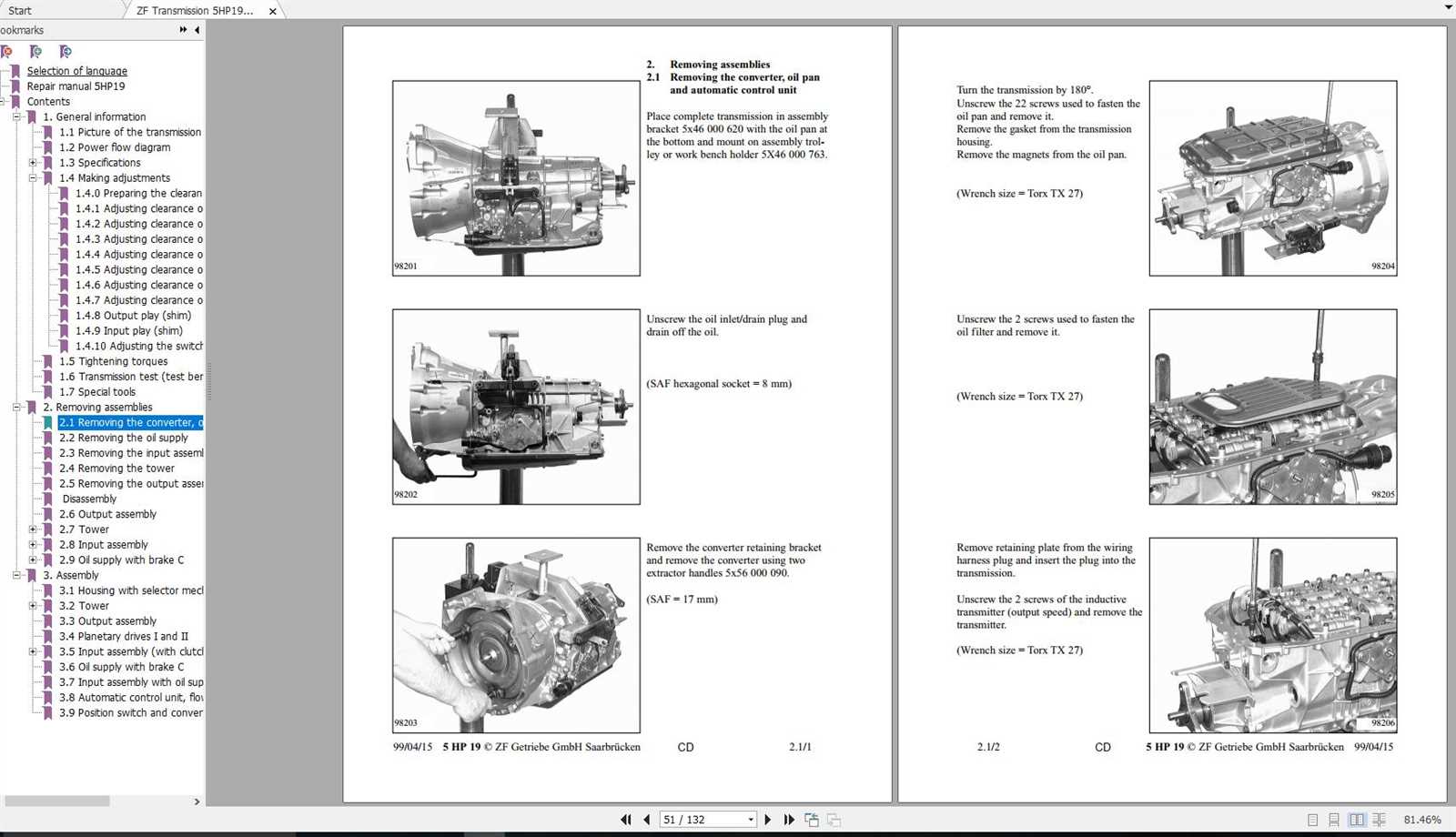
The inner workings of an automotive system are complex and demand a solid understanding of multiple components. For those aiming to delve into the intricacies of maintaining certain high-performance systems, a clear approach to foundational knowledge is essential. This section provides insights into how various parts interact within the broader system, promoting efficient functionality and prolonging the life of essential mechanisms.
