For those who rely on robust outdoor equipment, understanding how to effectively maintain and service these machines is essential. Proper care ensures that the engine remains reliable and delivers the performance needed for demanding tasks. This guide will introduce key concepts, techniques, and insights into maintaining high-powered engines in excellent working condition, offering users the confidence to handle common issues and ensure smooth operation.
Focusing on essential aspects of engine upkeep, this resource covers everything from initial diagnostics to identifying signs of wear. It emphasizes methods that help extend the lifespan of the machinery, detailing proactive measures to prevent breakdowns. In addition to providing practical instructions, it offers valuable tips for troubleshooting and optimizing performance.
Whether you’re an experienced technician or a DIY enthusiast, this guide is designed to help you become more familiar with specific engine components, how they interact, and the best practices for keeping them in top form. Dive in to gain the knowledge needed to keep your equipment running at its peak for years to come.
Briggs and Stratton Twin Cylinder L Head Repair Guide
This guide provides comprehensive instructions for maintaining and troubleshooting a specific model of small engines commonly used in various machines. These engines are known for their durability and efficiency, making them a popular choice in power equipment. Regular upkeep and timely adjustments are essential to ensuring optimal function and extending the life of this equipment.
Understanding Key Components
Knowing the primary parts involved is crucial for anyone handling these engines. This section breaks down the essential components you’ll interact with most frequently. By understanding how each part operates, you can better diagnose issues and perform maintenance tasks effectively.
| Component | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Ignition System | Responsible for generating the initial spark needed for engine startup, the ignition system ensures a consistent spark delivery under various conditions. | |
| Fuel Delivery | This system manages the flow of fuel into the engine, adjusting to maintain ideal performance levels and efficiency. | |
| Cooling Mechanism | Designed to prevent overheating, the cooling mechanism helps maintain a safe operating temperature for continuous operation. |
| Component | Inspection Tips | Replacement Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Piston | Check for scratches or scoring on the surface. | Visible damage or excessive play in the cylinder. |
| Rings | Inspect for wear patterns and proper seating. | Loss of compression or oil consumption issues. |
| Valves | Look for carbon buildup and proper alignment. | Leakage or poor sealing when closed. |
| Crankshaft | Assess for bends or unusual vibrations during operation. | Excessive noise or oil leaks at the seals. |
| Gaskets | Check for cracks, warps, or signs of leaking. | Fluid leaks or degraded sealing performance. |
By diligently checking these parts, one can ensure that the engine remains in prime condition, avoiding more severe issues down the line. Proper replacement when necessary will contribute to overall efficiency and performance.
Cleaning and Rebuilding Carburetor System

Maintaining optimal performance of an engine often hinges on the condition of its fuel delivery components. A well-functioning fuel mixer is essential for ensuring that the mixture of air and fuel reaches the combustion chamber efficiently. Over time, these systems can accumulate debris and varnish, leading to poor performance and potential engine issues. This section will guide you through the essential steps to clean and restore the functionality of this critical component.
Steps for Cleaning the Fuel Mixer
- Begin by disconnecting the fuel supply and removing the assembly from the engine.
- Disassemble the unit carefully, noting the arrangement of parts for reassembly.
- Use a carburetor cleaner solution to thoroughly soak all metal components. Ensure that any jets and passages are free of obstructions.
- Inspect all gaskets and seals for wear; replace them as necessary to ensure a proper seal during reassembly.
Rebuilding the Fuel Mixer

Once cleaned, the next phase is to put the components back together systematically. Follow these steps to ensure proper assembly:
- Begin with the installation of new gaskets, ensuring they are seated properly.
- Reassemble the parts in the reverse order of disassembly, taking care to torque bolts to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Reconnect the fuel lines and ensure there are no leaks before starting the engine.
- Test the operation by running the engine and observing its performance, making any necessary adjustments.
By following these steps, you can effectively enhance the longevity and efficiency of the engine’s fuel system, leading to improved overall performance.
