
Understanding the intricacies of machinery maintenance is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This section delves into the vital aspects of servicing specific equipment designed for material handling tasks. Regular upkeep not only enhances efficiency but also significantly reduces the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns, which can disrupt operations and incur substantial costs.
Equipped with the right knowledge and techniques, operators can tackle common issues effectively, extending the lifespan of their tools. This guide offers detailed insights into troubleshooting and enhancing functionality, enabling users to address potential challenges proactively. By mastering these maintenance strategies, one can maintain peak operational standards and ensure safety in the workplace.
The information provided herein is tailored to empower individuals with the skills needed for effective management of their equipment. Through a comprehensive understanding of the components and their workings, users can cultivate a more reliable and efficient working environment.
Crown Pallet Jack Overview
This section provides an insightful look into a highly efficient material handling solution designed to streamline various industrial operations. These devices are essential for transporting goods within warehouses and other commercial environments.
Key features include:
- Robust construction ensuring durability and reliability.
- Ergonomic design promoting operator comfort during use.
- Advanced hydraulic systems for smooth lifting and lowering.
- Compact size enabling easy maneuverability in tight spaces.
Applications of this equipment are diverse, including:
- Moving pallets of goods across short distances.
- Facilitating loading and unloading processes.
- Enhancing efficiency in inventory management.
Overall, these devices play a crucial role in optimizing workflows and improving productivity in various settings.
Common Issues with Pallet Jacks
Handling equipment can encounter a variety of problems that hinder their performance and safety. Recognizing these issues early is essential to ensure efficient operations and prevent potential accidents. Below are some frequent challenges that users may face.
- Hydraulic Problems:
- Fluid leaks leading to reduced lifting capability.
- Air in the hydraulic system causing sluggish movement.
- Wheel Wear:
- Excessive wear and tear affecting maneuverability.
- Debris accumulation causing uneven movement.
- Steering Issues:
- Difficulties in turning, leading to operational inefficiency.
- Loose or damaged steering components resulting in instability.
- Frame Damage:
- Cracks or bends compromising structural integrity.
- Corrosion affecting durability and performance.
- Electrical Malfunctions:
- Faulty wiring leading to failure in electric models.
- Battery issues causing unreliable power supply.
Addressing these common issues promptly can enhance the lifespan of the equipment and maintain workplace safety. Regular maintenance checks are recommended to identify and rectify problems before they escalate.
Tools Needed for Repairs
When it comes to maintaining and fixing equipment, having the right instruments at your disposal is crucial. Proper tools not only enhance efficiency but also ensure safety during the maintenance process. Below is a list of essential implements required for effective servicing of your equipment.
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Wrench Set | For loosening and tightening bolts and nuts. |
| Screwdriver Set | To fasten or remove screws from various components. |
| Torque Wrench | Ensures proper tightening of fasteners to specified torque levels. |
| Pry Bar | Useful for separating components and applying leverage. |
| Multimeter | For checking electrical connections and diagnosing issues. |
| Safety Gloves | To protect hands during disassembly and maintenance tasks. |
| Flashlight | For illuminating dark areas when inspecting components. |
Equipped with these tools, you can effectively address various issues, ensuring your equipment remains in optimal working condition.
Step-by-Step Repair Process
This section outlines a systematic approach to fixing common issues encountered with lifting equipment. Following these steps will ensure a thorough and efficient resolution of problems, enhancing the longevity and performance of the device.
Initial Assessment
Before starting any work, it is crucial to evaluate the situation carefully. Identify the symptoms and any unusual behaviors of the machinery. This initial examination will guide you in determining the appropriate corrective measures.
