Understanding the intricacies of engine upkeep is essential for anyone working in the automotive or heavy machinery sectors. This resource provides an in-depth look at essential practices, offering insights into optimal performance and longevity. By familiarizing yourself with the nuances of engine servicing, you can ensure reliability and efficiency in your operations.
With the right techniques and knowledge, maintaining high-performance engines becomes a manageable task. The information presented here covers critical aspects such as troubleshooting, routine checks, and necessary adjustments. By implementing these strategies, you can address common challenges and enhance the functionality of your machinery.
Moreover, learning about the inner workings of these engines empowers you to make informed decisions regarding maintenance schedules and necessary interventions. This understanding can lead to improved safety, reduced downtime, and ultimately, greater productivity in your work environment.
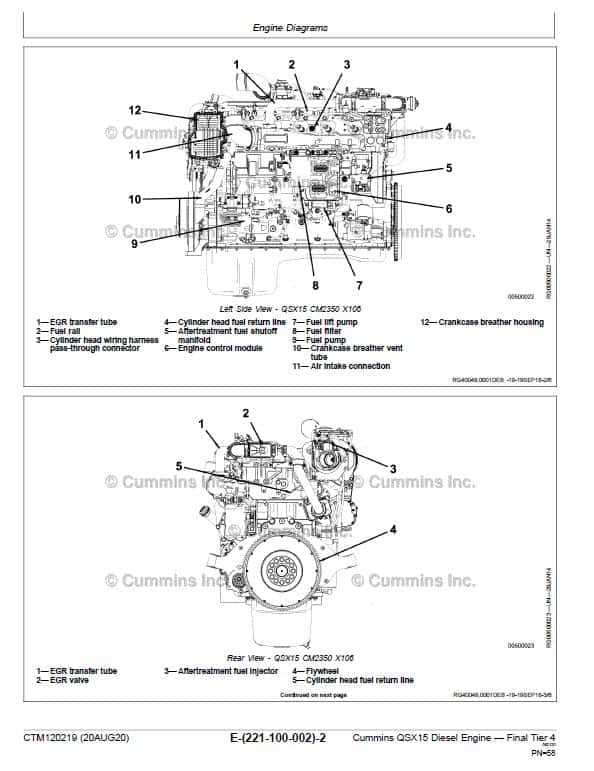
Overview of Cummins ISX Engine
This section provides a comprehensive look at a specific line of heavy-duty power units designed for superior performance in various applications. These robust machines are engineered to deliver outstanding reliability and efficiency, making them a popular choice among professionals in the industry.
Key Features
- Advanced fuel injection technology for optimal combustion
- Durable construction for longevity under extreme conditions
- Variety of power outputs to suit different vehicle needs
- Enhanced electronic controls for improved performance monitoring
Applications
The versatility of these power units allows them to be utilized across a range of settings, including:
- Long-haul trucking
- Construction machinery
- Agricultural equipment
- Marine vessels
Common Issues and Symptoms
When operating a heavy-duty engine, various challenges can arise, manifesting through specific indicators. Recognizing these signs early can prevent more severe problems and ensure optimal performance. Below are some prevalent concerns that users may encounter, along with their typical symptoms.
| Issue | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Overheating | Engine temperature rising above normal, coolant leaks, or steam from the radiator. |
| Poor Fuel Efficiency | Increased fuel consumption, black smoke from the exhaust, or difficulty maintaining speed. |
| Starting Problems | Difficulty in starting, slow cranking, or unusual noises during ignition attempts. |
| Excessive Vibration | Unusual shaking or rattling during operation, which may indicate alignment or balance issues. |
| Check Engine Light | Illumination of the warning light on the dashboard, often requiring diagnostics to identify the issue. |
Maintenance Best Practices

Ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your engine requires adherence to a series of best practices. Regular upkeep not only enhances efficiency but also prevents potential issues from escalating into significant problems. Emphasizing preventive measures can save time and resources in the long run.
Routine Inspections: Conducting frequent assessments of essential components can identify wear and tear before it leads to failure. Check fluid levels, filters, and hoses, and replace any worn parts promptly.
Scheduled Servicing: Adhering to a predetermined service schedule ensures that your engine remains in peak condition. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for oil changes, filter replacements, and other essential tasks.