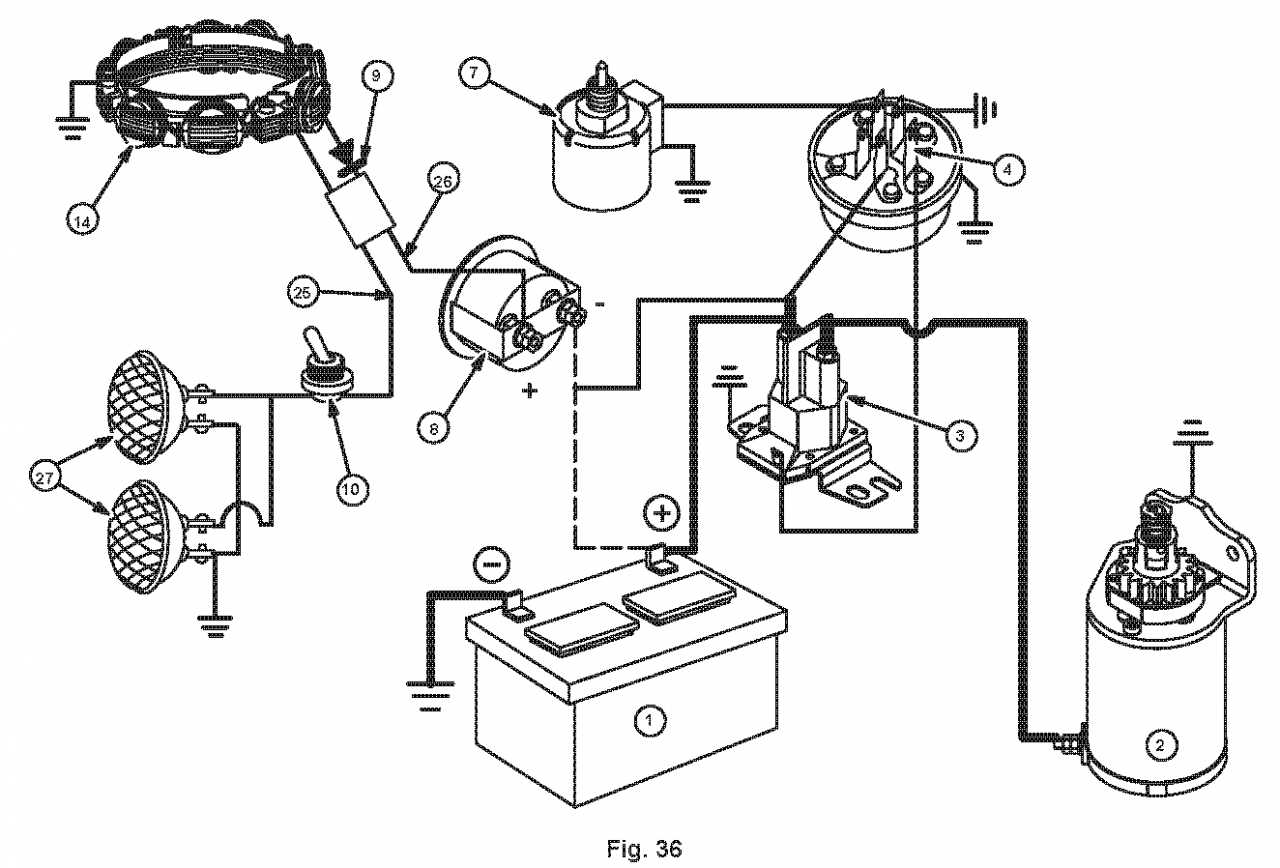
Troubleshooting Ignition and Electrical Problems
Addressing ignition and electrical issues is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance. These problems can arise from various sources, such as faulty components, improper connections, or wear and tear over time. Understanding how to diagnose these issues can significantly enhance the longevity and reliability of your engine.
Identifying Common Issues
Common symptoms of ignition malfunctions include difficulty starting, uneven running, or stalling. Inspecting the spark plug is a good starting point; a worn or dirty spark plug can lead to inadequate ignition. Check the ignition coil as well, as a malfunctioning coil can cause weak or no spark. Ensure all connections are secure and free from corrosion to promote proper electrical flow.