Disassembly and Inspection
Once the assessment is complete, proceed with disassembly. Carefully take apart the components, noting the arrangement for reassembly. Inspect each part for signs of wear, damage, or malfunction. Document your findings to keep track of necessary replacements or repairs.
| Component | Common Issues | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Wheels | Excessive wear, misalignment | Replace or realign |
| Hydraulic System | Leaks, poor lifting | Seal replacements, fluid refill |
| Handle | Loose, difficult to operate | Tighten screws, replace if damaged |
Following these structured steps will facilitate a successful troubleshooting and maintenance process, ensuring optimal functionality and safety of the equipment.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Proper upkeep of your equipment is essential to ensure its durability and optimal performance. Implementing a routine maintenance schedule can significantly extend the lifespan of your machinery, reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs. By following a few straightforward guidelines, you can keep your equipment in top condition and enhance its efficiency.
Regular Inspections
Cleaning and Lubrication
Maintaining cleanliness is vital for the smooth operation of your machinery. Regularly clean the exterior and interior to remove debris and contaminants. Additionally, ensure that moving parts are adequately lubricated to minimize friction and wear. Using the right lubricant as recommended can significantly improve functionality and reduce the risk of malfunctions.
Identifying Parts and Components
Understanding the various elements and mechanisms of lifting equipment is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Each part plays a critical role in ensuring optimal performance and safety during operation. Familiarity with these components allows for timely identification of issues and better management of machinery.
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Chassis | The main frame of the unit | Provides structural support and stability |
| Forks | The horizontal arms that lift the load | Engage with and elevate loads |
| Hydraulic System | Includes cylinders and pumps | Facilitates lifting and lowering actions |
| Wheels | Located at the base | Enables movement and maneuverability |
| Control Handle | Operator interface for controls | Regulates lifting and movement functions |
Troubleshooting Electrical Problems
Identifying and resolving electrical issues is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and safety of material handling equipment. Proper diagnosis can prevent further complications and ensure optimal functionality. This section will guide you through common electrical concerns and their potential solutions.
Common Electrical Issues
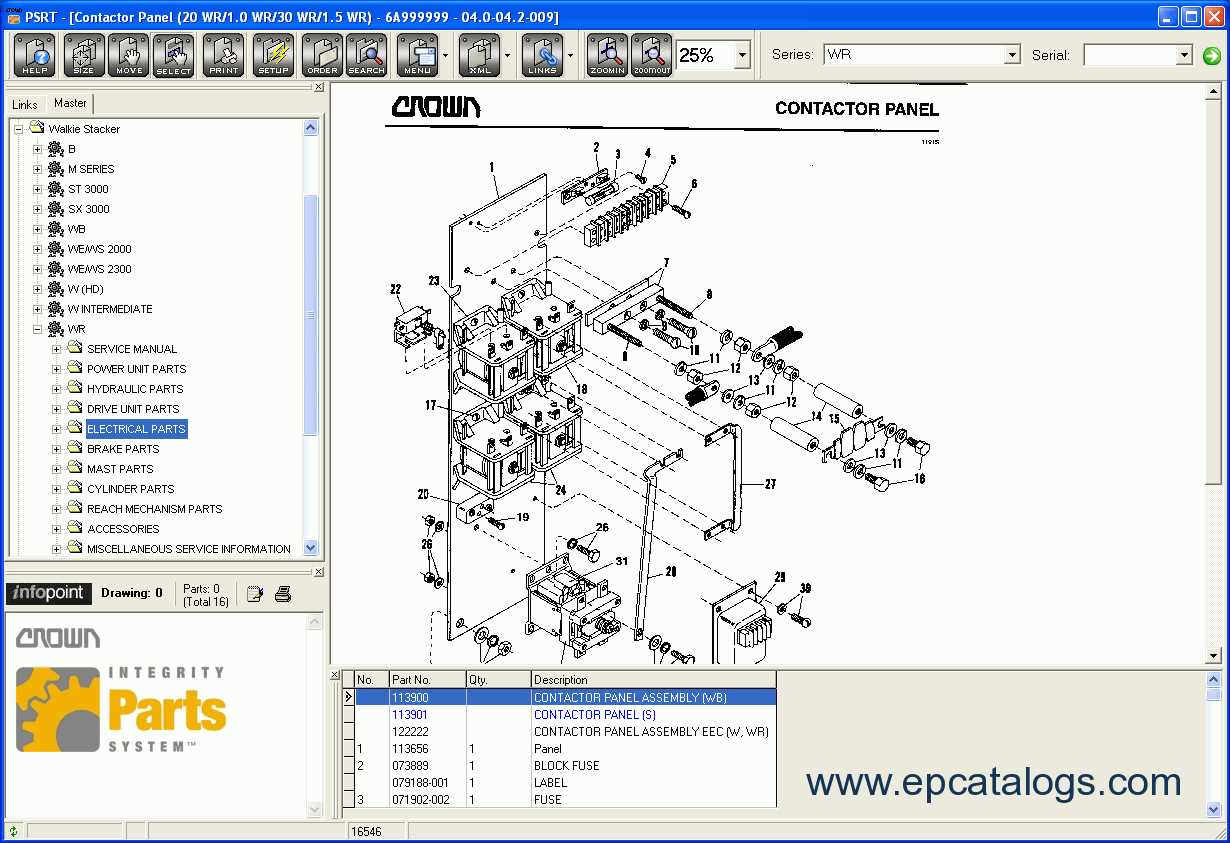
- Battery not charging
- Intermittent power loss
- Faulty control panel functions
- Inconsistent movement response
