
Efficient upkeep of agricultural machinery ensures long-term performance and reduces downtime during critical seasons. This section outlines the essential procedures required to maintain older models, focusing on common challenges that arise with continuous use in the field.
Addressing mechanical issues promptly can extend the life of equipment significantly. This guide provides practical solutions for frequent faults, covering engine troubleshooting, hydraulic system adjustments, and gearbox maintenance. Whether tackling routine upkeep or more complex fixes, these steps aim to simplify the process.
Each subsection contains detailed recommendations to help operators diagnose issues effectively. From component inspections to step-by-step instructions, the following content equips users with valuable knowledge to restore machines to optimal condition and ensure reliable performance in every season.
Overview of Common Mechanical Issues

Machinery used in agriculture and construction often experiences wear over time, resulting in a variety of malfunctions. Identifying recurring technical challenges allows operators to maintain performance and extend the equipment’s lifespan. Understanding these typical problems is essential for minimizing downtime and preventing more severe damage.
Engine performance decline is a frequent issue caused by factors such as fuel system inefficiencies or improper air intake. Regular inspections and timely maintenance can help detect these problems early.
Another challenge involves hydraulic system failures, which may occur due to fluid leaks, clogged filters, or pump malfunctions. Ensuring the system is free of contaminants and properly lubricated can mitigate many of these complications.
Transmission issues often manifest as gear shifting difficulties or unusual noises, indicating the need for adjustments or part replacements. Addressing such concerns promptly helps maintain smooth operation and avoids further mechanical stress.
Finally, electrical faults, including wiring damage or malfunctioning sensors, can disrupt functionality. Regular monitoring of connections and control units is essential to keep the equipment running efficiently and safely.
Troubleshooting Electrical System Failures
Identifying and resolving faults within a machine’s electrical network ensures uninterrupted operation. Electrical issues often manifest through non-functional components, intermittent power loss, or irregular system behavior, which requires systematic diagnostics to pinpoint the underlying cause.
Battery and Wiring Check: Begin by verifying the battery’s charge level and inspecting wiring connections for signs of corrosion or loose terminals. A weak or disconnected battery can lead to starting issues or irregular voltage delivery.
Fuse and Relay Inspection: Blown fuses or faulty relays can disrupt the electrical flow. Replace any damaged parts and confirm the relay clicks when activated to ensure proper functionality.
Testing Switches and Sensors: Malfunctioning switches or sensors may cause system failures. Use a multimeter to check for continuity and proper readings across these components.
Alternator and Regulator Diagnosis: An alternator that fails to charge the battery properly or a defective voltage regulator can result in power shortages. Measure the alternator output and ensure the regulator maintains consistent voltage levels.
Comprehensive electrical troubleshooting demands patience and precise testing to eliminate guesswork and prevent recurring issues. Regular inspections and timely repairs of electrical components safeguard equipment from unexpected downtime.
Understanding the Hydraulic System Components
The hydraulic system plays a vital role in ensuring smooth and efficient operation of agricultural equipment. It is designed to transfer energy through pressurized fluid, enabling various mechanical functions such as lifting, lowering, and steering. Familiarity with the key components and their roles helps in diagnosing issues and maintaining optimal performance.
Pump and Fluid Reservoir

The hydraulic pump generates the flow of fluid necessary to power the system. It draws oil from the reservoir, which stores and supplies the fluid required for operation. A properly maintained pump ensures consistent pressure, while the reservoir helps regulate temperature and prevent contamination.
Cylinders, Valves, and Hoses
Cylinders convert hydraulic pressure into mechanical force, allowing for the movement of components like lifting arms or steering mechanisms. Control valves regulate the flow and direction of fluid, ensuring precise operation. Hoses and fittings serve as conduits for fluid transfer, with their integrity being essential to prevent leaks and maintain pressure throughout the system.
Transmission Repair Guide for Beginners
Understanding how to maintain and service a transmission system is essential for keeping agricultural machinery in good working order. This guide offers a basic overview for those new to the process, helping to build confidence in identifying common issues and performing essential maintenance tasks.
Identifying Common Symptoms
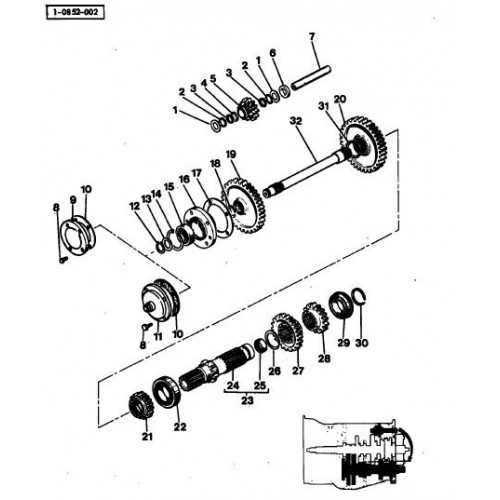
Before diving into adjustments, it’s crucial to recognize the early signs of potential transmission problems. Look for unusual noises such as grinding or whining, delayed gear shifts, and difficulty engaging gears. Leaking fluid around the gearbox can also indicate issues that need attention.
Step-by-Step Maintenance Process