Cleanliness: Keeping the engine and surrounding areas clean helps prevent dirt and debris from entering critical systems. Regularly cleaning components not only improves functionality but also allows for easier inspections.
Documentation: Maintaining detailed records of all maintenance activities aids in tracking performance and planning future upkeep. It can also provide valuable insights for troubleshooting any emerging issues.
Tools Required for Repair
When undertaking maintenance tasks on heavy-duty engines, having the right equipment is essential for ensuring efficiency and accuracy. This section outlines the necessary instruments that facilitate effective service operations, enhancing the overall performance and longevity of the machinery.
Basic Hand Tools: A comprehensive set of hand tools, including wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers, forms the foundation for any repair activity. These tools are crucial for loosening and tightening various components, making them indispensable for both minor and major tasks.
Diagnostic Equipment: Utilizing diagnostic tools such as scanners and pressure gauges allows technicians to assess the condition of the engine. These devices help identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring timely interventions and optimal functionality.
Specialized Instruments: Specific tasks may require specialized instruments, such as torque wrenches and engine hoists. These tools provide the precision needed for intricate adjustments and component replacements, making them vital for successful service operations.
Safety Gear: Personal protective equipment, including gloves, goggles, and hearing protection, is essential to ensure the safety of technicians while working. Adhering to safety standards not only protects individuals but also promotes a safer work environment.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
This section provides a comprehensive approach to identifying and resolving issues commonly encountered with large diesel engines. By following a systematic procedure, you can efficiently diagnose problems and implement effective solutions, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the equipment.
Identifying Common Symptoms

Begin by observing the symptoms presented by the engine. Common indicators may include unusual noises, decreased power output, or excessive emissions. Take note of any warning lights or error codes displayed on the dashboard, as these can provide valuable clues regarding the underlying issues.
Systematic Approach to Diagnosis
Utilize a logical method to isolate the problem. Start with visual inspections, checking for leaks, loose connections, or damaged components. Follow up with diagnostic tools to assess electronic systems and perform tests on various engine parameters. Document each step taken to track your findings and refine your approach as needed.
Understanding Engine Components
The intricate assembly of an internal combustion engine plays a pivotal role in its overall performance and efficiency. Each part serves a specific function, contributing to the smooth operation and longevity of the system. Grasping the essential elements and their interactions is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Key Parts of an Engine

Among the many components, a few stand out as fundamental to engine functionality. Understanding these key elements provides insight into how the engine operates as a cohesive unit.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cylinder | Houses the piston and is where the combustion process occurs. |
| Piston | Moves up and down within the cylinder, converting combustion energy into mechanical work. |
| Crankshaft | Transforms the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion. |
| Camshaft | Controls the opening and closing of the engine’s valves. |
| Fuel Injector | Delivers fuel into the combustion chamber for ignition. |
Interactions Between Components
The seamless operation of these parts relies on their precise coordination. For instance, the timing between the camshaft and the crankshaft is vital for ensuring that the valves open and close in synchronization with the pistons’ movement. Understanding these interactions can significantly enhance troubleshooting efforts when issues arise.
Repair Techniques and Methods
When dealing with complex engine systems, understanding the various techniques and approaches for maintenance and restoration is crucial. These methods ensure optimal performance and longevity, allowing for effective troubleshooting and efficient solutions.
One widely adopted approach involves the systematic inspection of components. This includes examining parts for wear and tear, which is essential for identifying potential failures before they escalate. Regular assessments can lead to timely interventions that prevent significant issues.
Another key strategy is the application of specialized tools and technologies. Utilizing advanced diagnostic equipment helps in pinpointing specific problems within the engine. This method not only enhances accuracy but also streamlines the overall maintenance process.
Moreover, following established protocols for disassembly and reassembly is vital. Maintaining the integrity of components during these processes minimizes the risk of damage and ensures that everything functions as intended upon reinstallation. Proper alignment and torque specifications are critical in this regard.
Finally, continuous education on the latest techniques and advancements in engine technology plays an essential role. Staying informed about new methodologies enhances the ability to perform effective maintenance and fosters a proactive approach to potential challenges.
Aftermarket Parts vs. OEM

The choice between alternative components and original manufacturer offerings is a crucial consideration for many vehicle owners. Each option presents distinct advantages and disadvantages that can influence performance, longevity, and overall satisfaction. Understanding these differences can aid in making an informed decision when it comes to maintenance and upgrades.
