
Maintaining and troubleshooting your power equipment is essential for ensuring its longevity and performance. A comprehensive approach to understanding its components can significantly enhance your ability to diagnose issues and implement effective solutions. This section delves into the essential aspects of managing your machinery, offering insights that empower users to navigate challenges with confidence.
Familiarity with the internal structure is crucial for any operator. Recognizing how different elements interact not only facilitates better maintenance practices but also allows for quicker identification of potential problems. By mastering the layout and functionality of your apparatus, you position yourself to make informed decisions regarding its upkeep.
Visual aids play a vital role in this learning process. They serve as invaluable references, helping you visualize connections and relationships within the equipment. As you familiarize yourself with these resources, you will find that troubleshooting becomes a more intuitive and manageable task, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency.
Understanding Coleman Powermate 5000 Wiring
When it comes to comprehending the electrical connections and circuits of a portable energy source, it is essential to grasp how different components interact. This knowledge not only aids in troubleshooting but also ensures optimal performance during usage. By familiarizing oneself with the layout and functionalities, users can enhance their experience and prolong the life of the equipment.
Key Components
- Power Source: The heart of the system, providing the necessary energy.
- Control Panel: Houses switches and indicators for managing operations.
- Output Ports: Where the energy is delivered to external devices.
- Safety Features: Elements designed to protect both the user and the equipment.
Basic Principles
- Understanding Circuits: Recognizing how electricity flows through various paths.
- Identifying Connections: Learning to pinpoint how different parts are linked.
- Testing for Faults: Knowing techniques to diagnose issues when they arise.
By grasping these fundamental aspects, users can ensure efficient operation and maintain safety throughout the use of their portable energy device.
Common Issues with Generators
Understanding frequent problems that arise with portable power sources can help users maintain optimal performance and extend their lifespan. Identifying symptoms early on can prevent minor inconveniences from escalating into major faults. Here are some typical challenges that might be encountered.
| Issue | Symptoms | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Contamination | Poor performance, stalling, difficulty starting | Replace fuel, clean the tank, check lines |
| Oil Leaks | Visible puddles, low oil levels | Inspect seals, tighten bolts, replace gaskets |
| Battery Issues | Inability to start, dimming lights | Check connections, charge or replace battery |
| Overheating | High temperatures, automatic shutdown | Ensure proper ventilation, check coolant levels |
| Electrical Short Circuits | Tripped breakers, unusual noises | Inspect wiring, replace damaged components |
Essential Tools for Generator Repairs
When it comes to maintaining and fixing portable power devices, having the right instruments at your disposal can make all the difference. These tools not only enhance efficiency but also ensure safety during the maintenance process. A well-equipped toolkit empowers you to tackle a variety of tasks, from routine upkeep to more complex troubleshooting.
Basic Toolkit Essentials
To start, a few fundamental tools are indispensable for anyone looking to perform maintenance. These items are versatile and can handle a range of minor issues:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Screwdriver Set | For loosening and tightening screws in various components. |
| Wrench Set | Essential for gripping and turning nuts and bolts. |
| Pliers | Useful for gripping, twisting, and cutting wires or small parts. |
| Multimeter | For measuring voltage, current, and resistance to diagnose electrical issues. |
| Flashlight | Helps illuminate dark areas during inspections and repairs. |
Advanced Tools for Comprehensive Maintenance
For more in-depth tasks, certain advanced instruments can enhance your capabilities. Investing in these tools can lead to better troubleshooting and more thorough maintenance:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Torque Wrench | Ensures bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications. |
| Compression Tester | Measures the pressure in the combustion chamber to assess engine performance. |
| Oil Filter Wrench | Facilitates the easy removal of oil filters during maintenance. |
| Fuel Pressure Gauge | Monitors the fuel system’s pressure to identify potential issues. |
| Safety Goggles | Protects your eyes during maintenance to ensure safety. |
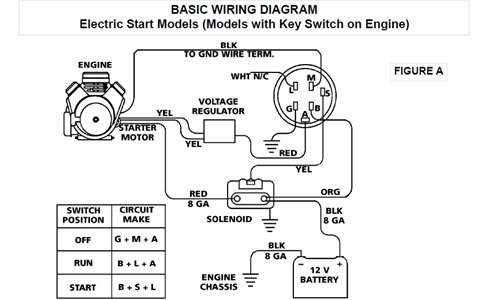
Step-by-Step Wiring Diagram Guide
This section aims to provide a comprehensive approach to understanding the connections and circuitry involved in the operation of your device. By following a structured method, users can gain clarity on how various components interact, ensuring efficient troubleshooting and maintenance.