Start by draining the old transmission fluid to prevent contamination. Inspect all seals and gaskets for wear, replacing them if necessary to avoid future leaks. Tightening loose connections and cleaning the gearbox will improve performance. After refilling with fresh fluid, test the system by shifting through all gears to ensure smooth operation.
Pro Tip: Regular inspections help spot minor issues before they escalate, saving both time and resources in the long run.
Fuel System Maintenance Tips
Proper care of the fuel system ensures smooth operation and longevity of the engine. Regular inspections and timely upkeep prevent clogging, reduce wear, and enhance fuel efficiency, ensuring consistent performance over time. Keeping the system clean and functioning well also minimizes the risk of unexpected breakdowns during use.
Inspect and Replace Filters
Fuel filters play a crucial role in keeping contaminants away from the engine. Over time, dirt and debris accumulate, reducing the flow of fuel. It’s essential to check the filters periodically and replace them as needed to avoid damage. Make sure to follow recommended intervals for filter changes to keep the system in optimal condition.
Check Fuel Lines for Leaks
Fuel lines can develop cracks or wear due to age and exposure to varying temperatures. Regularly inspecting these lines helps identify potential leaks early. If you notice any signs of damage, such as cracks or the smell of fuel, replace the lines immediately to prevent hazardous situations and maintain smooth engine performance.
Brake System Adjustment Instructions
Properly adjusting the braking system is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety of the vehicle. This section outlines the necessary steps to achieve accurate alignment and functionality of the brake components, thereby enhancing overall braking efficiency.
Understanding the Brake Components
The braking system comprises various elements, including the brake pads, rotors, and hydraulic components. Familiarizing yourself with these parts is essential for effective adjustments. Regular inspections can help identify any wear or issues that might affect braking performance.
Adjustment Procedure
Begin the adjustment process by checking the brake pads for wear. If they are significantly worn down, replacing them is advisable. Next, ensure that the brake fluid level is adequate and free from contamination. Adjust the brake shoes or pads as necessary, ensuring they are positioned correctly against the rotor. Finally, test the brakes by applying them gently to ensure they engage smoothly and respond appropriately.
Note: Regular maintenance and timely adjustments are vital for the longevity of the braking system and the safety of the vehicle.
Clutch Replacement Step-by-Step Process
Replacing the clutch in a tractor is a vital procedure that ensures optimal performance and functionality. This process involves several critical steps to ensure that the new component is correctly installed and that the machinery operates smoothly. Following a systematic approach can help in achieving a successful installation without complications.
First, begin by securing the tractor in a safe and stable position. Disconnect the battery to prevent any electrical hazards during the procedure. Next, remove any necessary covers or components that obstruct access to the clutch assembly. It is crucial to take note of the arrangement of parts to facilitate reassembly.
Once you have clear access, proceed to detach the existing clutch from the engine. This typically involves unscrewing bolts and carefully pulling the clutch away from its housing. Inspect the release bearing and other associated components for wear and replace them if necessary to ensure longevity and reliability.
After removing the old clutch, clean the mounting surface to eliminate any debris or old lubricant. Position the new clutch in place, aligning it correctly with the input shaft. Secure it using the appropriate bolts, making sure to follow the manufacturer’s torque specifications for a secure fit.
Reassemble any removed components in reverse order, ensuring everything is tightly secured. Finally, reconnect the battery and perform a test run to verify that the new clutch operates smoothly. This step-by-step approach not only enhances the machine’s efficiency but also extends its lifespan.
How to Rebuild the Engine Block

