
Understanding the intricacies of small engine upkeep is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This section delves into various techniques and procedures necessary for maintaining the functionality of a specific engine type. Emphasizing the importance of routine checks and thorough servicing, this guide aims to provide comprehensive insights into the processes involved.
Throughout this exploration, readers will gain valuable knowledge on addressing common issues, recognizing wear, and implementing corrective measures. With a focus on practical applications and detailed instructions, the information presented here is designed to empower users in their maintenance endeavors. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced mechanic, the principles outlined will enhance your ability to manage engine-related challenges effectively.
Understanding L Head Engines

The L-type engines are notable for their unique design, featuring a simple yet effective configuration that contributes to their reliability and efficiency. These power units are commonly found in various applications, from lawn care equipment to small machinery. Their straightforward mechanics make them accessible for maintenance and troubleshooting, appealing to both professionals and enthusiasts.
Key Features of L-Type Engines

These engines are characterized by their overhead valve design, which enhances performance and fuel efficiency. The compact layout allows for easy installation and maintenance. Below are some essential attributes:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Compact Size | Designed to fit into small spaces without sacrificing power. |
| Fuel Efficiency | Optimized to consume less fuel while providing reliable output. |
| Easy Maintenance | Simple components make routine upkeep straightforward. |
Common Issues and Solutions
Like any engine, L-type units can experience issues over time. Familiarity with potential problems can help in addressing them effectively. Common concerns include starting difficulties, irregular operation, and fuel leaks. Understanding these issues facilitates efficient troubleshooting and restoration of optimal performance.
Common Issues with L Head Models

Many users encounter typical challenges with certain engine types that can hinder performance and efficiency. Recognizing these frequent problems can assist in maintaining optimal functionality and prolonging the lifespan of the equipment.
One prevalent issue involves starting difficulties, often linked to fuel delivery problems or ignition system failures. Additionally, irregular operation may arise from debris accumulation within critical components, disrupting smooth performance.
Another common concern is overheating, which can stem from inadequate cooling or insufficient lubrication. Regular maintenance practices, such as checking oil levels and ensuring proper airflow, are essential to mitigate these risks.
Lastly, vibrations and noise may indicate mechanical wear or misalignment within the engine assembly. Addressing these signs promptly can prevent further damage and ensure a reliable operational state.
Tools Needed for Repairs

When undertaking maintenance tasks on small engines, having the right instruments is essential for achieving optimal results. Proper equipment not only facilitates the process but also ensures safety and efficiency.
- Wrenches: A variety of sizes, including both standard and metric, are necessary for loosening and tightening bolts.
- Screwdrivers: Both flathead and Phillips types are crucial for removing and securing screws.
- Pliers: These assist in gripping, twisting, and cutting wires or small components.
- Socket Set: A comprehensive set allows for quick removal of fasteners in tight spaces.
- Torque Wrench: Ensures that components are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Feeler Gauges: Useful for measuring gaps and ensuring correct settings on various parts.
Having these tools readily available will streamline the maintenance process, making it more straightforward and effective.
Step-by-Step Disassembly Process
This section outlines the procedure for carefully dismantling the engine components for maintenance or troubleshooting purposes. Following a systematic approach ensures that each part is handled properly, minimizing the risk of damage and facilitating easier reassembly.
Begin by gathering the necessary tools, including wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers. Make sure to work in a clean, well-lit area to avoid losing small components. Start by disconnecting the spark plug to prevent accidental ignition during the process.
Next, remove any covers or protective shields that may obstruct access to the internal parts. Pay attention to the sequence of removal, as it can affect how easily the components come apart. Labeling or organizing parts as you go can be helpful.
Once you have access, proceed to detach the components, starting with the larger items before moving to smaller pieces. Use appropriate force and avoid excessive torque to prevent stripping screws or damaging fragile parts. Ensure that all fasteners are stored securely to avoid misplacement.
After all components are removed, inspect each part for wear or damage, which will inform your next steps in maintenance or replacement. Document any findings as you go to assist in reassembly and future reference.
Diagnosing Engine Performance Problems
Identifying issues that affect the operation of an engine is crucial for maintaining optimal functionality. Various symptoms can signal underlying troubles, and recognizing these early can prevent more severe damage. This section provides guidance on assessing performance-related concerns to ensure efficient operation.
Common Symptoms to Observe
Engine performance issues may manifest through various signs. Frequent stalling, reduced power, or unusual noises are primary indicators. Additionally, difficulties in starting or inconsistent idling can point to specific malfunctions.
Initial Checks and Procedures
Begin the diagnostic process by examining the fuel supply. Ensuring clean, sufficient fuel is vital for proper operation. Next, inspect the air intake system for obstructions that may impede airflow. Lastly, evaluate the electrical components, including spark plugs and wiring, to identify potential faults.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
If basic checks do not reveal the issue, more advanced diagnostic methods may be required. Utilizing compression testing can help assess the internal condition of the engine. Monitoring exhaust emissions can also provide insights into fuel mixture problems or combustion inefficiencies.
Reassembling the Engine Correctly