Examining core elements and understanding their role in overall performance helps enthusiasts and specialists alike to approach maintenance with confidence. Key topics include recognizing signs of wear, identifying pivotal components, and gaining familiarity with effective methods to ensure optimal performance. Detailed knowledge on these aspects enables users to tackle adjustments and replacements accurately, minimizing risks while enhancing reliability.
Each part plays a role in contributing to the fluid movement and control within the system, and understanding these dynamics is crucial. T
Overview of ZF 5HP19 Gearbox
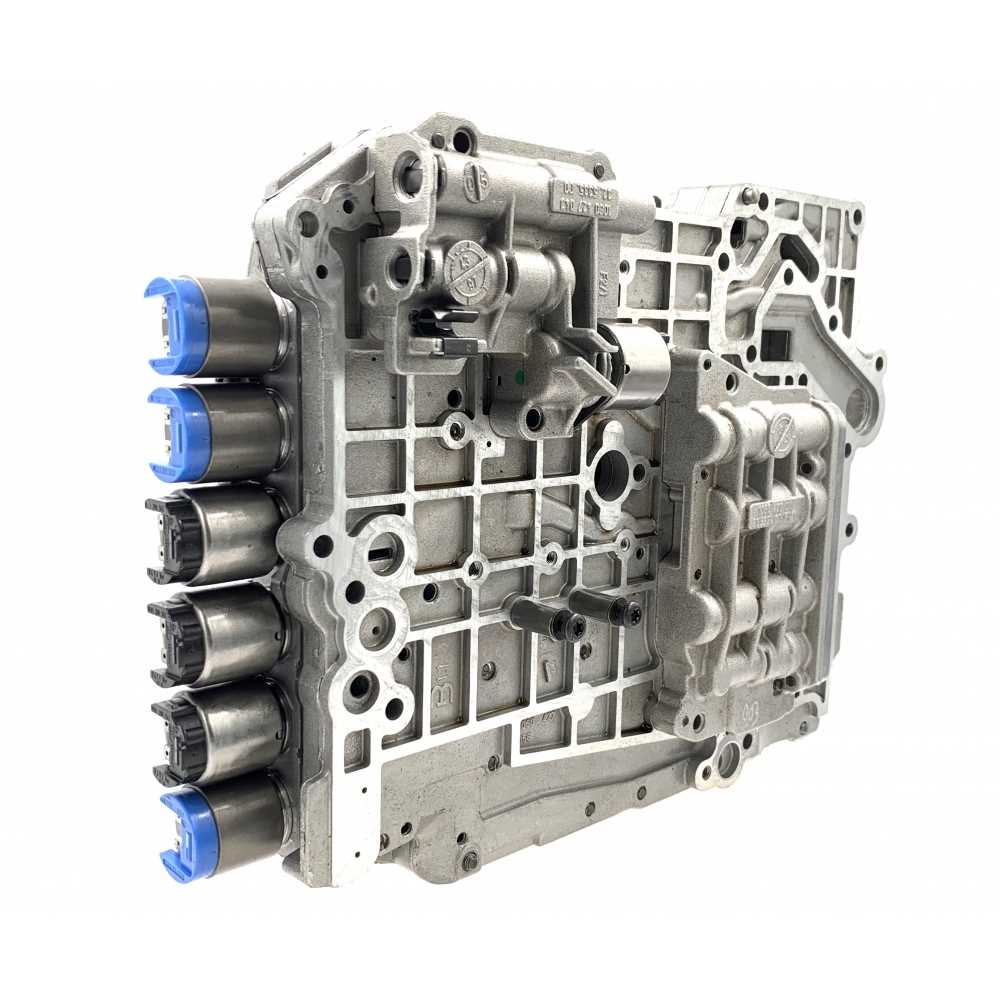
The ZF unit, known for its durability and precision engineering, is integral to enhancing vehicle performance and efficiency. This gearbox is highly regarded for smooth shifts, balanced torque distribution, and overall reliability, making it a popular choice in a range of vehicles.