Steps for Diagnosis
- Check the Battery: Ensure that the battery connections are secure and free from corrosion. Test the voltage to confirm proper charge levels.
- Inspect Wiring: Examine all wiring for signs of wear or damage. Look for frayed insulation or loose connections that could disrupt power flow.
- Test the Control Circuit: Use a multimeter to check the control circuit for continuity. Identify any components that may be malfunctioning.
- Evaluate Safety Features: Ensure that all safety switches and sensors are functioning correctly, as they can inhibit operation if triggered.
By following these steps, you can systematically address electrical problems, ensuring your equipment operates smoothly and reliably.
Hydraulic System Repair Techniques
Maintaining the functionality of hydraulic systems is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Understanding the intricacies of these mechanisms allows for effective troubleshooting and restoration, ensuring smooth operation in various applications. This section outlines key methodologies for addressing common issues encountered within hydraulic systems.
Leak Identification is often the first step in the assessment process. Regularly inspecting hoses, connections, and seals can reveal potential sources of fluid loss. Using a hydraulic fluid dye can aid in pinpointing leaks that are not immediately visible. Once identified, replacing damaged components is crucial to restore system integrity.
Fluid Replacement is another vital technique. Over time, hydraulic fluid can degrade due to contamination or thermal breakdown. Ensuring the system is filled with high-quality fluid not only enhances performance but also protects internal components from wear. It is advisable to follow manufacturer guidelines regarding fluid types and change intervals.
Filter Maintenance plays a significant role in system health. Clogged filters can impede flow and reduce efficiency. Regular inspection and timely replacement of filters will help maintain the cleanliness of the hydraulic fluid and prevent damage to sensitive components.
Component Testing is essential for diagnosing operational issues. Utilizing pressure gauges and flow meters can provide valuable insights into the system’s performance. By analyzing pressure readings, technicians can determine if components such as pumps or cylinders are functioning within acceptable parameters.
Seals and Gaskets Replacement is necessary when wear becomes evident. Damaged seals can lead to leaks and compromised performance. Choosing the right materials for replacements is critical, as it ensures compatibility with the hydraulic fluid and the system’s operating conditions.
By employing these techniques, technicians can effectively address common hydraulic system challenges, thereby extending the lifespan and reliability of the equipment. Regular maintenance and proactive measures will result in enhanced efficiency and reduced downtime.
