to the longevity and reliability of your equipment, allowing you to capture moments with confidence.
Calibration Techniques for Accuracy
Ensuring precision in optical devices is essential for achieving optimal performance. Calibration methods play a critical role in aligning components and verifying measurements to maintain the integrity of the equipment.
Various techniques can be employed to achieve accurate calibration:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly examining the device for any visible signs of wear or misalignment can help identify potential issues early.
- Test Measurements: Conducting systematic measurements against known standards allows for comparison and adjustment.
- Adjustment Procedures: Following specific procedures for adjusting settings or components can ensure that all elements function harmoniously.
- Use of Calibration Tools: Utilizing specialized instruments designed for calibration enhances the reliability of the adjustments made.
- Documentation: Keeping a detailed log of calibration processes and results aids in tracking performance over time and facilitates future adjustments.
Implementing these techniques will contribute significantly to the longevity and accuracy of optical equipment, ensuring that it operates at peak efficiency.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity

Proper care and regular upkeep are essential for ensuring the extended lifespan of your photographic equipment. By following a few simple practices, you can keep your device functioning optimally and enhance its durability.
Regular Cleaning

Dust and grime can accumulate over time, affecting performance and image quality. Here are some cleaning tips:
- Use a soft microfiber cloth to gently wipe the exterior.
- Utilize a blower to remove dust from sensitive areas.
- Clean the lens with a dedicated lens cleaner and cloth.
Storage Practices

Storing your equipment properly is just as important as cleaning it. Consider the following suggestions:
- Keep the device in a padded case to protect it from shocks.
- Avoid exposing it to extreme temperatures and humidity.
- Remove batteries if the device will not be used for an extended period.
Implementing these maintenance tips will help preserve your equipment’s functionality and prolong its life, allowing you to enjoy capturing moments for years to come.
Finding Replacement Parts Online
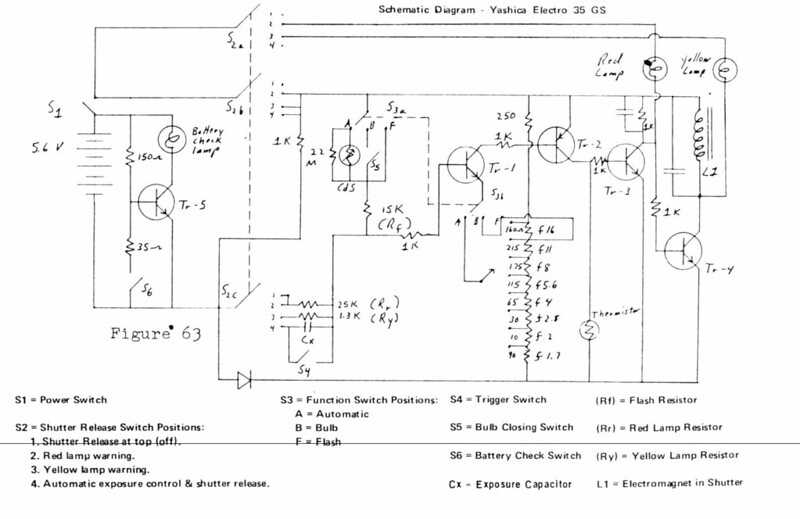
Locating components for vintage photographic devices can be a rewarding yet challenging endeavor. With the right approach, you can access a variety of online resources to find the necessary pieces for your specific model. Understanding where to search and how to evaluate potential sellers is key to ensuring you obtain high-quality items.
Online Marketplaces: Popular platforms such as eBay and Amazon often have listings for rare parts. Be sure to check seller ratings and reviews to gauge reliability. It’s also beneficial to use specific keywords related to the components you need, as this can help narrow down the search results effectively.
Specialized Forums and Communities: Engaging with photography enthusiasts through forums or social media groups can yield valuable leads. Members often share insights about where to find specific parts or may even have spare components available for sale or trade.
Manufacturer’s Resources: Although the original manufacturer may not produce these items anymore, some websites maintain inventories of old stock. Checking their websites or contacting customer service can sometimes uncover options that are not widely advertised.
Repair Shops: Local or online repair specialists often have access to a range of components and might be willing to sell parts directly. Establishing a relationship with these professionals can provide additional support and advice for your restoration projects.
By leveraging these avenues, you can increase your chances of successfully finding the components you need, ensuring your device continues to function optimally.
Resources for Further Assistance

When encountering challenges with vintage photographic devices, it’s essential to seek out reliable sources of information and support. The following resources can provide valuable insights and guidance for enthusiasts looking to restore or troubleshoot their equipment.
- Online Forums: Engaging with communities dedicated to classic cameras can yield helpful tips and shared experiences. Websites like photo.net and rangefinderforum.com host discussions where users exchange advice.
- Repair Guides: Many enthusiasts have documented their restoration journeys through detailed guides and blog posts. Websites such as filmwasters.com offer in-depth tutorials that can assist in understanding specific issues.
- Social Media Groups: Platforms like Facebook feature groups focused on vintage camera enthusiasts. Joining these communities can help users connect with knowledgeable individuals willing to share their expertise.
- YouTube Channels: Visual learners may benefit from video tutorials that showcase common problems and solutions. Channels dedicated to film photography often provide step-by-step demonstrations for various models.
- Local Camera Repair Shops: For those who prefer hands-on assistance, visiting a local technician can be invaluable. Experienced professionals can offer personalized guidance and potentially fix intricate issues.
By utilizing these resources, individuals can enhance their understanding and improve their chances of successful restoration.