Design and Functionality: The engineering behind this model focuses on optimizing energy transfer while maintaining a high degree of control and responsiveness. Its design incorporates sophisticated components and mechanisms that work in harmony to provide seamless gear transitions and manage power flow effectively.
Technical Specifications: The internal structure of this system features advanced hydraulic circuits and well-calibrated components, engineered to adapt to various driving conditions. Its setup allows for precise adjustments, resulting in a balanced performance across different speed ranges, maximizing both power and fuel efficiency.
Common Usage and Applications: This type of gearbox is frequently found in mid- to high
Understanding Common Transmission Issues
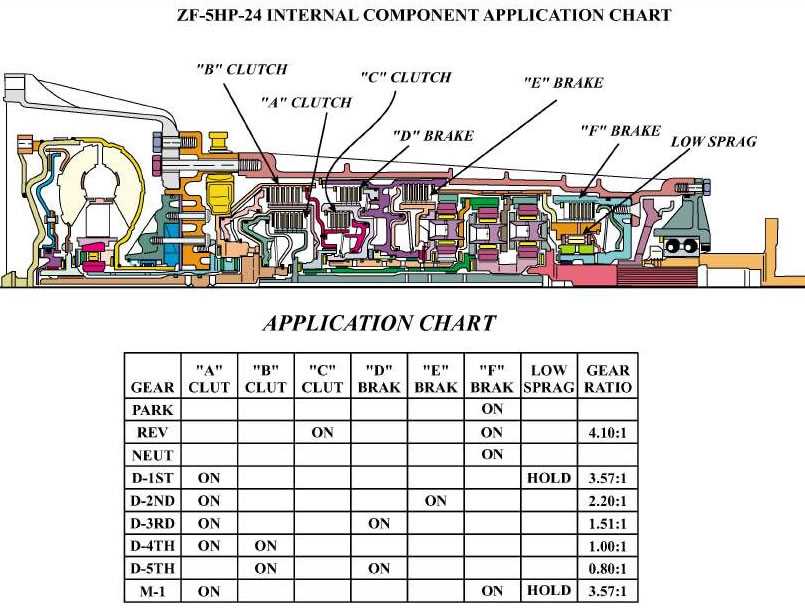
Understanding the range of operational challenges within complex automotive systems can help in identifying symptoms and determining effective solutions. Many issues arise from wear over time, fluid management, and component interactions. Recognizing early signs of inefficiency or irregularities can prevent more extensive concerns, making basic knowledge of common issues valuable for anyone maintaining or servicing these mechanisms.
Frequent Mechanical Problems
- Unusual Noises: Whining, clunking, or humming can indicate wear in moving parts or fluid inconsistencies.
- Unexpected Jerking: Sudden movements may result from faulty connections or insufficient lubrication within moving parts.
- Delayed Shifts: Hesitation or resistance during gear changes often suggests potential fluid blockages or worn internal elements.
Fluid Concerns and Maintenance
Tools Required for Effective Repairs
For any successful mechanical project, having the right selection of instruments is essential. Precision and efficiency depend heavily on utilizing well-suited equipment designed for each specific task, ensuring smoother procedures and reliable results. Below, we outline some critical devices and items that can simplify and enhance the process.
Essential Hand Tools

Basic hand tools are at the core of every mechanical task. Wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers form the foundation, allowing for secure handling and adjustment of various components. Torque wrenches are particularly important for precise adjustments, providing the correct pressure levels without risking overtightening. Meanwhile, a sturdy set of sockets in varying sizes will accommodate most needs, making each step more manageable.