Step 1: Begin by identifying all essential parts of the system. Familiarize yourself with each component’s role and functionality. This foundational knowledge will help you visualize the overall layout.
Step 2: Next, gather all necessary tools and materials. Having everything at hand will streamline the process and minimize disruptions.
Step 3: Proceed to outline the connections. Take note of where each element connects, focusing on ensuring that power flows correctly throughout the setup.
Step 4: As you move through the connections, pay close attention to any color coding or labeling present on wires. This detail can significantly assist in avoiding mistakes.
Step 5: After establishing all connections, double-check your work. Verification is key to preventing issues during operation. Ensure that everything is secure and correctly positioned.
Step 6: Finally, conduct a test run. Observe the system closely to confirm that it functions as intended. If any anomalies arise, revisit the earlier steps to troubleshoot potential problems.
By following these outlined steps, you can achieve a clear understanding of the electrical connections, ultimately leading to a more efficient and reliable system operation.
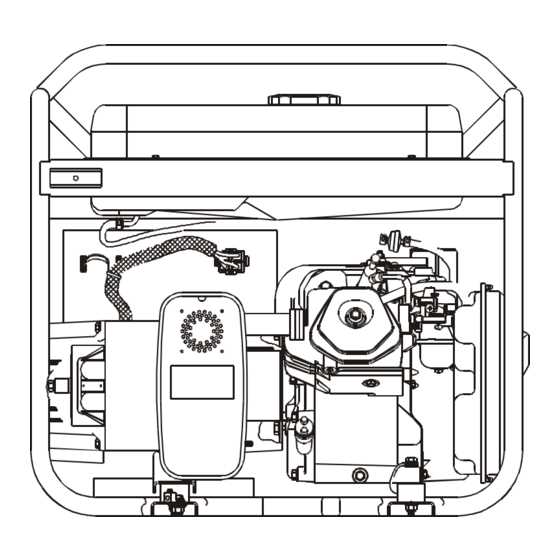
Identifying Generator Components
Understanding the various parts of a power-producing machine is essential for effective troubleshooting and maintenance. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring the unit operates efficiently and safely. This section will guide you through the key components, enabling you to recognize their functions and importance.
Here are the primary components you should be familiar with:
- Engine: The heart of the system, responsible for converting fuel into mechanical energy.
- Alternator: Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, providing power for various applications.
- Fuel System: Comprises the tank, lines, and carburetor, essential for delivering fuel to the engine.
- Cooling System: Maintains optimal operating temperatures, often including a fan and cooling fins.
- Control Panel: Houses the switches and outlets used to operate and monitor the machine.
- Frame: Provides structural support and protection for internal components.
Familiarizing yourself with these parts will enhance your ability to diagnose issues and perform necessary upkeep. Each component’s functionality contributes to the overall performance and reliability of the unit.
Troubleshooting Electrical Problems
Identifying issues within an electrical system can be challenging, yet it is essential for maintaining optimal performance. Common symptoms, such as inconsistent power output or failure to start, often indicate underlying faults that need addressing. By systematically analyzing the components and connections, users can isolate and rectify problems effectively.
Step 1: Inspect Connections
Begin by examining all connections for signs of wear or damage. Loose or corroded terminals can impede electrical flow, leading to performance issues. Ensure that all connections are secure and free from oxidation.
Step 2: Check Components
Evaluate key components such as fuses, switches, and circuit breakers. A blown fuse or a tripped breaker can halt operation and may require replacement or resetting. Pay attention to any unusual smells or visual signs of failure.
Step 3: Test Voltage
Utilize a multimeter to measure voltage at various points within the system. This will help identify areas where power may not be reaching the intended components. Ensure that readings align with specified parameters for proper functionality.
Step 4: Assess Load Conditions
Examine the load on the system to ensure it is not exceeding capacity. Overloading can lead to overheating and damage. Distributing the load more evenly can often resolve performance issues.
Step 5: Consult Documentation
Refer to technical specifications and troubleshooting guides for additional insights into common problems and solutions. Understanding the intricacies of the system will aid in more effective diagnostics.