Replacing Wheels and Rollers
Maintaining optimal functionality of your equipment often requires attention to its mobility components. This section focuses on the procedure for swapping out the wheels and rollers, ensuring smooth operation and longevity of the unit.
Tools and Materials Needed
Before beginning the replacement process, gather the necessary tools and parts. You will need a wrench, screwdrivers, and new wheels or rollers that are compatible with your device. Having everything ready will streamline the task.
Step-by-Step Replacement Process
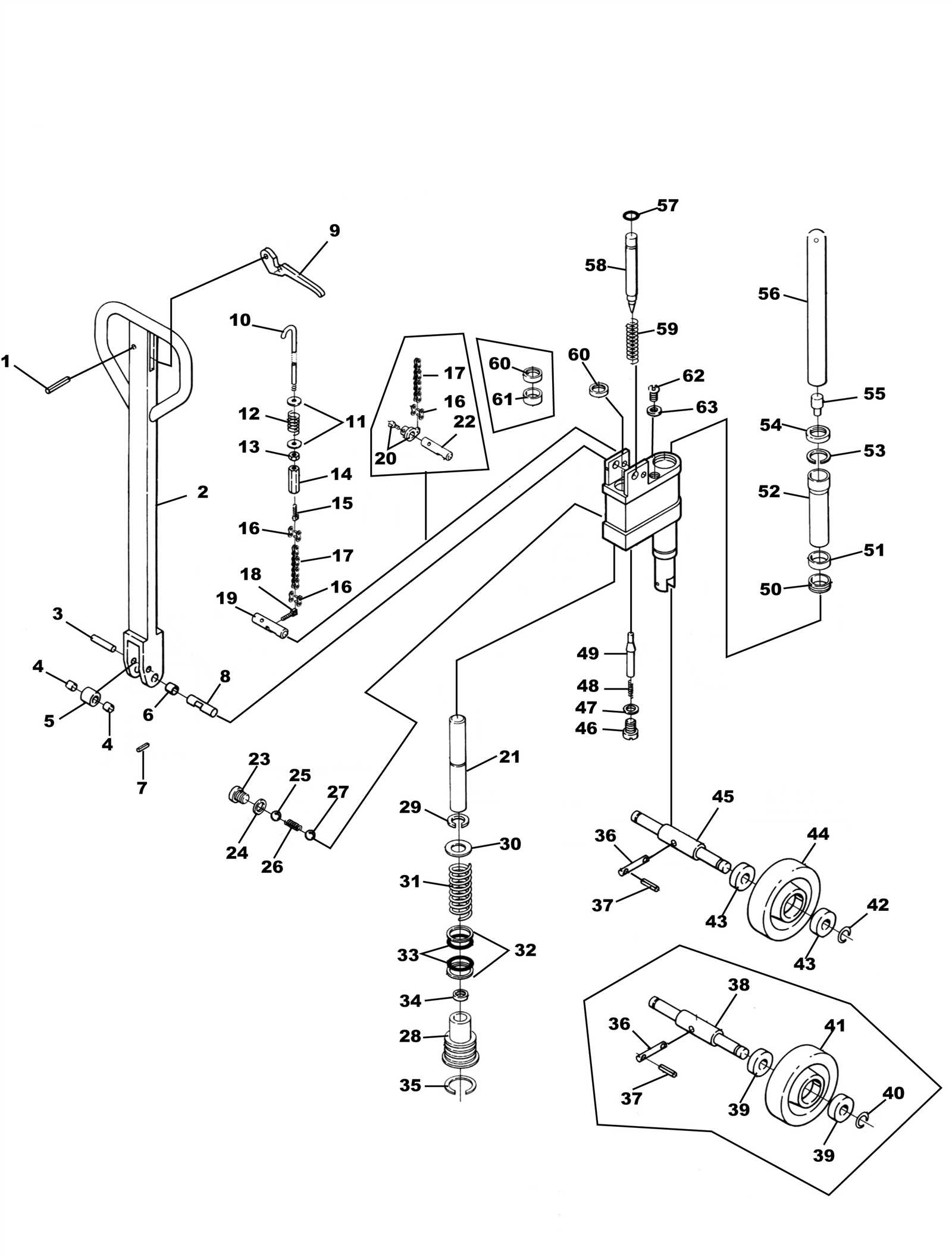
1. Safety First: Ensure the equipment is powered down and secure. 2. Remove Old Components: Carefully detach the existing wheels or rollers using your tools. 3. Install New Parts: Align and fix the new wheels or rollers in place, making sure they are tightly secured. 4. Test Functionality: Once installed, check the movement to confirm proper installation.
