
The performance of a sophisticated braking system is crucial for the safe operation of commercial vehicles. Understanding the intricacies of these systems enhances reliability and longevity. This section aims to provide essential insights into maintaining and troubleshooting specific components that contribute to efficient braking operations.
In this guide, we will delve into the operational principles and key features of the braking technology. By familiarizing yourself with the underlying mechanisms, you will be better equipped to identify issues and ensure optimal functionality. A thorough understanding of the system will enable operators and technicians to enhance performance and extend the lifespan of these vital components.
Regular upkeep and timely interventions play a pivotal role in maintaining safety standards. The subsequent sections will outline effective strategies for diagnosing common problems, ensuring that the braking system continues to function smoothly and effectively. Emphasizing proactive measures will not only enhance performance but also reduce the likelihood of costly disruptions.
Zf Intarder Repair Manual
This section provides essential guidance for addressing issues related to the specific braking system used in commercial vehicles. Understanding its components and functionality is crucial for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. Following the appropriate procedures ensures optimal performance and longevity of the system.
Components Overview
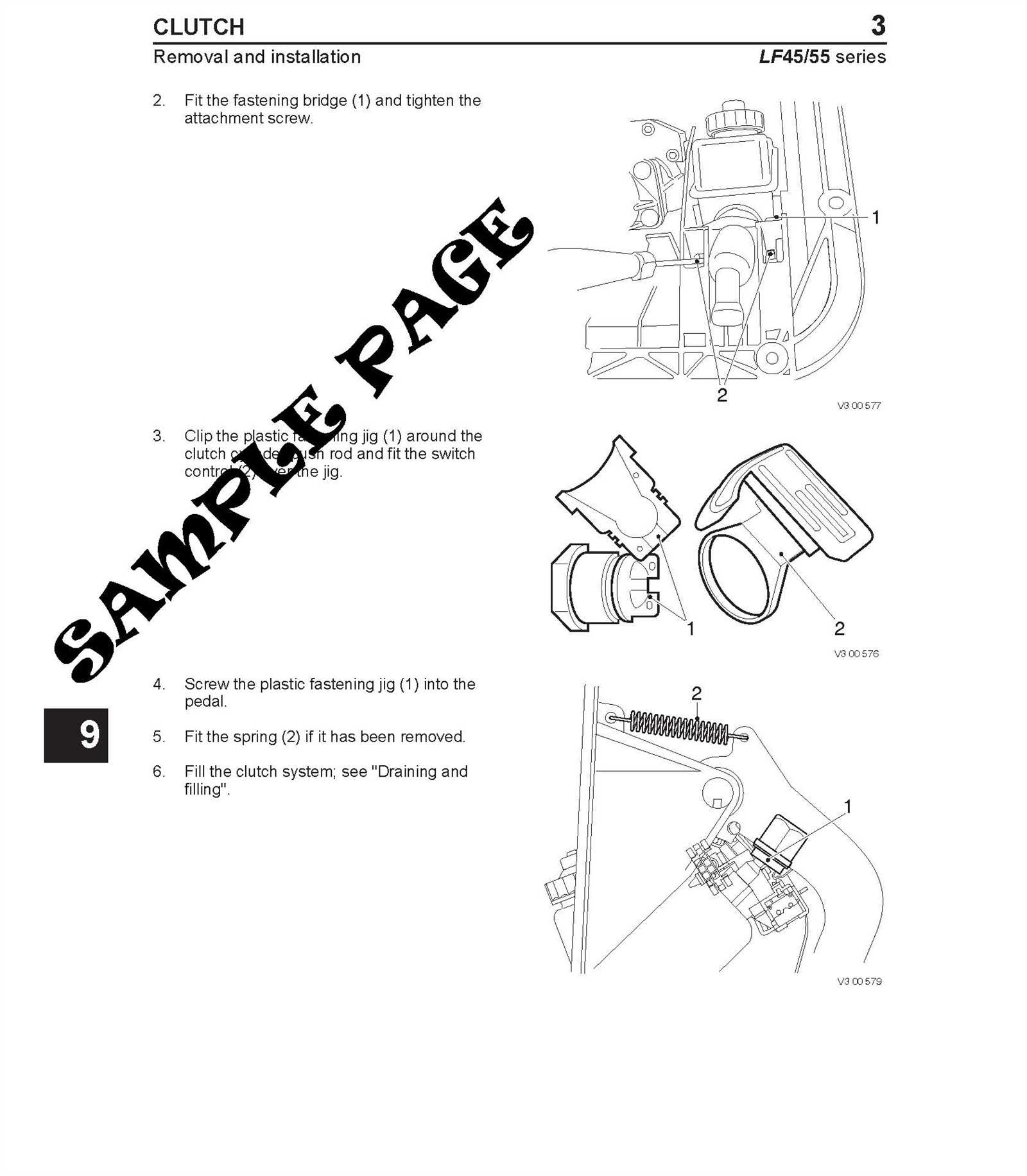
Familiarizing yourself with the key parts of this braking system is vital. The main elements include the control unit, hydraulic components, and the cooling system. Each part plays a significant role in the overall functionality, and knowing how they interact helps in identifying problems efficiently.