Rebuilding an engine block is a critical process that can restore the performance and reliability of a vehicle. This task involves meticulous attention to detail and a solid understanding of engine components. The following guide outlines the necessary steps and considerations for successfully completing this endeavor.
Preparation and Tools
Before starting the rebuilding process, it is essential to gather the necessary tools and prepare the workspace:
- Engine hoist or crane
- Socket set and wrenches
- Torque wrench
- Cleaning supplies
- Gasket sets and sealants
- Replacement parts (if needed)
Disassembly and Inspection
Begin by carefully disassembling the engine block. Take the following steps:
- Remove the engine from the vehicle using an engine hoist.
- Drain all fluids, including oil and coolant.
- Take off the cylinder head, crankshaft, and other components in a systematic manner.
- Inspect each part for wear and damage, noting any areas that require replacement or repair.
After the inspection, proceed with the necessary repairs, ensuring all surfaces are clean and free of debris. This foundational step is crucial for a successful rebuild.
Cooling System Inspection and Repairs
The cooling mechanism is a vital component that maintains optimal operating temperatures in engines. Regular examination and maintenance of this system are crucial to prevent overheating and ensure efficient performance. This section outlines essential procedures for evaluating and servicing the cooling apparatus.
Inspection Procedures

To effectively assess the cooling system, follow these steps:
- Check coolant levels regularly to ensure they are within the recommended range.
- Inspect for leaks around hoses, connections, and the radiator.
- Examine the radiator for any signs of corrosion or damage.
- Assess the condition of the coolant itself; it should be clean and free of debris.
Maintenance and Repairs
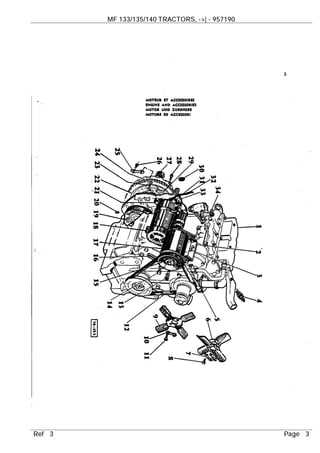
Performing necessary repairs can prolong the lifespan of the cooling system. Consider the following actions:
- Flush the cooling system to remove any sediment or contaminants.
- Replace worn or damaged hoses to prevent coolant loss.
- Install a new thermostat if the engine is experiencing temperature regulation issues.
- Ensure the radiator fan is functioning correctly to promote adequate airflow.
By adhering to these guidelines, one can ensure the cooling system operates efficiently and effectively, enhancing overall engine performance.
Steering System Calibration and Tuning
Proper calibration and tuning of the steering mechanism are essential for ensuring optimal performance and handling of agricultural machinery. This process involves adjusting various components to achieve the desired responsiveness and accuracy when maneuvering the equipment. A well-tuned steering system not only enhances operational efficiency but also improves safety during use.
To begin the calibration process, it is crucial to inspect the entire steering assembly for any signs of wear or damage. Components such as the steering wheel, linkages, and hydraulic systems should be examined thoroughly. Any worn parts must be replaced to prevent malfunction during operation.
Next, adjustments should be made to align the steering system correctly. This involves fine-tuning the angles of the steering components to ensure that the wheels respond accurately to the driver’s input. Proper alignment minimizes uneven tire wear and enhances overall handling.
Additionally, hydraulic pressures must be checked and adjusted to ensure that the steering assist functions correctly. This step is vital for achieving a balance between steering effort and responsiveness, making it easier for operators to navigate through challenging terrains.
Finally, it is recommended to conduct a test drive after making adjustments. This allows for the evaluation of the steering system’s performance under actual working conditions. Any necessary refinements can be identified during this phase, ensuring that the machinery operates at its best.
Seasonal Maintenance Checklist

Regular upkeep of your agricultural machinery is essential to ensure optimal performance throughout the year. A well-structured seasonal maintenance checklist helps identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring that the equipment operates efficiently and safely. This proactive approach not only extends the lifespan of the machinery but also enhances productivity in the field.
Spring Maintenance: As the planting season approaches, inspect the engine and fluid levels, including oil and coolant. Check the air filters and replace them if necessary to ensure proper airflow. Review the tire pressure and tread depth, and adjust as needed to maintain stability and traction.
Summer Maintenance: During the hot months, monitor coolant levels and ensure the radiator is clear of debris. Inspect belts and hoses for signs of wear, as high temperatures can accelerate deterioration. Additionally, keep an eye on fuel quality, especially if storing fuel for extended periods.
Autumn Maintenance: Before winter sets in, conduct a thorough inspection of the electrical systems and connections. Replace any worn-out batteries and ensure that all lights are functioning. Also, prepare the machine for storage by cleaning it thoroughly and lubricating moving parts to prevent rust and corrosion.
Winter Maintenance: In cold conditions, regularly check the battery and electrical systems to prevent failures. Ensure that the machine is kept in a dry, sheltered environment to avoid frost damage. If the equipment will be inoperative for an extended period, consider using a fuel stabilizer to maintain fuel quality.
By following this seasonal maintenance checklist, operators can maximize the efficiency and reliability of their machinery, ultimately leading to a more successful and productive farming season.