
In the realm of small engine management, understanding the nuances of maintenance and troubleshooting is essential for optimal performance. This section serves as a valuable resource for those seeking insights into common issues and solutions related to engine upkeep. With a focus on practical knowledge, users can enhance their skills in handling various mechanical challenges.
Whether you are a novice looking to familiarize yourself with engine functionalities or an experienced technician aiming to refine your expertise, this guide provides a thorough examination of the fundamental aspects of engine care. From identifying symptoms of malfunction to implementing effective remedies, the information presented here empowers users to take proactive measures in ensuring the longevity of their equipment.
Engaging with this material not only fosters a deeper understanding of engine mechanics but also encourages a hands-on approach to maintenance. By applying the principles discussed, individuals can navigate the intricacies of engine performance with confidence and ease. The journey toward becoming proficient in engine management begins here, laying the groundwork for successful and efficient operation.
Briggs and Stratton 300 Series Overview
This section provides an insight into a renowned line of small engine models that are widely utilized in various applications. These power sources are celebrated for their reliability and efficiency, making them a popular choice among users. Understanding their features and specifications can greatly enhance the user experience and ensure optimal performance.
Key Features
The following table outlines the essential attributes that characterize these engines:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Output | These units deliver a range of horsepower suitable for light to medium-duty tasks. |
| Fuel Type | Designed to operate efficiently on regular gasoline, ensuring ease of use. |
| Starting System | Equipped with an easy pull-start mechanism for quick ignition. |
Applications
These engines are typically employed in various equipment, including lawn mowers, generators, and pressure washers. Their versatility allows them to adapt to multiple environments, making them a preferred choice for both residential and commercial use.
Common Issues with 300 Series Engines
When dealing with small engines, several frequent problems can arise that may affect their performance and reliability. Understanding these typical challenges is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
1. Fuel System Problems: One of the most prevalent issues is related to the fuel system. Clogs in the fuel lines or a dirty carburetor can lead to inadequate fuel delivery, resulting in poor engine performance. Regular cleaning and proper fuel storage can mitigate these problems.
2. Starting Difficulties: Many users report difficulties in starting the engine, often caused by a weak battery, faulty spark plug, or improper choke settings. Ensuring all components are in good condition can enhance the starting process.
3. Overheating: Engines may overheat due to low oil levels or blocked air vents. Monitoring oil levels and ensuring that air intake areas are clear can help prevent overheating issues.
4. Unusual Noises: Strange noises during operation can indicate mechanical issues. Listening for knocking or grinding sounds is essential, as these may signal wear in internal components that require immediate attention.
5. Vibration: Excessive vibration may be a sign of unbalanced components or loose parts. Regular inspections can help identify and correct these issues before they escalate.
Essential Tools for Repairs
Having the right equipment is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting tasks. The following items are fundamental for ensuring a smooth process when working on small engines.
- Wrenches: A set of adjustable and socket wrenches will help you tackle various bolts and nuts.
- Screwdrivers: Both flathead and Phillips head screwdrivers are necessary for accessing different components.
- Multimeter: This device is essential for diagnosing electrical issues, allowing you to measure voltage and continuity.
- Torque Wrench: Ensures that fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Pliers: Needle-nose and regular pliers are useful for gripping, twisting, and cutting wire or other materials.
In addition to these tools, a clean workspace and proper safety gear, such as gloves and goggles, are recommended for a safe and efficient working environment.
Step-by-Step Maintenance Procedures
This section provides a comprehensive guide to performing essential upkeep tasks that ensure optimal performance and longevity of your equipment. By following these systematic steps, you can effectively maintain your machine and prevent potential issues.
Regular maintenance involves several key activities that should be conducted periodically. Below is a detailed table outlining these procedures, their frequency, and a brief description of each task.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Change | Every 50 hours | Replace old oil with fresh oil to ensure smooth engine operation. |
| Air Filter Cleaning | Every 25 hours | Remove and clean the air filter to improve airflow and performance. |
| Spark Plug Inspection | Every 100 hours | Check the spark plug for wear and replace it if necessary to ensure proper ignition. |
| Fuel System Check | Before each use | Inspect fuel lines and tank for leaks and ensure fresh fuel is used. |
| Blade Sharpening | Every season | Sharpen blades to maintain cutting efficiency and prevent damage to the lawn. |
By adhering to this maintenance schedule, you can enhance the reliability of your equipment and prolong its operational life. Regular attention to these tasks is crucial for ensuring that everything runs smoothly and efficiently.
