
Maintaining small engines requires precision and knowledge, especially when dealing with machines that see regular use. This guide offers valuable insights into proper upkeep, ensuring smooth operation and longevity. Understanding the correct way to approach maintenance can prevent common issues and reduce the need for costly interventions.
Detailed instructions cover every essential aspect, from routine inspections to more involved tasks. Whether you’re facing performance inconsistencies or preparing for seasonal storage, having a step-by-step reference ensures you address all key components with confidence.
Clear diagnostics are essential for efficient troubleshooting. This guide not only explains how to identify mechanical problems but also provides targeted solutions to restore full functionality. It’s a go-to resource for
Briggs and Stratton 21032 Repair Manual

This section provides essential insights into maintaining and troubleshooting a popular engine model. The focus is on ensuring longevity and optimal performance through regular upkeep and addressing common malfunctions. Detailed guidance helps users identify issues early, preventing more extensive damage.
Key components like the carburetor, ignition system, and air filter play critical roles in the engine’s operation. Understanding their function allows users to effectively handle adjustments or replacements when needed.
Troubleshooting techniques covered here range from diagnosing starting issues to resolving pe
Overview of Engine Maintenance Practices
Proper care for combustion systems ensures smooth operation, extends longevity, and reduces the risk of unexpected failures. Routine upkeep allows operators to identify potential issues early, preventing costly repairs and downtime. This section highlights essential maintenance routines to keep engines in top condition.
Key Routine Inspections

- Check oil levels regularly to ensure optimal lubrication and prevent friction-related damage.
- Inspect air filters for debris buildup and clean or replace them as needed to maintain airflow efficiency.
-
Identifying Common Issues and Failures

Understanding recurring malfunctions and typical breakdowns helps in maintaining equipment performance and avoiding unexpected downtime. Detecting symptoms early allows for timely interventions, preventing minor faults from escalating into costly repairs.
A frequent source of trouble involves difficulties with fuel delivery, often caused by clogged lines or old gasoline. This can lead to inconsistent engine operation or failure to start entirely. Another common failure relates to the ignition system, where worn-out spark plugs or faulty connections result in weak or no sparks, disrupting combustion.
Overheating can also arise due to blocked cooling fins or insufficient oil levels, posing a risk of component damage. Additionally, air filter obstructions can restrict airflow, reducing efficiency and causing rough running. P
Understanding the Ignition System Setup

The ignition system plays a crucial role in the operation of small engines, ensuring proper combustion and efficient performance. This system comprises several components that work together to generate a spark, igniting the air-fuel mixture within the combustion chamber. Understanding each part’s function and interaction is essential for effective troubleshooting and maintenance.
Key Components of the Ignition System
Various elements constitute the ignition system, each contributing to its overall functionality. Below is a summary of the primary components:
Component Function Spark Plug Generates the spark needed to ignite the air-fuel mixture. Ignition Coil Transforms low voltage from the battery to high voltage needed for the spark plug. Flywheel Contains magnets that trigger the ignition coil, producing a spark at the right time. Starter Engages the flywheel to start the engine and initiate the ignition process. Troubleshooting Common Ignition Issues