Troubleshooting Procedures
When facing operational challenges, systematic diagnosis is essential. Start by examining the control signals and fluid levels. Look for any signs of wear or damage in the hydraulic components. Implementing these steps will help in pinpointing the source of issues and facilitate effective interventions.
Understanding the Zf Intarder System
The system designed for enhancing braking efficiency plays a crucial role in ensuring vehicle safety and performance. This innovative technology assists in reducing the reliance on conventional braking methods, thereby extending their lifespan and improving overall functionality. By utilizing a sophisticated mechanism, it allows for a smoother deceleration experience, particularly in heavy-duty applications.
Core Functionality: At its core, this system operates by harnessing hydraulic forces to provide additional stopping power. This mechanism engages seamlessly with the vehicle’s existing braking components, creating a synergistic effect that optimizes performance under various driving conditions.
Operational Benefits: One of the key advantages of this advanced technology is its ability to minimize wear and tear on traditional braking systems. By distributing the braking effort, it helps maintain effective control, particularly when navigating steep gradients or during prolonged braking scenarios. This not only enhances safety but also contributes to significant maintenance cost savings over time.
Common Issues and Symptoms
Understanding potential problems and their indicators is crucial for maintaining optimal performance in vehicle systems. Various factors can lead to malfunctions, and recognizing these signs early can prevent further complications.
Unusual Noises: Hearing strange sounds, such as grinding or clunking, may signal internal issues. These noises often indicate wear or misalignment in components, requiring immediate attention.
Reduced Performance: A noticeable decline in efficiency or responsiveness can point to underlying mechanical faults. This could manifest as decreased power during operation or sluggish response to input commands.
Overheating: Elevated temperatures beyond normal operating levels are a critical warning sign. This condition may result from inadequate lubrication or blockages, potentially leading to severe damage if left unchecked.
Fluid Leaks: Any visible leakage of fluids around connections can indicate seal failures or damage. Monitoring these areas for signs of wear is essential for early detection of issues.
Warning Lights: Activation of dashboard indicators related to system monitoring can signify problems. These alerts should not be ignored, as they often provide direct insight into malfunctioning components.
By being aware of these common issues and their symptoms, vehicle operators can take proactive measures to ensure longevity and reliable operation.
Essential Tools for Repair
Having the right equipment is crucial when working on complex mechanical systems. A well-equipped workspace not only facilitates efficient handling of components but also ensures that tasks are completed safely and effectively. This section outlines the key items needed for successful maintenance and troubleshooting.
Basic Hand Tools
Start with a set of high-quality hand tools, including wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers. These instruments are essential for loosening and tightening various fittings. A sturdy toolkit allows for flexibility when addressing different issues that may arise during servicing.
Diagnostic Equipment
Incorporating diagnostic tools is vital for identifying faults and monitoring system performance. Devices such as multimeters and pressure gauges can provide valuable insights into the operational state. Utilizing these instruments enhances accuracy in detecting problems, allowing for targeted interventions.
Step-by-Step Disassembly Process
This section outlines the methodical approach to dismantling a specific component in a systematic way. Following these steps ensures that each part is handled correctly and reassembly will be straightforward.
-
Begin by ensuring that the workspace is clean and well-lit. Gather all necessary tools to avoid interruptions.
-
Disconnect any power sources. Safety is paramount when working with mechanical systems.
-
Carefully remove any outer casing. This typically involves unscrewing bolts or clips that secure the cover.
-
Identify and label all connectors and wires. Use tape or markers to ensure they are easy to recognize during reassembly.
-
Proceed to detach internal components sequentially. Take care to note the order and orientation of each piece:
- Remove the first internal part by unscrewing its fasteners.
- Gently lift it out, avoiding force that could damage adjacent components.
- Continue this process for each subsequent piece, maintaining a methodical order.
-
Inspect each component for wear or damage. This is a critical step in assessing the need for replacements.
-
Once all parts are removed, organize them in a manner that facilitates easy access during the reassembly process.
Completing these steps thoroughly will ensure a successful disassembly, setting the stage for any necessary modifications or evaluations of the component.
Inspecting Components for Damage
Conducting a thorough examination of parts is essential to ensure optimal functionality and longevity. This process involves identifying any signs of wear, fractures, or other types of deterioration that could compromise performance. By meticulously assessing each element, potential issues can be detected early, allowing for timely interventions.
Begin the inspection by visually examining all accessible components for any noticeable defects. Look for cracks, chips, or discoloration that may indicate underlying problems. Pay close attention to areas that experience significant stress or heat, as these are often the most susceptible to damage.
Next, utilize appropriate tools to check for precision and alignment. A misaligned part can lead to inefficiencies and increased wear on surrounding components. Ensure that fasteners are secure and that there is no excessive play in moving elements. Any irregularities should be documented for further evaluation.
Finally, consider the operational history of the components. Parts that have been subjected to harsh conditions or have exceeded their service life may require more extensive scrutiny. Implementing a systematic approach to the inspection process will facilitate the identification of potential failures and ensure reliability in operation.