Understanding Engine Specifications
When working with small engines, grasping the technical details is crucial for optimal performance and maintenance. Engine specifications encompass various aspects such as power output, displacement, and fuel requirements, which collectively determine the efficiency and capability of the machine. Familiarity with these details enables users to make informed decisions regarding operation and troubleshooting.
Key Specifications to Consider
Several vital specifications play a significant role in engine functionality:
- Displacement: This refers to the total volume of the engine’s cylinders, influencing power generation and torque.
- Horsepower: A measure of the engine’s power, indicating its ability to perform work efficiently.
- Torque: This represents the rotational force produced, essential for tasks requiring heavy lifting or sustained operation.
Fuel and Lubrication Requirements
Understanding the appropriate fuel type and oil viscosity is vital for maintaining engine health. Using the correct fuel prevents damage and ensures smooth operation. Likewise, regular oil changes based on manufacturer recommendations help in minimizing wear and prolonging engine life.
Troubleshooting Starting Problems
When facing difficulties with engine ignition, it’s essential to identify and rectify the underlying issues to ensure reliable performance. This section outlines common challenges encountered during the starting process and provides guidance on diagnosing and resolving these problems.
Common Issues
Several factors can contribute to starting difficulties, including fuel supply, electrical components, and mechanical conditions. Below are typical problems and their potential causes:
| Problem | Possible Causes |
|---|---|
| Engine won’t start | Empty fuel tank, clogged fuel line, faulty fuel pump |
| Engine cranks but won’t start | Weak battery, defective starter motor, spark plug issues |