Problems within the ignition system can lead to engine performance issues or failure to start. Identifying symptoms such as difficulty starting, inconsistent running, or engine stalling can help pinpoint specific component failures. Regular inspection and maintenance of these elements are vital to ensure optimal engine performance.
Inspecting and Cleaning Fuel Lines
Maintaining optimal performance in small engines requires regular checks and maintenance of the fuel delivery system. Fuel lines, which transport gasoline from the tank to the engine, can become clogged or damaged over time, impacting efficiency and function. Ensuring these lines are clean and in good condition is essential for reliable operation.
Begin by carefully examining the fuel lines for any signs of wear, cracks, or leaks. Any visible damage can lead to fuel loss and potentially hazardous situations. If issues are detected, replacement of the affected segments may be necessary.
Next, follow these steps to clean the fuel lines:
Step Action 1 Disconnect the fuel lines from the tank and engine. 2 Use a suitable cleaning solution or compressed air to clear any obstructions. 3 Inspect the inner walls of the lines for residue or buildup. 4 Rinse the lines thoroughly with clean fuel to remove any remaining cleaner. 5 Reattach the fuel lines securely, ensuring all connections are tight. Regular inspection and cleaning of the fuel delivery system contribute significantly to the longevity and efficiency of small engines. By taking these steps, users can prevent common fuel-related issues and maintain their equipment in peak condition.
How to Replace Air Filters
Maintaining optimal performance in outdoor power equipment involves regular changes of the air filtration components. This process ensures that the engine receives clean air, enhancing efficiency and prolonging its lifespan. Properly replacing these filters is a straightforward task that can be accomplished with minimal tools and some basic understanding.
Tools and Materials Needed
- New air filter
- Screwdriver (if necessary)
- Clean cloth
- Protective gloves
Step-by-Step Guide
- Ensure the equipment is turned off and completely cooled down.
- Locate the air filter cover, which is typically situated on the side or top of the engine.
- If applicable, remove any screws or clips holding the cover in place using the screwdriver.
- Carefully lift off the cover to expose the air filter.
- Take out the old filter, noting its orientation for correct installation of the new one.
- Clean the filter housing with a cloth to remove any debris or dirt.
- Insert the new air filter in the same orientation as the old one.
- Replace the air filter cover and secure it with screws or clips as necessary.
- Dispose of the old filter properly.
Following these steps will help maintain the efficiency of your equipment and prevent potential issues related to poor airflow.
Troubleshooting Carburetor Malfunctions

Diagnosing issues with fuel delivery systems is crucial for ensuring optimal engine performance. Various symptoms can indicate problems within the carburetor, affecting its functionality and efficiency. Understanding these signs is the first step toward restoring proper operation.
Common symptoms of carburetor issues include:
- Difficulty starting the engine
- Engine stalling or rough idling
- Poor acceleration or sluggish performance
- Excessive fuel consumption
- Black smoke from the exhaust
To effectively troubleshoot these issues, follow these steps:
- Check the fuel supply: Ensure that the fuel tank has an adequate supply of clean fuel. Inspect fuel lines for leaks or blockages.
- Inspect the air filter: A clogged air filter can restrict airflow, affecting combustion. Clean or replace the filter as needed.
- Examine the carburetor: Remove the carburetor and inspect it for dirt, debris, or varnish buildup. Cleaning the internal components may resolve many issues.
- Adjust the mixture settings: Incorrect air-fuel mixture can lead to poor performance. Consult specifications for appropriate settings and adjust accordingly.
- Test the float level: Ensure the float is set to the correct level. An improperly adjusted float can cause flooding or insufficient fuel delivery.
- Check for vacuum leaks: Inspect gaskets and seals for wear. Leaks can disrupt fuel flow and cause erratic engine behavior.
By systematically addressing these areas, you can identify and rectify issues, ensuring reliable operation and enhanced performance.
Importance of Oil Change Intervals
Regularly scheduled oil changes are essential for maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of small engines. Proper lubrication is crucial for minimizing friction and wear on internal components. Neglecting these intervals can lead to severe engine damage and costly repairs.
Adhering to recommended oil change frequencies ensures that contaminants and impurities do not accumulate, which can compromise engine efficiency. Fresh oil not only helps in cooling the engine but also provides better protection against corrosion. Understanding the significance of these maintenance practices can prevent unexpected breakdowns and extend the life of the equipment.
Interval (Hours) Action Reason 0-25 Initial oil change Remove contaminants from manufacturing 25-50 Change oil Reduce buildup of particles and debris 50-100 Change oil Ensure proper lubrication and performance 100+ Regular oil changes Maintain efficiency and prevent wear In summary, adhering to the prescribed oil change intervals is vital for ensuring the reliability and efficiency of small engines. Prioritizing this aspect of maintenance can lead to improved performance and a longer lifespan for the equipment.
Steps to Adjust Valve Clearance

