
Every vehicle owner knows the importance of a reliable entry system. Over time, these systems can experience issues that prevent seamless access. Understanding the intricacies of these mechanisms can empower individuals to address problems effectively without relying solely on professional assistance.
Many factors contribute to the deterioration of these essential components, from environmental wear to everyday usage. Identifying the specific causes of malfunction can save both time and money. This section will guide you through the process of diagnosing and resolving common issues, allowing for a smoother experience when entering your vehicle.
Whether it’s a stubborn handle or a faulty mechanism, restoring functionality is often simpler than it seems. With the right tools and a bit of patience, many individuals can tackle these challenges independently. Join us as we explore practical solutions and helpful tips for rejuvenating your vehicle’s entry system.
Understanding Manual Door Lock Mechanisms
This section delves into the intricate systems that facilitate the securing and access of vehicle entry points. By examining the components and operations involved, one can gain insight into how these mechanisms function efficiently to ensure safety and convenience for users.
Key Components of the Mechanism
The primary elements involved in the functioning of these systems include various levers, rods, and springs. Each part plays a crucial role in the overall operation, contributing to the effectiveness and reliability of the access system.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Lever | Transmits force from the handle to the locking mechanism. |
| Rod | Connects the lever to the locking element, allowing movement. |
| Spring | Returns the mechanism to its original state after use. |
Operating Principles
These systems typically operate through a combination of mechanical interactions. When a user engages the handle, the corresponding lever activates, causing the attached rod to move. This action either engages or disengages the locking mechanism, allowing or preventing access as needed.
Common Issues with Manual Locks

Many individuals encounter challenges with their locking mechanisms, leading to frustration and inconvenience. Understanding these common problems can assist in identifying potential solutions and preventing future occurrences.
Frequent Problems

Issues can range from minor annoyances to major malfunctions. Below are some prevalent concerns that users might experience:
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Stiff Operation | Difficulty in turning the key or pushing the mechanism due to dirt or lack of lubrication. |
| Misalignment | Components not aligning properly, leading to inability to engage or disengage the mechanism. |
| Key Breakage | Keys snapping inside the mechanism, creating access issues and requiring extraction. |
| Rust and Corrosion | Degradation due to moisture exposure, affecting functionality and longevity. |
Preventative Measures
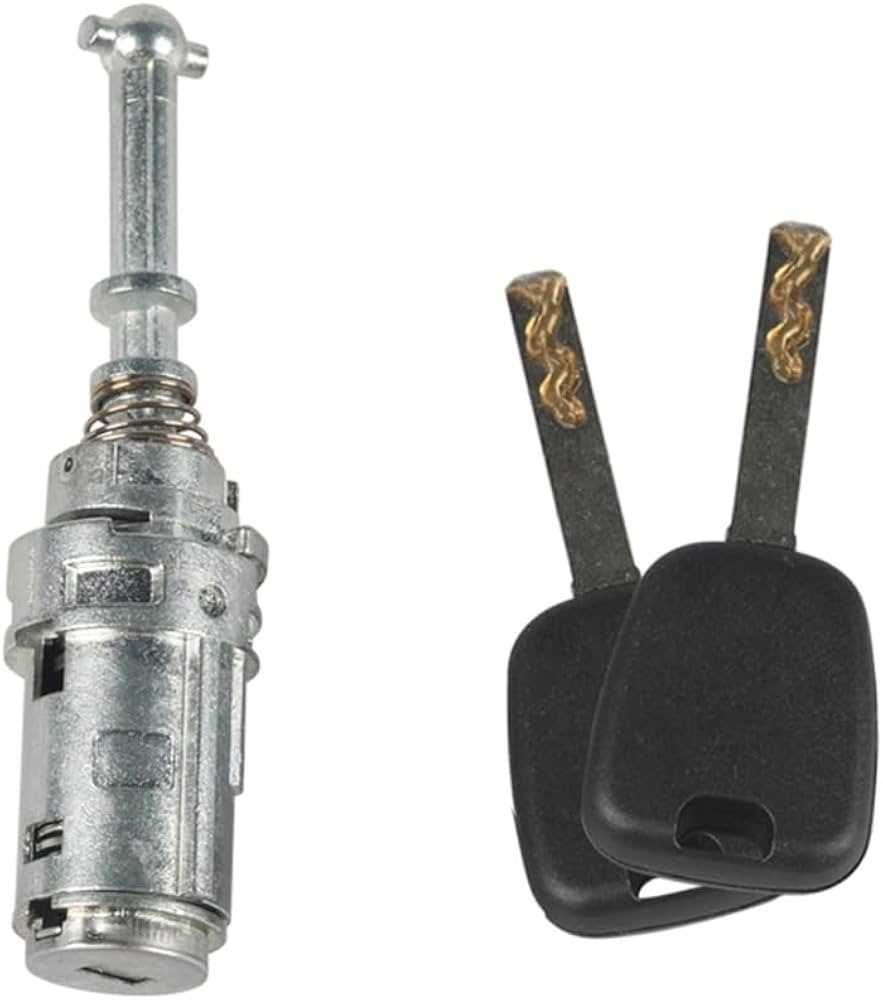