Testing Electrical Components
To effectively troubleshoot, utilize a multimeter to test voltage levels at various points within the ignition system. Start by measuring the voltage at the battery terminals; a weak battery can lead to performance issues. Proceed to test the wiring harness and connectors, looking for signs of damage or loose connections. If all components appear functional but issues persist, consider consulting a professional for advanced diagnostics.
Reassembling the Engine Components
Reassembling engine parts requires careful attention to detail and a systematic approach. This stage is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the machine. Following a structured process will facilitate a smooth assembly and help avoid common pitfalls.
To begin the reassembly process, gather all necessary components and tools. This will help maintain an organized workspace and streamline the task at hand. Ensure that all parts are clean and free from any debris or contaminants that could impede functionality.
- Step 1: Align the crankcase and ensure that the surfaces are properly prepared.
- Step 2: Insert the crankshaft, making sure it fits snugly into the designated slots.
- Step 3: Carefully position the connecting rods, ensuring they are properly oriented.
- Step 4: Attach the pistons to the connecting rods and secure them using the specified hardware.
- Step 5: Place the cylinder assembly onto the crankcase, ensuring a tight fit.
- Step 6: Fasten the head assembly, making sure to use the appropriate torque specifications.
- Step 7: Reconnect all necessary linkages, ensuring each component is securely fastened.
Throughout the assembly, double-check each step to confirm that all parts are installed correctly. Following the outlined sequence will greatly enhance the likelihood of a successful reassembly. After completing the process, perform a thorough inspection to verify that everything is in order before proceeding to test the engine.
Testing Engine Performance After Repairs

Evaluating the functionality of an engine following maintenance is essential to ensure its efficiency and longevity. Proper assessment allows you to identify any lingering issues and confirm that all adjustments have been successful. This section outlines key steps to effectively test the engine’s performance after completing maintenance work.
To conduct a thorough evaluation, follow these guidelines:
- Initial Inspection:
- Check for any visible leaks in hoses and connections.
- Ensure all components are securely fastened and properly aligned.
- Inspect the ignition system for any signs of wear or damage.
- Starting the Engine:
- Turn on the power supply and initiate the starting sequence.
- Listen for unusual noises that could indicate problems.
- Observe the engine’s idle stability; it should be smooth and consistent.
- Performance Testing:
- Utilize a tachometer to measure engine RPM at idle and full throttle.
- Monitor exhaust emissions to ensure compliance with environmental standards.
- Conduct a load test to evaluate performance under different operating conditions.
- Final Review:
- Document all observations and any abnormalities noted during testing.
- Compare performance metrics to manufacturer specifications.
- If any issues arise, address them promptly to avoid further complications.
Following these steps will help ensure that the engine operates optimally and reliably after maintenance. Regular testing not only extends the life of the engine but also enhances overall performance.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity and Efficiency
Regular upkeep is essential for maximizing the lifespan and performance of small engines. By implementing a few straightforward practices, users can ensure that their equipment operates smoothly and efficiently, minimizing the risk of costly breakdowns.
1. Regular Oil Changes: Frequent oil changes are crucial. Fresh oil reduces friction, enhances lubrication, and helps keep components cool. Aim to replace the oil after every 50 hours of operation or at least once a season, whichever comes first.
2. Air Filter Maintenance: A clean air filter is vital for optimal airflow. Check the filter regularly and clean or replace it as needed. This simple step can significantly improve engine performance and fuel efficiency.
3. Spark Plug Inspection: Spark plugs are essential for ignition and combustion. Inspect them periodically for wear or deposits. Replacing worn plugs can lead to better starts and improved fuel consumption.
4. Fuel Quality: Use high-quality fuel to prevent engine issues. Old or contaminated fuel can cause starting problems and decreased efficiency. Consider using fuel stabilizers if the equipment is stored for extended periods.
5. Cooling System Maintenance: Ensure that the cooling fins and air passages are clean and free from debris. Overheating can lead to severe damage, so regular inspections are crucial.
6. Seasonal Storage: Properly prepare the equipment for off-season storage. This includes cleaning, draining fuel, and protecting against rust. Such precautions can extend the life of the engine and components significantly.
By following these essential maintenance practices, users can enjoy enhanced reliability and performance, ultimately leading to a more satisfying ownership experience.