Proper maintenance of engine components ensures optimal performance and longevity. One crucial aspect of this process is the adjustment of valve spacing. Incorrect clearance can lead to poor engine efficiency, increased wear, and even potential damage. Below are detailed steps to effectively adjust the valve clearance in your engine.
Preparation
Before proceeding, gather the necessary tools, including a feeler gauge, wrenches, and a socket set. Ensure the engine is cool and positioned on a stable surface. Disconnect the spark plug wire to prevent accidental ignition during the adjustment process.
Adjustment Process
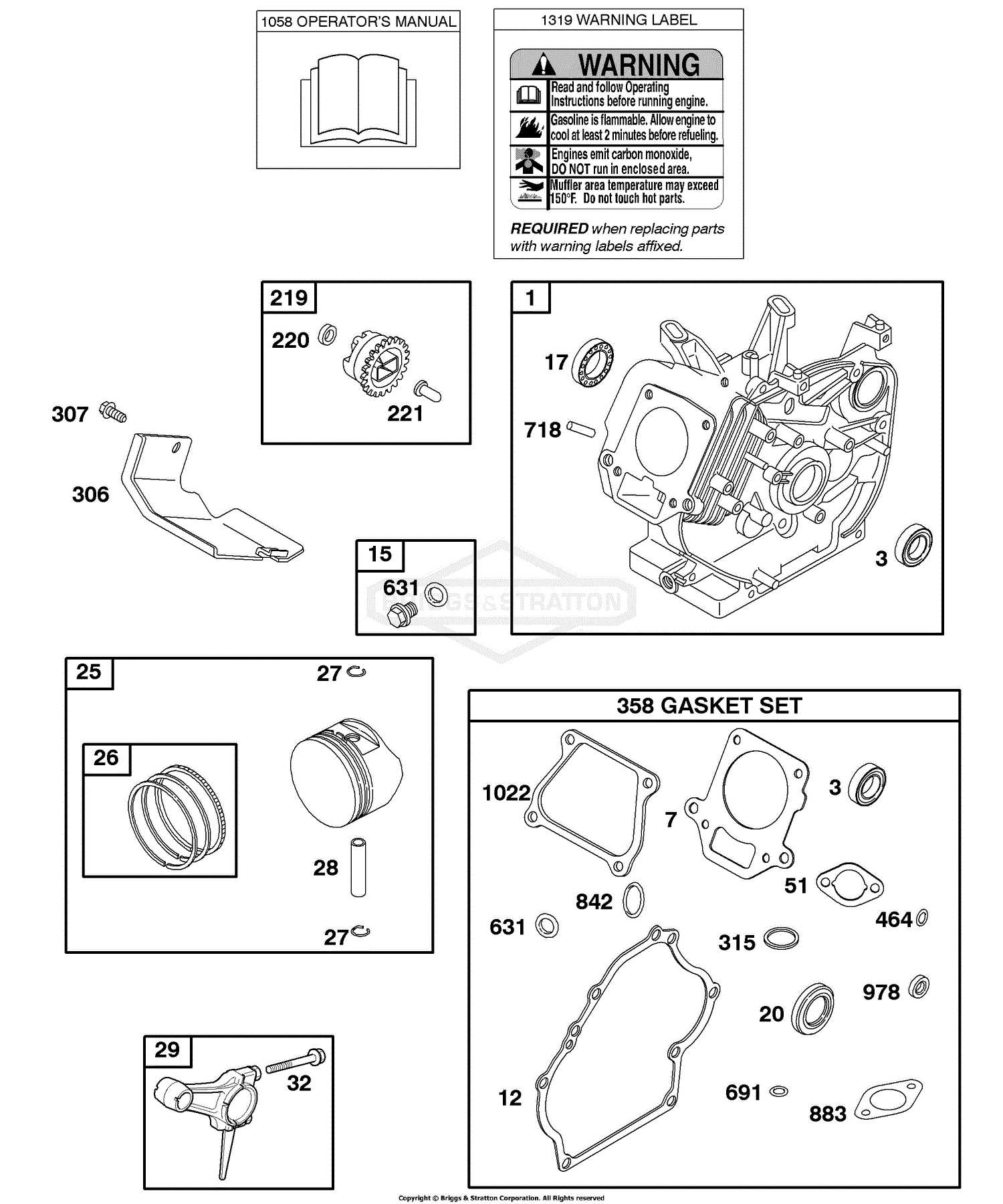
Follow these steps to accurately adjust the valve spacing:
Step Description 1 Remove the valve cover to access the rocker arms and pushrods. 2 Rotate the engine manually to position the piston at the top dead center on the compression stroke. 3 Using the feeler gauge, check the clearance between the rocker arm and valve stem. Compare with manufacturer specifications. 4 If adjustments are needed, loosen the lock nut on the rocker arm. 5 Turn the adjusting screw to achieve the desired clearance, then re-tighten the lock nut. 6 Repeat the process for all valves as specified in the engine’s guidelines. 7 Reinstall the valve cover, ensuring a proper seal to prevent leaks. After completing the adjustments, reconnect the spark plug wire. Start the engine to ensure smooth operation and check for any unusual noises. Regular maintenance of valve clearance will help maintain the engine’s efficiency and reliability.
Diagnosing Spark Plug Problems
Identifying issues with the ignition component is crucial for ensuring optimal engine performance. This section explores common symptoms that indicate a faulty part and provides guidance on troubleshooting these problems effectively. Understanding how to assess these components can help maintain smooth operation and prevent further complications.
Common Symptoms of Spark Plug Malfunction
Several indicators can suggest that the ignition component is not functioning properly. One of the most noticeable signs is difficulty starting the engine. If the engine cranks but fails to ignite, this may point to a malfunctioning part. Additionally, irregular performance, such as misfiring or rough idling, can signal issues. Observing unusual deposits or discoloration on the component can also provide insight into its condition.
Troubleshooting Steps