Regular maintenance and attention can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering these problems. Simple actions such as cleaning and applying lubricant can extend the life of these essential components.
Tools Needed for Repairing Locks
When tackling the intricacies of securing mechanisms, having the right implements is essential for effective intervention. Each tool plays a specific role, facilitating the process and ensuring a successful outcome.
- Screwdrivers: Essential for removing and securing screws of various sizes.
- Wrenches: Useful for loosening or tightening nuts and bolts that hold components in place.
- Pliers: Handy for gripping, bending, or cutting wires and small parts.
- Tweezers: Ideal for handling tiny components that require precision.
- Lubricant: Necessary for ensuring smooth movement of internal parts.
Additionally, having specialized tools can enhance efficiency:
- Lock picks: Assist in diagnosing issues within the mechanism.
- Feeler gauges: Help measure gaps and tolerances for proper alignment.
- Multimeter: Useful for checking electrical connections in electronic systems.
Equipping yourself with these essential items will pave the way for a successful troubleshooting experience.
Step-by-Step Lock Disassembly Guide
This section provides a detailed approach to carefully taking apart a locking mechanism. Understanding the inner workings is essential for effective troubleshooting and reassembly. Follow these steps to ensure a smooth disassembly process.
Tools Needed

- Screwdriver set
- Pliers
- Tweezers
- Small container for screws
- Flashlight
Disassembly Steps
- Start by ensuring you have a clean, well-lit workspace.
- Locate and remove any visible screws using the appropriate screwdriver.
- Gently pry apart any clips or tabs that may be holding the assembly together.
- Carefully lift the outer casing to expose the internal components.
- Take note of the arrangement of parts as you remove them to aid reassembly.
- Place all removed parts in a small container to avoid losing them.
- Examine the internal mechanism for any signs of wear or damage.
Following these steps will allow you to disassemble the locking unit efficiently, paving the way for further examination or maintenance. Always handle parts with care to avoid causing any unnecessary damage.
Identifying Broken Components in Locks
Understanding the key elements that may fail within a fastening mechanism is crucial for effective restoration. By recognizing signs of dysfunction, one can pinpoint the specific areas requiring attention, ultimately ensuring smooth operation and security.
Common Indicators of Malfunction
- Difficulty in turning the key
- Unusual noises during operation
- Visible wear on the mechanism
- Key not aligning properly
Components to Inspect

- Spring: Check for breakage or stiffness that may hinder movement.
- Pin Cylinder: Inspect for misalignment or wear that affects key engagement.
- Housing: Look for cracks or corrosion that could compromise integrity.
- Actuator: Ensure it operates smoothly and does not stick or jam.
By systematically examining these areas, one can effectively diagnose the issues and take steps towards resolution.
Cleaning and Lubricating Lock Parts
Maintaining the functionality of intricate mechanisms is essential for ensuring smooth operation and longevity. Regular cleaning and the application of appropriate substances can greatly enhance performance and prevent potential issues. This section delves into the importance of upkeep for various components that facilitate secure access.
Cleaning is the first step in maintaining these systems. Over time, dirt, dust, and grime can accumulate, leading to hindered movement and inefficiency. To initiate this process, it’s crucial to gently disassemble the relevant parts. Using a soft brush or cloth, carefully remove any debris without causing damage. For stubborn residues, a mild solvent may be employed, ensuring it evaporates completely before reassembly.
Following the cleaning phase, lubrication plays a vital role in ensuring seamless functionality. Selecting the right type of lubricant is key; options such as silicone spray or graphite powder can be effective, as they minimize friction without attracting dirt. Apply the lubricant sparingly, focusing on pivot points and other areas of movement. This step not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of the components.
In conclusion, regular attention to these essential tasks can prevent larger issues and promote reliable operation. By implementing these straightforward practices, one can ensure the continued effectiveness of the mechanism, ultimately leading to a more secure and user-friendly experience.
Reassembling the Door Lock Assembly
Putting together the mechanism once again is a crucial step that ensures everything functions properly. Careful attention to detail during this phase can prevent future issues and guarantee a smooth operation. It’s important to follow a systematic approach to reassemble the components correctly.
Steps to Follow
- Begin by placing the base of the assembly in a stable position.
- Align the internal parts, ensuring they fit snugly into their designated slots.
- Secure any springs or clips that may have been removed during disassembly.
- Test the movement of each part as you proceed, making adjustments if necessary.
Final Checks
After reassembly, conduct a thorough examination to ensure everything is functioning smoothly:
- Verify that all components are correctly seated.
- Check for any unusual resistance or obstruction when testing the mechanism.
- Make sure all screws and fasteners are tightened appropriately.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can confidently ensure that the entire assembly is reassembled correctly, ready for further use.
Testing the Lock Functionality