| Engine starts and stalls | Dirty air filter, fuel contamination, low oil level |
Diagnostic Steps
To troubleshoot starting issues effectively, follow these steps:
- Check the fuel level and ensure it is clean and uncontaminated.
- Inspect electrical connections for corrosion or damage.
- Test the battery voltage to confirm it meets the required specifications.
- Examine the air filter and replace it if necessary.
Replacing Key Engine Components
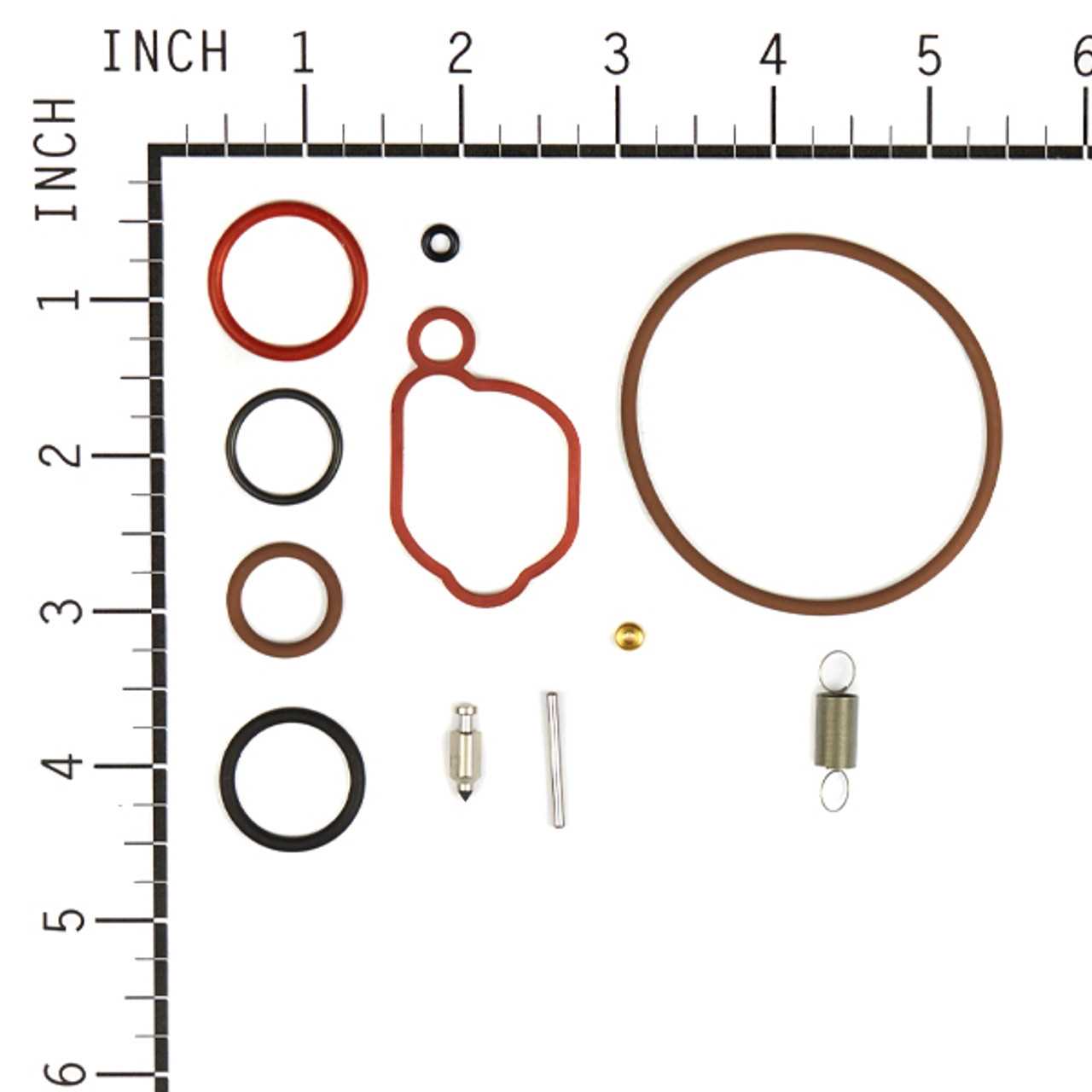
Maintaining the performance of small engines often requires the replacement of essential parts. Understanding how to properly replace these components can significantly enhance the longevity and efficiency of your machinery. This section will outline the fundamental steps to follow for successful component replacement.
Essential Components to Replace
- Fuel Filter
- Air Filter
- Spark Plug
- Oil Filter
- Starter Motor
Replacement Steps
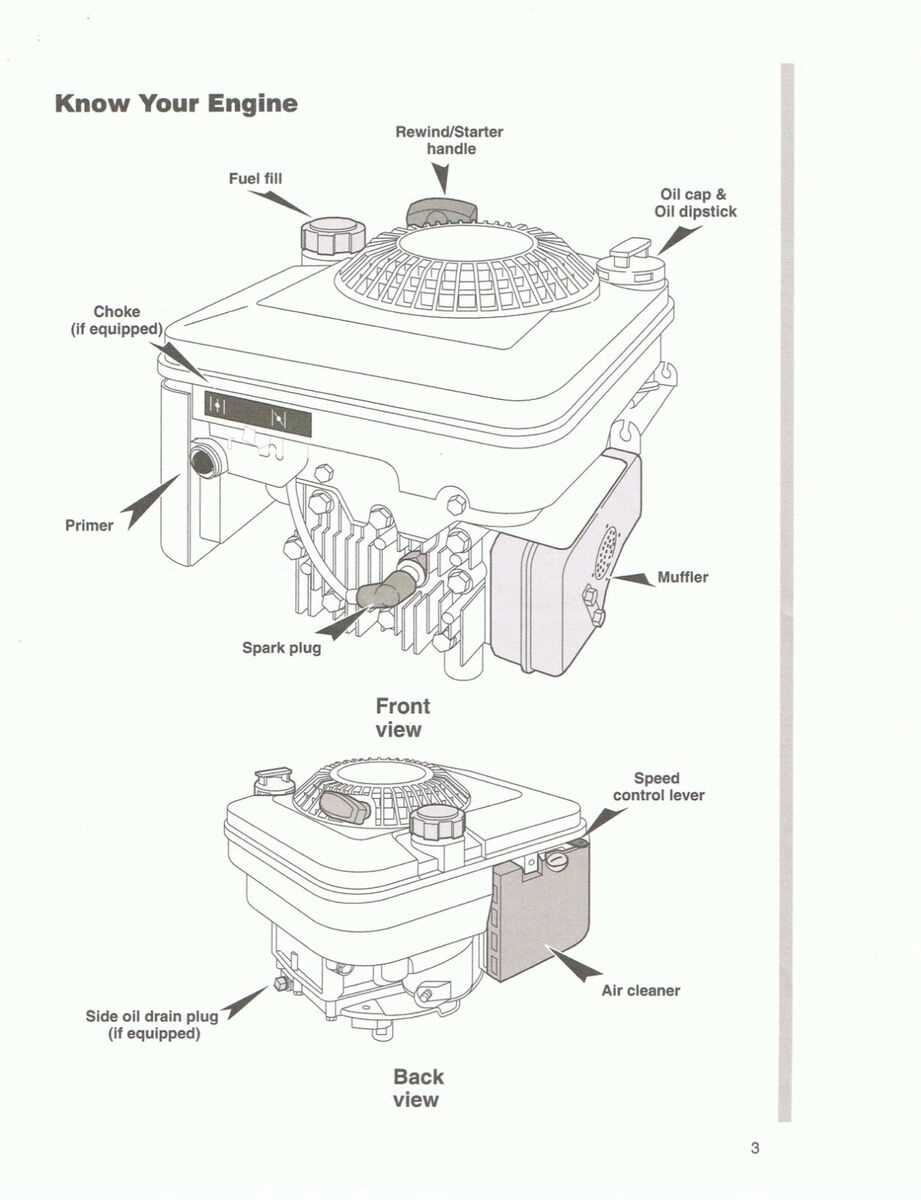
- Ensure the engine is turned off and cool before starting any work.
- Gather the necessary tools and replacement parts.
- Consult the owner’s documentation for specific instructions related to each component.
- Carefully remove the old part, taking note of how it is installed.
- Install the new part, ensuring a secure fit.
- Dispose of the old components responsibly.
Regularly replacing these vital parts not only prevents potential issues but also optimizes the overall function of your engine. Always prioritize safety and accuracy during the replacement process.
Fuel System Maintenance Tips
Maintaining the fuel system is essential for optimal engine performance and longevity. Regular care can prevent issues such as clogging and inefficient fuel delivery, ensuring that the equipment runs smoothly. Here are some important practices to follow for effective maintenance.