By following these steps, users can systematically address and resolve electrical complications, ensuring reliable operation and longevity of the equipment.
Safety Precautions During Repairs
Ensuring safety while conducting maintenance on any equipment is paramount. Adopting proper practices not only protects the individual performing the task but also safeguards the machinery from potential damage. Familiarity with safety measures can greatly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.
Before beginning any work, it is crucial to disconnect the power source. This step prevents unintended activation, which could lead to electrical shock or other hazards. Additionally, wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles, minimizes the risk of injury from sharp edges or flying debris.
Maintaining a clean and organized workspace is another vital aspect of safety. Clutter can lead to trips and falls, while a tidy area ensures easy access to tools and components. It is also important to keep flammable materials away from the workspace, as these can pose a significant risk when working with machinery.
Lastly, being aware of one’s surroundings and working with a partner can provide extra safety. Having someone else present ensures that help is available in case of an emergency. By following these precautions, individuals can enhance their safety and effectiveness during maintenance tasks.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the durability and efficient performance of your power equipment requires regular care and attention. Adopting a proactive maintenance routine can significantly extend its lifespan, preventing unexpected failures and costly repairs.
Regular Inspections: Conduct frequent checks to identify any signs of wear or damage. This includes examining components for loose connections, rust, or corrosion that could hinder functionality.
Cleanliness is Key: Keep the machine clean by removing dirt, dust, and debris. A clean exterior not only looks good but also prevents overheating and allows for better air circulation.
Fluid Levels: Monitor oil and fuel levels diligently. Replace oil according to the manufacturer’s recommendations and use high-quality fuel to ensure optimal operation.
Air Filter Maintenance: Replace or clean the air filter periodically to maintain proper airflow. A clogged filter can lead to inefficiency and increased wear on internal components.
Battery Care: If your equipment is battery-operated, check the battery’s condition regularly. Clean the terminals and ensure a secure connection to prevent starting issues.
Storage Considerations: When not in use, store the unit in a dry, protected location. Cover it to shield it from dust and moisture, which can cause significant damage over time.
Professional Servicing: Schedule routine professional check-ups to address any complex issues. Experts can spot potential problems that may not be evident during casual inspections.
By implementing these practices, you can ensure your power equipment remains reliable and efficient for years to come.
Replacing Faulty Wiring in Generators
Over time, electrical systems can develop faults that lead to malfunctions or complete failures. Identifying and replacing damaged components is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring safety. This process involves careful assessment and appropriate action to restore functionality.
Identifying Damaged Components
The first step in addressing issues within the electrical system is to locate the faulty elements. Look for signs such as frayed insulation, burnt connections, or corrosion. These indicators can help pinpoint areas that require attention. Regular inspections can prevent further damage and extend the lifespan of the entire unit.
Replacing Defective Parts
Once the problematic areas are identified, the next step is to remove and replace the damaged sections. Ensure that you use high-quality replacements that match the specifications of the original components. When making replacements, it is essential to follow safety protocols, including disconnecting power sources and using appropriate tools. After completing the replacement, conduct thorough testing to confirm that everything is functioning as intended.
Regular maintenance and timely interventions can significantly enhance the reliability of your equipment, ensuring that it operates smoothly and efficiently.
When to Seek Professional Help
Determining the right moment to call in an expert can be crucial for ensuring the longevity and functionality of your equipment. While some issues may seem manageable with basic knowledge, others can pose risks that require specialized skills. Recognizing these instances is essential for avoiding potential hazards and further damage.
If you encounter persistent problems despite your attempts at troubleshooting, it may indicate a deeper underlying issue. Unusual noises or irregular operation can signify complications that demand professional assessment. Attempting to resolve such matters without adequate experience can lead to safety risks or exacerbate existing faults.
Additionally, if the task involves intricate components or electrical systems, it is wise to consult a qualified technician. Professionals possess the necessary training and tools to diagnose issues accurately and implement effective solutions. In cases of uncertainty, prioritizing safety by seeking assistance is always a prudent choice.
Finally, if you feel overwhelmed or lack confidence in your ability to address a problem, reaching out for help is the best course of action. Ensuring your equipment operates safely and efficiently is paramount, and professionals are equipped to provide the expertise needed in challenging situations.