Alternative components often appeal to those seeking cost-effective solutions. They can provide similar functionality at a reduced price, making them attractive for budget-conscious consumers. However, there may be variability in quality and compatibility that should be carefully evaluated.
On the other hand, original manufacturer parts are designed specifically for the vehicle, ensuring a perfect fit and compatibility. While they may come at a premium, they often guarantee performance standards that can enhance reliability and durability.
| Aspect | Aftermarket Parts | OEM Parts |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
| Quality | Varies widely | Consistent |
| Compatibility | May require additional checks | Guaranteed fit |
| Warranty | Varies | Often extensive |
Service Intervals and Schedules
Regular maintenance is essential for optimal performance and longevity of heavy-duty engines. Establishing a well-defined schedule for servicing ensures that all components operate efficiently and reduces the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns.
Maintenance tasks should be performed at specific intervals, which can vary based on operating conditions, engine usage, and manufacturer recommendations. Adhering to these intervals helps to identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems, ensuring a smooth operation.
Common schedules may include routine checks on oil levels, air filters, fuel systems, and coolant conditions. Frequent inspections play a vital role in maintaining engine health. Operators should keep a log of all services performed to track compliance with recommended schedules and facilitate future maintenance planning.
Diagnostic Codes Explained
Understanding diagnostic codes is essential for identifying issues within advanced engine systems. These codes serve as indicators, guiding technicians through the troubleshooting process. Each code corresponds to specific faults, enabling efficient diagnosis and resolution of problems.
Importance of Diagnostic Codes
These codes play a crucial role in maintenance and performance optimization. By interpreting the codes, technicians can pinpoint the root cause of malfunctions, leading to timely repairs and reduced downtime. Here are some key benefits:
- Facilitates quick identification of issues
- Enhances overall system reliability
- Reduces unnecessary part replacements
Common Diagnostic Codes
Familiarity with frequently encountered codes can streamline the troubleshooting process. Below are examples of common codes and their meanings:
- SPN 123: Engine temperature too high
- FMI 2: Voltage out of range
- SPN 456: Fuel pressure low
Understanding these codes equips operators with the knowledge to address issues proactively, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the engine system.
Upgrades and Performance Enhancements
Improving engine efficiency and overall power can significantly enhance vehicle performance. Various modifications can be implemented to achieve better responsiveness, fuel economy, and torque output. Here are some popular options to consider for elevating performance.
- Turbocharger Upgrades: Installing a larger or more efficient turbocharger can increase airflow, resulting in greater power and improved throttle response.
- High-Performance Fuel Injectors: Upgrading to injectors designed for higher flow rates can optimize combustion and enhance engine output.
- Enhanced Cooling Systems: Upgrading the cooling system with a larger radiator or more efficient intercooler can help maintain optimal operating temperatures during demanding conditions.
- ECU Remapping: Reprogramming the engine control unit can optimize fuel mapping and ignition timing, leading to improved performance metrics.
- Exhaust System Improvements: Installing a high-flow exhaust system can reduce back pressure and enhance the overall exhaust flow, allowing the engine to breathe more easily.
Implementing these enhancements can lead to significant gains in performance and efficiency. When selecting upgrades, it’s essential to consider the compatibility with existing components and the specific goals for performance improvement.
Safety Precautions During Repairs
Ensuring a secure environment while conducting maintenance tasks is crucial for the well-being of both the technician and the equipment. Adhering to specific guidelines can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and enhance overall efficiency. This section emphasizes the importance of preparation and awareness before undertaking any service activities.
First and foremost, wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential. Items such as gloves, safety glasses, and steel-toed boots provide a necessary barrier against potential hazards. Additionally, ensuring that the workspace is well-ventilated and free from clutter contributes to a safer atmosphere.
Moreover, it’s vital to familiarize oneself with the machinery involved. Understanding the various components and their functions allows for more effective handling and minimizes the likelihood of errors. Prior to beginning any task, conducting a thorough inspection of tools and equipment helps to identify any defects that could pose risks during operation.
Finally, maintaining clear communication with team members is key. Establishing signals or protocols for alerting others of potential dangers ensures that everyone remains informed and can react appropriately in case of emergencies. A proactive approach to safety not only protects individuals but also promotes a culture of responsibility within the workspace.