- Regularly Inspect Fuel Lines: Check for cracks or leaks in fuel lines. Replace any damaged sections promptly to prevent fuel loss and ensure safe operation.
- Clean Fuel Filter: Replace or clean the fuel filter regularly to remove debris and contaminants that could hinder fuel flow.
- Use Fresh Fuel: Always use fresh fuel to avoid problems caused by stale or degraded gasoline. Fuel should be stored in a cool, dry place and used within a few months.
- Add Fuel Stabilizer: If storing equipment for an extended period, adding a fuel stabilizer can help maintain fuel quality and prevent gumming.
- Check for Water Contamination: Water in the fuel can cause serious damage. Regularly check for signs of water contamination and remove any affected fuel.
Following these tips will help ensure that the fuel system remains in good condition, promoting reliable performance and reducing the risk of engine issues.
Electrical System Diagnostics

This section focuses on the essential procedures for diagnosing issues within the electrical framework of small engines. Proper assessment of electrical components is vital for ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Understanding Common Issues
Several typical problems can affect the functionality of the electrical system. These may include faulty wiring, weak connections, or malfunctioning components. Identifying these issues early can prevent more extensive damage and costly repairs.
Diagnostic Procedures

To effectively evaluate the electrical system, follow these steps:
- Inspect all wiring for visible damage or wear.
- Check connections for corrosion or looseness.
- Utilize a multimeter to measure voltage levels at various points.
- Test individual components for functionality as needed.
Regular maintenance and prompt diagnostics are crucial for keeping the electrical system in good working order. By being proactive, you can enhance the reliability of your equipment and extend its operational life.