Advanced Diagnostic Equipment

For complex mechanical systems, basic tools alone are often not enough. Diagnostic scanners and pressure gauges assist in identifying underlying issues that may not be immediately visible. These tools
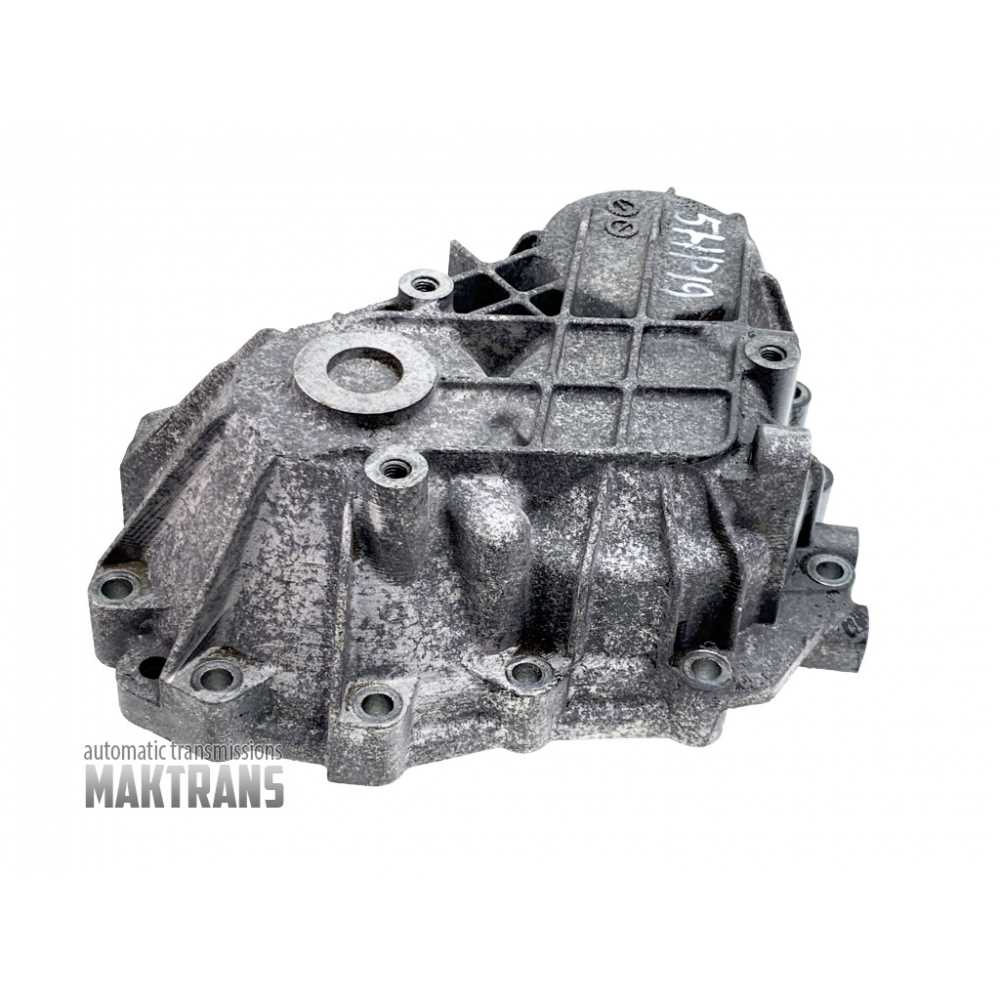
Step-by-Step Gearbox Disassembly
This section provides a detailed guide to disassembling the gearbox, covering essential steps for safely and effectively taking apart its components. Proper disassembly is crucial to ensure each part is handled carefully and remains organized for subsequent inspection or reassembly. Following this sequence helps minimize the risk of damaging sensitive elements within the mechanism.
Preparation and Initial Checks

Before starting, gather all necessary tools and establish a clean, organized workspace. Begin by checking for any external issues, such as visible wear or leakage points, as these can offer insights into potential internal wear. Make a note of connections and mounting points, as these will need careful attention during reassembly.