Reassembling an engine involves careful attention to detail and systematic organization. This stage is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Following the appropriate procedures and utilizing the correct tools can prevent future issues and enhance functionality.
Gathering Necessary Tools and Parts
Before beginning the assembly process, ensure all components are clean and inspected for wear. Having the right tools on hand, such as torque wrenches and screwdrivers, will streamline the work. Organizing parts systematically can help avoid confusion and facilitate a smoother reassembly.
Following Proper Assembly Steps
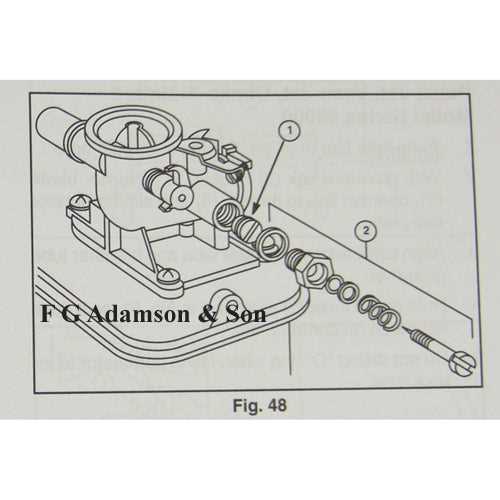
Start by carefully aligning all components, ensuring that gaskets are in place to prevent leaks. It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding torque specifications to avoid over-tightening or under-tightening. Regularly double-checking each step will contribute to a successful reassembly.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring the extended lifespan of your outdoor power equipment. Implementing simple maintenance practices can prevent unnecessary wear and enhance performance, allowing your machinery to function optimally for years to come.
Routine Inspections
Conducting frequent checks on your equipment helps identify potential issues before they escalate. Look for signs of wear, loose components, or leaks. Addressing these concerns early can save time and money in the long run.
Proper Storage Techniques

Storing your equipment correctly during off-seasons is crucial. Keep it in a dry, sheltered location to protect it from moisture and debris. Additionally, consider using covers to shield it from dust and extreme temperatures.
Replacing Worn-Out Components
Over time, certain parts of an engine may experience wear and tear, leading to decreased performance and efficiency. Addressing these issues promptly can significantly enhance the longevity and functionality of the machinery.
Identifying Worn Components

Recognizing when a component needs replacement is crucial for maintaining optimal operation. Here are some signs to look out for:
- Unusual noises during operation
- Decreased power output
- Visible damage or deformation
- Increased fuel consumption
Steps for Replacement

Once worn parts are identified, follow these steps to ensure proper replacement:
- Gather necessary tools and replacement parts.
- Disconnect the power source for safety.
- Carefully remove the damaged component.
- Install the new part, ensuring a secure fit.
- Reconnect the power and test the engine.
Regular maintenance and timely replacement of components not only improve performance but also prevent future complications.
Understanding Engine Specifications

Engine specifications are crucial for assessing performance, efficiency, and compatibility with various applications. By examining these details, users can ensure that their power units operate optimally and meet the necessary requirements for specific tasks.
Key Performance Metrics

Several key metrics define engine performance, including displacement, horsepower, and torque. Displacement refers to the total volume of all the cylinders in the engine, while horsepower measures the engine’s power output. Torque, on the other hand, indicates the engine’s ability to perform work, particularly in demanding situations.
Operational Efficiency Factors