This section focuses on verifying the performance of the securing mechanism, ensuring it operates smoothly and reliably. Proper assessment is essential for maintaining security and ease of use.
To effectively evaluate the functionality, follow these steps:
- Start by visually inspecting the mechanism for any signs of damage or wear.
- Engage the securing system manually to check for any resistance or unusual sounds.
- Test the mechanism in various positions to confirm it responds correctly.
- Observe the alignment of the components to ensure they fit together seamlessly.
If issues are detected during testing, consider the following potential causes:
- Debris or dirt obstructing the mechanism
- Worn-out components that require replacement
- Misalignment due to improper installation
- Lack of lubrication affecting smooth operation
Regular testing can help prevent future complications and extend the lifespan of the securing device.
Tips for Preventing Future Problems
Maintaining the functionality of access mechanisms is essential for ensuring smooth operation and avoiding future inconveniences. By adopting proactive measures, you can enhance the longevity and reliability of these components, preventing issues before they arise.
Regular Maintenance Checks
Conduct routine inspections to identify any signs of wear or damage. Lubricating moving parts with suitable products can significantly reduce friction and prolong the lifespan of the mechanism. Additionally, ensure that all components are free from dirt and debris, which can impede functionality.
Awareness of Usage Habits

Be mindful of how these systems are utilized. Avoid excessive force when engaging the mechanism, and educate others on proper handling techniques. This simple awareness can help prevent unnecessary strain and reduce the likelihood of future complications.
When to Seek Professional Help
Determining when to involve an expert can save time, effort, and potentially further complications. While some issues can be resolved through personal effort and basic tools, others may require specialized knowledge or equipment. Recognizing the limits of one’s skills is crucial to ensure the task is completed safely and effectively.
Signs of Complex Issues

If you encounter persistent problems despite attempts to address them, this could indicate underlying complexities. Strange noises, difficulty in operation, or complete failure to function are all signals that a trained technician should assess the situation. Ignoring these warning signs can lead to more significant damage and higher costs down the line.
Safety Concerns
Whenever safety is at stake, it is wise to consult a professional. If the mechanism involves electrical components or potential hazards, prioritizing safety should guide your decision. An expert can ensure that the situation is handled correctly and securely, preventing personal injury or further equipment damage.
Comparing Manual and Electric Locks
This section delves into the differences between traditional and modern locking mechanisms, highlighting their functionalities, advantages, and potential drawbacks. Understanding these distinctions can help users make informed decisions based on their needs and preferences.
Functionality and Ease of Use
Traditional systems typically rely on physical manipulation for securing or releasing, while their modern counterparts often provide automated solutions, enhancing convenience. Users may find that the ease of operation can significantly impact their daily routines.
Security and Reliability

When evaluating safety, it’s essential to consider how each system responds to various challenges. Traditional methods may offer robustness, while advanced technologies often incorporate features designed to thwart unauthorized access. Here’s a comparison of key aspects:
| Aspect | Traditional Systems | Modern Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Access | Requires physical key or manual operation | Often includes remote or app-based access |
| Durability | Generally long-lasting with minimal maintenance | Components may require updates or replacements |
| Security Features | Basic physical protection | Advanced technology with potential alerts and monitoring |
Understanding Warranty and Repair Policies

When it comes to maintaining and fixing mechanisms, having a clear grasp of the associated warranties and policies is crucial. This knowledge helps consumers make informed decisions and ensures they are protected in the event of unforeseen issues.
Types of Warranties

Warranties generally fall into several categories, each offering different levels of coverage. Understanding these can significantly impact your choices:
- Manufacturer’s Warranty: Typically provided by the creator, covering defects in materials and craftsmanship.
- Extended Warranty: Often purchased separately, this offers additional coverage beyond the standard period.
- Limited Warranty: Covers specific components or issues, usually with restrictions on what is included.
Key Considerations
When evaluating warranty and repair options, keep these points in mind:
- Duration: Check how long the coverage lasts and what it entails.
- Exclusions: Be aware of what is not covered, as this can vary significantly.
- Claims Process: Understand how to file a claim, including necessary documentation and timelines.
By familiarizing yourself with these aspects, you can ensure a smoother experience when addressing any issues that may arise with your mechanisms.
Safety Precautions During Repairs
Ensuring personal safety while conducting maintenance tasks is crucial. It is essential to take appropriate measures to protect yourself and your surroundings from potential hazards. By following specific guidelines, you can minimize risks and work more effectively.
Personal Protective Equipment

Wearing suitable gear is fundamental when engaging in any form of maintenance work. Safety glasses can shield your eyes from debris, while gloves protect your hands from sharp objects and chemical exposure. Additionally, sturdy footwear can prevent injuries from heavy items and provide better grip during the process.
Workspace Organization
Keeping your workspace tidy can significantly reduce the likelihood of accidents. Make sure all tools are stored properly and that the area is free from clutter. Adequate lighting is also important to ensure visibility, allowing you to identify potential dangers before they cause issues.