Step-by-Step Component Removal

Start with the outer casing and gradually move inward, taking care to disconnect each linkage with precision. Use labeled containers to separate bolts, springs, and other small pieces to maintain order. When removing gears and shafts, avoid
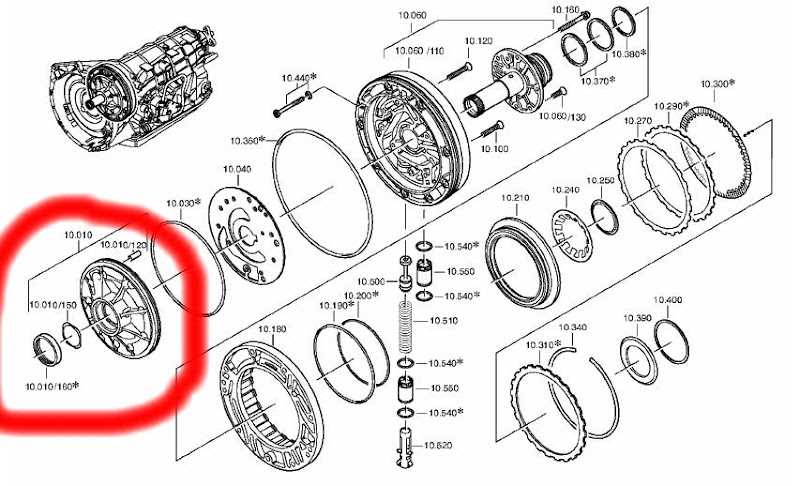
Inspecting and Replacing Key Components
Understanding the function and condition of essential parts is crucial to maintaining the overall effectiveness of this system. Detailed inspections can reveal wear, leaks, or other issues that may impact the efficiency and durability of the unit. Careful examination allows for timely adjustments or replacements, enhancing performance and preventing larger issues.
- Fluid Check: Ensure the fluid is clean and at the correct level. Discoloration or unusual texture may indicate internal issues or contamination.
- Valve Body Inspection: Examine the valve body, which manages pressure and flow. Clean any accumulated debris, and assess if valves or seals require replacement for improved response.
- Seals and Gaskets: Look for signs of leaks around seals and gaskets. Replacing damaged seals can prevent fluid loss and maintain pressure levels within the system.
- Clutch Pack E
Clutch Pack Diagnosis and Adjustment
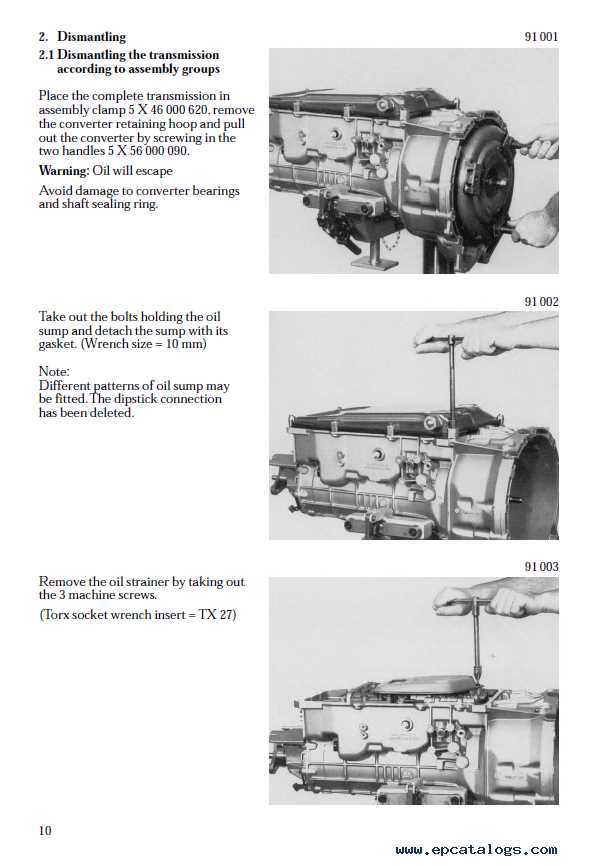
The proper functioning of a hydraulic system is crucial for optimal performance. Understanding how to identify issues with the friction assemblies is essential for maintaining efficiency and prolonging the life of the system. This section outlines the key steps for diagnosing and adjusting these components to ensure smooth operation.