To effectively diagnose problems, begin by inspecting the ignition component for visible damage or wear. Remove it from the engine and examine the electrode for signs of corrosion or excessive carbon buildup. Utilizing a multimeter can help test for continuity and ensure the part is functioning within the appropriate specifications. Cleaning or replacing the component may resolve many performance issues, restoring efficient engine operation.
Replacing a Damaged Recoil Starter
When a recoil starter becomes compromised, it can hinder the operation of small engines, making it difficult to initiate the machinery. Addressing this issue promptly ensures that equipment remains functional and ready for use. This section outlines the steps involved in substituting a malfunctioning recoil starter with a new one.
Before starting the replacement process, it is essential to gather the necessary tools and materials:
- New recoil starter assembly
- Socket wrench set
- Screwdriver set
- Pliers
- Cleaning cloth
Follow these steps to successfully replace the recoil starter:
- Ensure Safety: Disconnect the spark plug wire to prevent accidental ignition.
- Remove the Old Starter: Use the appropriate socket wrench to remove the screws securing the damaged recoil starter. Carefully detach it from the engine casing.
- Inspect the Area: Clean the mounting area to remove any debris or dirt that could interfere with the new installation.
- Install the New Starter: Position the new recoil starter in place, aligning it with the mounting holes. Secure it using the screws previously removed.
- Reconnect Components: Reattach the spark plug wire to its terminal.
After completing the installation, test the new recoil starter to ensure it functions properly. A successful replacement will enhance the engine’s reliability and performance.
Winter Storage Preparation Tips
As the cold season approaches, it is essential to ensure that your outdoor equipment is properly prepared for storage. Taking the right steps can help prolong the lifespan of your machinery and ensure it operates effectively when needed again.
- Clean Thoroughly: Before storing, make sure to clean all surfaces, removing dirt, debris, and any residues that may cause corrosion.
- Check Fluids: Drain and replace old fluids, including oil and fuel, to prevent contamination and buildup over time.
- Inspect Parts: Examine components for wear and tear. Replace any damaged or worn-out parts to avoid issues when you bring the equipment back into use.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Apply lubricant to moving parts to protect them from rust and ensure smooth operation when reactivated.
- Store in a Dry Location: Choose a dry, sheltered space for storage to protect the equipment from moisture and extreme temperature fluctuations.
- Cover Equipment: Use appropriate covers to shield your machinery from dust and pests during the storage period.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your equipment remains in optimal condition throughout the winter months and is ready for action when spring arrives.
Ensuring Optimal Cooling Performance

Maintaining effective temperature regulation is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of small engines. Proper cooling mechanisms help prevent overheating, which can lead to significant damage. By focusing on key elements of the cooling system, users can enhance the operational lifespan and performance of their machinery.
Regular Maintenance of Cooling Components
Routine inspection of cooling elements is essential for sustaining optimal performance. Ensure that cooling fins are free of debris and dirt, as these can obstruct airflow and lead to excessive heat buildup. Cleaning the air intake and ensuring unobstructed airflow will significantly improve engine efficiency. Additionally, check for any signs of wear or damage to cooling components that might hinder performance.
Utilizing the Correct Operating Conditions
Utilizing machinery within the recommended parameters can greatly enhance cooling efficiency. Avoid running the engine in extremely hot conditions for prolonged periods. If possible, operate in shaded areas or use additional cooling methods, such as fans or water sprays, to maintain a favorable temperature. Monitoring engine temperature during operation will also help in identifying potential issues before they escalate.