Preventive Measures for Longevity
Implementing proactive strategies is essential for ensuring the prolonged functionality and reliability of your outdoor equipment. By adhering to specific guidelines and maintenance practices, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your machine and enhance its performance.
Regular Maintenance Tasks
Routine upkeep is vital for optimal operation. Consider the following practices:
- Change the oil periodically to prevent engine wear.
- Inspect and clean air filters to ensure proper airflow.
- Check spark plugs and replace them if necessary to maintain ignition efficiency.
- Examine fuel lines and connections for leaks or cracks.
- Sharpen or replace blades as needed for effective cutting.
Storage Considerations
Proper storage can help prevent damage and deterioration. Follow these tips:
- Store the equipment in a dry, sheltered area to avoid moisture exposure.
- Use a cover to protect against dust and debris.
- Ensure fuel tanks are either drained or treated with a stabilizer before long-term storage.
- Disconnect the battery if applicable to prevent drainage.
Oil Change and Lubrication Guide
Maintaining optimal performance of your engine requires regular attention to its lubrication system. Proper oil changes and lubrication not only enhance efficiency but also extend the lifespan of the machinery. This section outlines the necessary steps and considerations for ensuring that your equipment remains in excellent working condition.
Steps for Oil Change
To successfully change the oil, follow these essential steps:
- Gather necessary tools and materials, including a wrench, oil pan, funnel, and new oil filter.
- Warm up the engine for a few minutes to allow the oil to flow out smoothly.
- Shut off the engine and disconnect the spark plug to ensure safety.
- Remove the oil drain plug and let the old oil drain completely into the pan.
- Replace the drain plug securely after draining.
- Install the new oil filter, ensuring a tight fit.
- Pour in the recommended amount of new oil using a funnel.
- Reconnect the spark plug and start the engine, allowing it to run for a few minutes to circulate the new oil.
Lubrication Tips
In addition to changing the oil, regular lubrication of moving parts is crucial for optimal function:
- Use high-quality lubricant specified for your equipment.
- Apply lubricant to joints, bearings, and other moving parts to prevent friction and wear.
- Check lubrication levels regularly and reapply as necessary.
| Component | Recommended Lubricant | Frequency of Application |
|---|---|---|
| Engine Oil | SAE 30 | Every 50 hours of use |
| Gearbox | EP Gear Oil | Every 100 hours of use |
| Chains and Cables | Chain Lubricant | Every 20 hours of use |
Seasonal Preparation and Storage

Preparing equipment for seasonal changes is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Proper storage techniques can prevent damage and maintain functionality, allowing for a smooth transition between usage periods.
Preparation Steps
Before storing your machinery, follow these steps to ensure it remains in excellent condition:
- Clean the exterior thoroughly to remove dirt and debris.
- Inspect all components for wear and damage.
- Change the oil and replace the filter to promote engine health.
- Drain the fuel tank or add a stabilizer to prevent fuel degradation.
Storage Recommendations
When it comes to storage, consider the following guidelines:
- Choose a dry, cool location to prevent moisture-related issues.
- Cover the equipment with a protective tarp to shield it from dust and debris.
- Elevate machinery off the ground using pallets or blocks to avoid contact with moisture.
- Regularly check on stored items to ensure they remain in good condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries related to maintenance and troubleshooting for small engine units. Here, you will find concise answers to some of the most prevalent questions that users often encounter during the operation and upkeep of their equipment.
Common Issues and Solutions
Understanding typical problems and their remedies can enhance the longevity and performance of your machine. Below are some frequent challenges faced by users:
| Issue | Possible Cause | Suggested Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Engine won’t start | Empty fuel tank or stale fuel | Refill with fresh fuel |
| Unusual noise during operation | Loose parts or low oil level | Inspect and tighten components; check oil level |
| Overheating | Blocked air filter or low coolant | Clean or replace the air filter; check coolant levels |
Maintenance Tips
Regular upkeep is essential to ensure optimal functionality. Here are some helpful tips for maintaining your unit:
- Check oil levels regularly and change as needed.
- Keep the air filter clean to prevent debris buildup.
- Inspect spark plugs for wear and replace them as necessary.