Regular checks and timely replacements of these components will ultimately enhance the efficiency of your equipment.
Safety Precautions During Repairs
Ensuring safety while performing maintenance tasks is crucial for both the technician and the equipment. Proper precautions help prevent accidents and injuries, leading to a more efficient and effective working environment.
Here are essential safety measures to consider:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate gear, including gloves, goggles, and steel-toed boots to protect against potential hazards.
- Work Area Organization: Keep the workspace clean and free from clutter. Ensure tools and materials are organized to avoid tripping hazards.
- Electrical Safety: Before starting any task, disconnect the power source to prevent accidental activation. Use insulated tools when working near electrical components.
- Use of Tools: Ensure that all tools are in good condition and suitable for the task. Regularly inspect and maintain equipment to avoid malfunctions.
Additional considerations include:
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always adhere to the specific instructions and safety recommendations provided by the manufacturer.
- Work with a Partner: Whenever possible, have a colleague assist you, especially when lifting or handling heavy components.
- Emergency Preparedness: Be aware of the location of first aid kits and emergency exits in case of an accident.
By following these precautions, you can significantly reduce the risk of injury and ensure a safe and efficient maintenance process.
Cost Considerations for Repairs
Understanding the financial aspects of maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your equipment. Various factors can influence the overall expenditure, from the nature of the issues encountered to the specific components requiring attention. Evaluating these elements can help in making informed decisions regarding service and upkeep.
One of the primary considerations is the cost of replacement parts. Prices can vary significantly depending on the brand and availability of the components. Additionally, the choice between original and aftermarket parts may impact both short-term expenses and long-term reliability. Evaluating the trade-offs between these options is essential.
Labor costs also play a significant role in the total expense of maintenance tasks. Hiring skilled technicians can ensure quality service, but it may come at a premium. Alternatively, some operators may opt for in-house maintenance, which could reduce costs but might require additional training and resources.
Another important aspect to consider is the frequency of maintenance activities. Regular servicing can help identify potential problems early, potentially saving money in the long run by preventing more extensive damage. Budgeting for routine checks and setting aside funds for unforeseen repairs can help maintain operational efficiency.
Finally, assessing the overall impact of downtime due to equipment malfunction is vital. Delays in operations can lead to financial losses that far exceed the cost of timely maintenance. Balancing the upfront expenses with the potential for increased productivity can provide a clearer picture of the total cost of ownership.
When to Seek Professional Help
Identifying the right moment to enlist the expertise of a specialist can significantly impact the longevity and efficiency of your equipment. While some issues may seem minor and manageable, there are certain circumstances where professional intervention is not just advisable, but necessary.
Signs of Major Malfunctions
If you notice persistent problems that do not resolve with basic troubleshooting, it is time to consult an expert. Indicators such as unusual noises, leaks, or inconsistent performance can signal deeper issues that require specialized knowledge and tools. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to further damage, escalating repair costs, and potential safety hazards.
Complex Repairs Beyond Your Skill Level
Even for those with some technical know-how, certain repairs may exceed personal capability. If a task involves intricate components or requires specific calibration, seeking professional assistance is prudent. Experts not only possess the necessary skills but also have access to quality parts and advanced equipment, ensuring that your machinery operates optimally and safely.