Identification of Issues
Common signs of malfunctioning friction assemblies include slippage, rough shifting, and unusual noises. Observing fluid conditions, such as discoloration or burnt smells, can provide important clues. Additionally, performing a pressure test can help determine whether the assemblies are engaging properly. Regular inspection is vital for early detection and correction of potential problems.
Adjustment Techniques
Once issues are identified, adjustments can be made to restore functionality. Begin by consulting specifications for pressure settings and clearance requirements. Using proper tools, make necessary tweaks to achieve the desired parameters. It’s important to conduct a test drive after adjustments to ensure that the system operates smoothly under various conditions. Consistent monitoring and timely adjustments can significantly enhance performance.
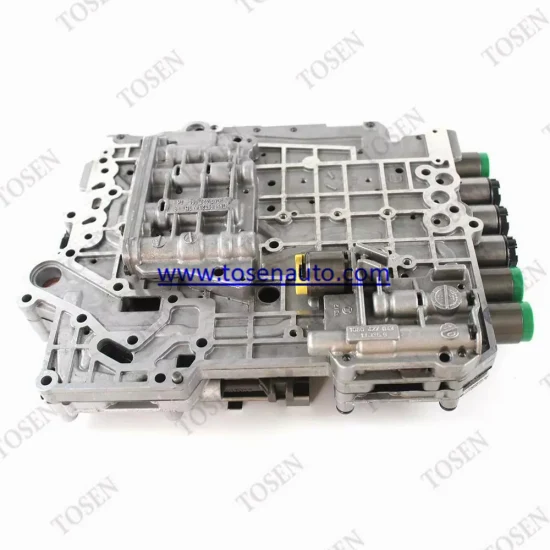
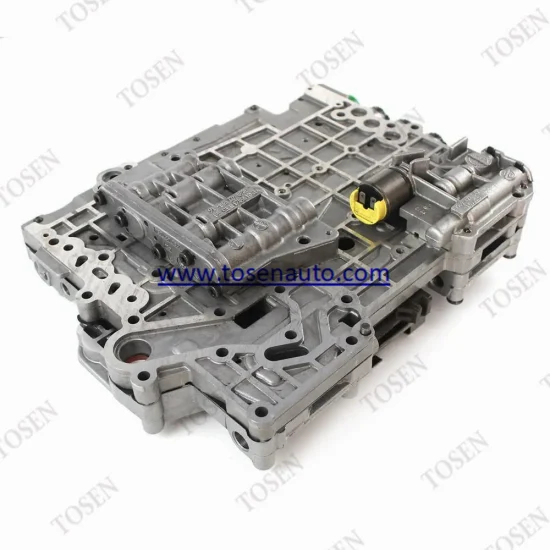
Valve Body Troubleshooting Techniques
The valve body is a critical component in any hydraulic system, responsible for directing fluid flow and controlling gear shifts. Proper diagnosis and resolution of issues related to this assembly are essential for optimal functionality. Understanding common problems and their symptoms can significantly enhance the troubleshooting process, leading to effective solutions.
Identifying Common Symptoms
Start by recognizing the typical indicators of valve body malfunctions. Delayed shifts or harsh engagements can signify fluid flow issues. Additionally, leaking fluids around the assembly may point to seal deterioration. Listening for unusual sounds, such as clunking or grinding, can also provide valuable insights into underlying problems.
Testing and Diagnostic Techniques
To effectively troubleshoot, conduct a series of tests. Begin with a fluid pressure test to assess hydraulic integrity. A low-pressure reading might indicate internal leaks, while erratic pressure can suggest blockages. Utilize a scan tool to read fault codes, providing further direction in identifying electronic issues linked to the valve body’s control mechanisms.