Cleaning and Maintenance Tips
Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your equipment. This section provides valuable insights into effective practices that enhance functionality and prevent potential issues. A proactive approach to care can significantly reduce the likelihood of malfunctions and enhance overall efficiency.
Here are some key practices to consider:
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Conduct frequent checks for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage to components. |
| Cleaning Components | Use appropriate cleaning agents to remove dirt and debris from surfaces, ensuring optimal operation. |
| Lubrication | Apply suitable lubricants to moving parts to minimize friction and wear. |
| Check Connections | Ensure all connections are secure and free from corrosion to maintain efficient energy transfer. |
| Follow Manufacturer Guidelines | Adhere to specific recommendations provided by the manufacturer for optimal care and maintenance. |
Implementing these practices will promote reliability and enhance the lifespan of your equipment. Regular attention to detail will ensure that all components function harmoniously, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
Reassembly Techniques Explained
Reassembling complex components requires a systematic approach to ensure proper functionality and longevity. Understanding the critical steps and methods can greatly enhance the reliability of the final assembly. This section provides insights into effective techniques that facilitate the correct reassembly of intricate systems.
Preparation is essential before beginning the reassembly process. Organizing all parts and tools in a clean workspace minimizes the risk of misplacing components. Carefully reviewing any documentation or diagrams available aids in visualizing the final configuration, thus enhancing accuracy during assembly.
During the reassembly, alignment of the components is crucial. Ensuring that each part fits together seamlessly prevents potential operational issues. Utilizing jigs or guides can be beneficial in maintaining the correct positioning of components throughout the process.
Furthermore, torque specifications must be adhered to when securing fasteners. Applying the correct amount of force prevents damage to the materials while ensuring that all elements are held firmly in place. This is particularly important in high-stress applications where vibration and movement could lead to loosening over time.
Finally, testing the assembled unit before full deployment is advisable. Conducting a series of checks allows for the identification of any inconsistencies or faults, ensuring that the component operates as intended. Proper testing not only enhances safety but also assures optimal performance in its designated application.
Testing the Functionality Post-Repair

Ensuring optimal performance after maintenance is crucial for the longevity and reliability of the system. This phase involves a systematic evaluation to confirm that all components are functioning as intended. A thorough check helps identify any issues that may have arisen during the servicing process.
Initial Functionality Check
Begin by conducting a basic assessment to verify that all parts are operational. This includes listening for unusual sounds and observing for any abnormal behaviors during operation. Monitoring gauges and indicators will provide insight into the overall performance of the system.
Comprehensive Testing Procedures
After the initial check, proceed with detailed testing to evaluate specific functionalities. Use diagnostic tools to measure performance metrics and compare them against standard operating parameters. Document the findings to establish a baseline for future reference and ensure all adjustments have been made effectively.
Safety Precautions During Repair
Ensuring a secure working environment is crucial when handling complex machinery. Adhering to specific safety guidelines minimizes risks and enhances the efficiency of the task at hand. Implementing these precautions is essential for both the technician’s well-being and the integrity of the equipment.
General Safety Guidelines
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and sturdy footwear.
- Keep the work area well-lit and free of clutter to avoid accidents.
- Ensure that all tools and equipment are in good condition before use.
- Be aware of your surroundings and the potential hazards associated with the machinery.
Handling Equipment Safely
- Disconnect power sources before starting any maintenance tasks.
- Use tools specifically designed for the job to prevent damage and enhance safety.
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for handling and storing parts.
- Always secure loose components to prevent them from falling during the procedure.
When to Seek Professional Help

Determining when to consult an expert can be crucial in maintaining optimal performance of your vehicle’s components. Certain signs and symptoms may indicate that specialized knowledge and tools are necessary to address underlying issues effectively.
Signs of Serious Malfunction
If you notice unusual noises, significant changes in performance, or warning lights on your dashboard, it is advisable to reach out to a qualified technician. Ignoring these indicators could lead to more extensive damage and costly repairs down the line.
Lack of Experience
For those unfamiliar with complex systems, attempting to troubleshoot without proper expertise can be risky. Seeking help from a professional ensures that repairs are conducted safely and efficiently, preventing potential hazards.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries related to the maintenance and troubleshooting of specific braking systems. Here, you’ll find useful insights and guidance to help users better understand the operational nuances and resolve prevalent issues effectively.
Common Issues and Solutions
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What are the signs of malfunction? | Indicators may include unusual noises, inconsistent performance, or warning lights on the dashboard. |
| How often should maintenance be performed? | Regular inspections are recommended every 10,000 kilometers or as specified by the manufacturer. |
| Can I perform maintenance myself? | Basic checks can be done independently, but complex tasks should be handled by professionals. |
| What tools are necessary for servicing? | A standard toolkit, including wrenches, screwdrivers, and diagnostic equipment, is generally sufficient. |
Operational Guidelines
Understanding how to utilize these systems properly can enhance safety and efficiency. Adhering to manufacturer guidelines will ensure optimal functionality and longevity.