Operational efficiency can be influenced by various factors, such as fuel type, compression ratio, and cooling mechanisms. Understanding these aspects helps users select the right engine for their needs, optimizing performance while minimizing fuel consumption and emissions.
Safety Precautions During Repairs
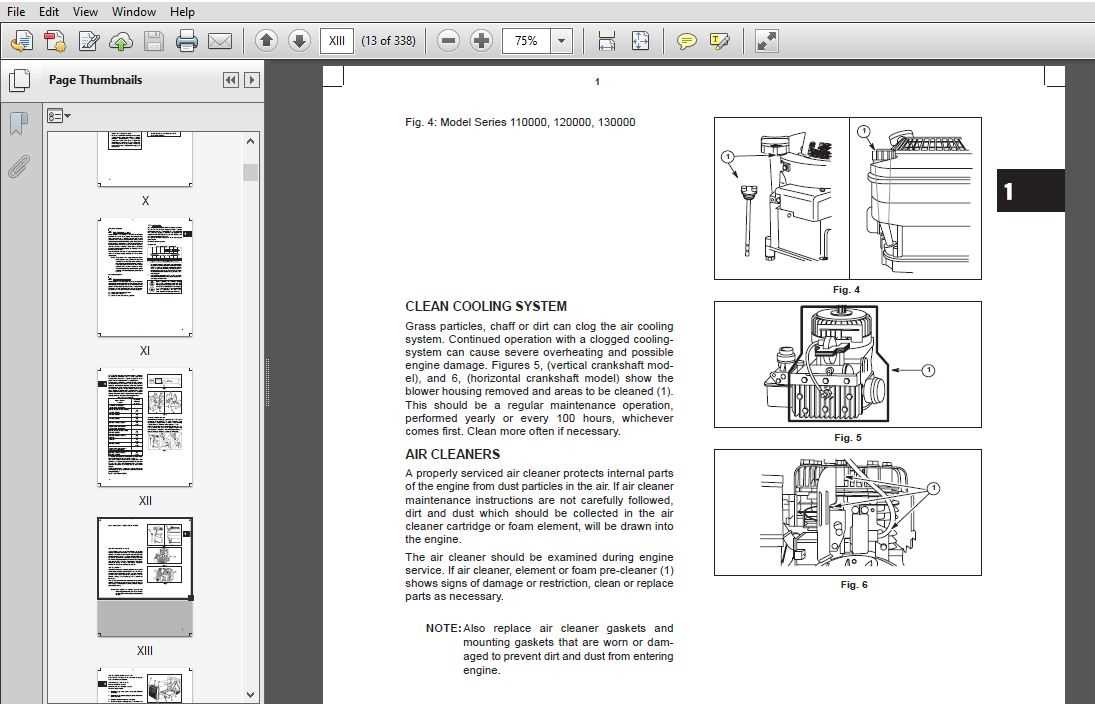
Ensuring a safe environment while conducting maintenance tasks is crucial for both personal safety and the longevity of the equipment. Adhering to basic safety measures can prevent accidents and injuries, making the process more efficient and effective.
Before starting any maintenance work, it is essential to gather the necessary tools and materials, ensuring that they are in good condition and suitable for the task at hand. Additionally, wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and masks is strongly recommended to safeguard against potential hazards.
| Precaution | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Off | Always disconnect the power source before beginning any service to avoid accidental starts. |
| Ventilation | Work in a well-ventilated area to minimize exposure to fumes and ensure a comfortable environment. |
| Tool Check | Inspect tools for any damage or wear before use to prevent failures during operation. |
| Clear Workspace | Keep the workspace organized and free of clutter to reduce the risk of tripping and accidents. |
By following these guidelines, individuals can promote a safer working atmosphere, ultimately leading to successful maintenance tasks without unnecessary risks.
Troubleshooting Common Failures
This section addresses frequent issues that can arise during the operation of small engines, providing insights into identifying and resolving them effectively. By understanding these common problems, users can maintain optimal performance and extend the lifespan of their equipment.
1. Engine Won’t Start
When the engine fails to ignite, several factors could be at play. Check the fuel level and ensure that the fuel is fresh. Verify that the spark plug is functioning correctly and is free from carbon buildup. Additionally, inspect the ignition system for any faults.
2. Poor Performance
If the engine runs but lacks power, consider examining the air filter for dirt or obstructions. A clogged filter can restrict airflow, leading to decreased efficiency. Also, assess the fuel system for potential blockages or leaks.
3. Excessive Vibration
Unusual vibrations may indicate loose components or imbalanced parts. Inspect all mounting bolts and fasteners to ensure they are secure. If the issue persists, check for damaged or worn-out blades that could affect balance.
Resources for Further Assistance
When facing challenges with small engine maintenance and troubleshooting, it’s beneficial to have access to various resources that can provide guidance and support. Whether you’re seeking detailed information, expert advice, or community insights, numerous options are available to enhance your understanding and resolve issues effectively.
Online Forums and Communities
- Engage with online platforms dedicated to engine enthusiasts, where users share experiences and solutions.
- Participate in discussion groups to ask questions and receive feedback from knowledgeable individuals.
- Explore social media groups focused on engine care for tips and shared resources.
Instructional Videos

- Utilize video platforms that offer tutorials on various aspects of engine upkeep and troubleshooting.
- Watch step-by-step guides that visually demonstrate repair processes and maintenance tips.
- Search for channels dedicated to engine enthusiasts for ongoing content and updates.