Transmission Fluid: Types and Replacement
Fluid plays a crucial role in the smooth operation of any automotive system, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Understanding the various types available and the process of changing it is essential for maintaining efficiency and preventing potential issues.
Types of Fluid
- Mineral Oil: A basic option derived from refining crude oil, suitable for older models.
- Synthetic Fluid: Engineered for enhanced performance, providing better temperature stability and resistance to breakdown.
- Blended Fluid: A mixture of mineral and synthetic oils, aiming to combine the benefits of both types.
Fluid Replacement Process
- Gather necessary tools and materials, including the appropriate fluid type and a suitable container for draining.
- Locate the fill and drain ports in the system.
- Drain the old fluid completely, ensuring no residue remains.
- Replace any filters or screens if applicable.
- Fill the system with the new fluid to the recommended level, checking for leaks.
- Test the system by running the engine briefly and recheck fluid levels, adding more if necessary.
Preventive Maintenance for Longevity
Ensuring the extended lifespan of your vehicle’s powertrain components requires consistent and proactive care. By implementing a regular maintenance routine, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of unexpected failures and enhance overall performance. This section will delve into key practices that promote durability and reliability over time.
Regular Fluid Checks

One of the most crucial aspects of maintenance involves monitoring fluid levels and quality. Fluids play a vital role in lubrication and cooling, helping to prevent wear and tear. Regularly inspecting and replacing fluids, such as lubricants and hydraulic substances, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations can vastly improve functionality and longevity.
Routine Inspections

Conducting periodic assessments of components is essential for identifying potential issues before they escalate. Look for signs of leaks, unusual noises, or any irregularities during operation. Early detection of anomalies allows for timely interventions, which can save on costly repairs and ensure the smooth operation of your vehicle.
Reassembly Tips for Optimal Performance

Ensuring peak efficiency during the reassembly of complex mechanical systems requires careful attention to detail and adherence to best practices. By following a few key strategies, you can enhance the reliability and longevity of your assembled components.
Start by thoroughly cleaning all parts before reassembly. Any residue or debris can interfere with the smooth operation of the system. Use appropriate solvents and tools to remove old lubricants and contaminants, ensuring each component is pristine.
When putting everything back together, refer to any available diagrams or guidelines to maintain the correct orientation and positioning of each piece. This is crucial for achieving seamless functionality. Take your time and do not rush this process, as precision is vital.
Utilize new seals and gaskets where applicable to prevent leaks and maintain pressure. Worn or damaged components can lead to failures, so investing in fresh parts is a smart move. Additionally, apply lubricant to moving parts during assembly to ensure smooth operation from the outset.
Finally, double-check all fasteners and connections for proper torque specifications. An evenly tightened assembly reduces the risk of mechanical failure and enhances the overall performance of the system. After reassembly, conduct a thorough testing procedure to confirm everything operates as intended before returning it to service.
Testing and Adjusting After Repairs

After completing maintenance or modifications on a vehicle’s gear shifting system, it is essential to conduct a series of evaluations and calibrations to ensure optimal performance. These procedures help confirm that all components are functioning correctly and that the system operates smoothly, providing a seamless driving experience.
Initial Assessment
The first step involves a comprehensive inspection of the modified elements. Check for any signs of leakage, unusual noises, or misalignments. This initial evaluation sets the groundwork for further adjustments and diagnostics.
Operational Testing

Once the inspection is complete, proceed to test the system under various conditions. This includes assessing the response during acceleration, deceleration, and while navigating through different driving scenarios. Adjustments may be necessary based on these observations to achieve precise functioning.
Test Type Description Adjustments Required Leak Check Inspect for any fluid leaks around connections. Tighten fittings or replace seals. Noise Test Listen for any abnormal sounds during operation. Check component alignment and torque settings. Performance Test Evaluate responsiveness during acceleration and shifting. Calibrate shift points or adjust cable tensions.