Understanding the complexities of mechanical transmission systems is crucial for maintaining their optimal performance. These intricate devices play a vital role in various industrial applications, ensuring smooth and efficient power transfer. As with any machinery, wear and tear are inevitable, necessitating a thorough approach to troubleshooting and revitalization.
Within this guide, we will delve into the essential techniques and best practices for enhancing the functionality of these mechanical components. Emphasizing systematic inspection, maintenance protocols, and effective techniques, this resource aims to equip technicians and engineers with the knowledge necessary for proficient restoration.
Whether you are addressing minor issues or undertaking significant refurbishment, a structured approach can yield impressive results. By employing detailed methodologies and understanding key principles, you can extend the lifespan of your equipment and enhance operational efficiency.
Understanding Sew Eurodrive Gearboxes
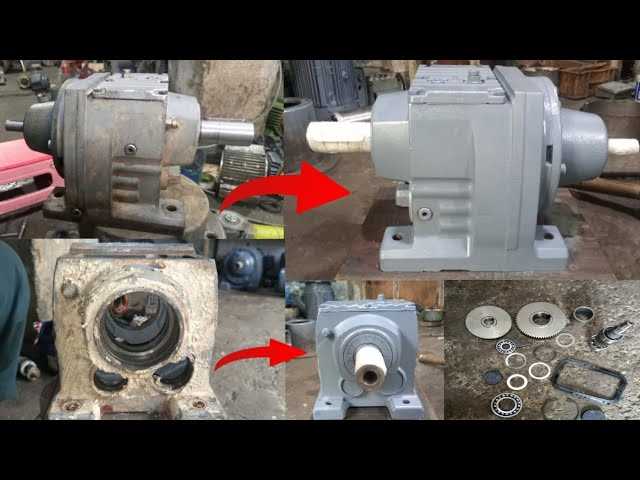

This section provides an overview of mechanical systems designed for power transmission, focusing on their functionality and applications. These units are integral in various industries, enabling efficient movement and control of machinery. Understanding their components and operation can significantly enhance maintenance practices and troubleshooting skills.
Key aspects to consider include:
- Types of Units: Various configurations exist, each tailored for specific applications.
- Components: Essential parts include the casing, input/output shafts, and internal gearing.
- Operating Principles: These systems operate based on the principles of torque conversion and rotational speed modification.
When examining these mechanisms, it’s important to recognize:
- Load Capacity: Understand the maximum loads that can be safely managed.
- Efficiency: Factors affecting performance, such as friction and design, are critical for optimal functioning.
- Maintenance Needs: Regular checks and servicing can prevent costly downtime and prolong lifespan.
Overall, gaining insight into these mechanical devices is crucial for effective operation and maintenance, ensuring reliability in various applications.
Common Issues with Gearboxes
Mechanical systems often encounter a range of challenges that can impede their efficiency and functionality. Understanding these prevalent problems is essential for maintaining optimal performance and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
- Wear and Tear: Continuous operation can lead to degradation of components, affecting overall performance.
- Noise and Vibration: Unusual sounds or excessive vibrations may indicate misalignment or internal damage.
- Overheating: Elevated temperatures can result from insufficient lubrication or excessive load, potentially causing serious damage.
- Leakage: Fluid leaks often signify seal failure, which can compromise lubrication and lead to further issues.
- Inadequate Lubrication: Insufficient lubrication can cause friction and wear, leading to premature failure.
Identifying and addressing these issues promptly is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and preventing costly downtimes.
Tools Needed for Repair
When undertaking the task of restoring mechanical components, having the right equipment is essential for ensuring efficiency and precision. A well-equipped workspace not only facilitates smoother operations but also minimizes the risk of damage to the parts being serviced.
Essential Tools
Start with basic hand tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers. These items are crucial for disassembly and assembly processes. Additionally, consider including a torque wrench to ensure that all fastenings are properly tightened to manufacturer specifications.
Specialized Equipment
For more complex tasks, investing in specialized instruments like alignment tools and dial indicators can greatly enhance accuracy. A suitable cleaning solution and a set of replacement components are also vital for ensuring optimal performance post-service.
Step-by-Step Repair Process
This section outlines a systematic approach to restoring mechanical assemblies, ensuring efficient functionality. Following a clear sequence not only simplifies the task but also enhances the likelihood of successful outcomes.
1. Preparation: Begin by gathering all necessary tools and materials. A clean workspace is essential to avoid losing components and to facilitate a smooth workflow.
2. Disassembly: Carefully detach the unit from its housing. Take note of the arrangement and condition of parts as you proceed. Utilize labeled containers to organize components for easier reassembly.
3. Inspection: Examine each part meticulously for wear or damage. Identify any elements that may need replacement or further attention. Document your findings for reference.
4. Cleaning: Remove any dirt, grease, or debris from the components. Use appropriate solvents and brushes to ensure all surfaces are clear and free of contaminants.
5. Replacement: If any parts were found to be defective during inspection, replace them with compatible alternatives. Ensure that new components are correctly installed to maintain the integrity of the system.
6. Reassembly: Reassemble the unit in the reverse order of disassembly. Pay close attention to torque specifications and alignment to prevent future issues.
7. Testing: Once reassembled, conduct thorough tests to confirm that everything operates as intended. Look for any unusual noises or performance issues that may indicate further adjustments are needed.
8. Finalization: After successful testing, securely reattach the unit to its original location. Ensure that all connections are tight and that safety measures are in place.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of mechanical systems. By adopting a proactive approach, operators can identify potential issues before they escalate into significant problems. This section outlines essential practices to enhance reliability and reduce unexpected downtime.
1. Routine Inspections: Conduct frequent assessments of equipment to spot any signs of wear or damage. Check for unusual noises, vibrations, or leaks that may indicate underlying issues.
2. Lubrication: Ensure that all moving parts are adequately lubricated. Use the recommended types of lubricants and follow the specified intervals for application to minimize friction and prevent overheating.
3. Cleanliness: Maintain a clean working environment. Regularly remove dust, dirt, and debris from around the machinery, as accumulation can lead to overheating and mechanical failure.
4. Alignment Checks: Regularly verify the alignment of shafts and couplings. Misalignment can cause excessive wear and energy loss, so ensure that all components are correctly positioned.
5. Monitor Operating Conditions: Keep an eye on the operating temperature and pressure. Deviations from the recommended ranges can signal potential issues that require immediate attention.
6. Documentation: Maintain accurate records of maintenance activities and inspections. This practice helps in identifying trends over time and assists in planning future maintenance schedules effectively.
7. Training and Awareness: Ensure that all personnel involved are trained in proper operating procedures and maintenance protocols. An informed team can contribute significantly to the reliability and efficiency of the systems.
By implementing these preventive strategies, operators can enhance the performance and durability of their equipment, ultimately leading to improved productivity and reduced operational costs.
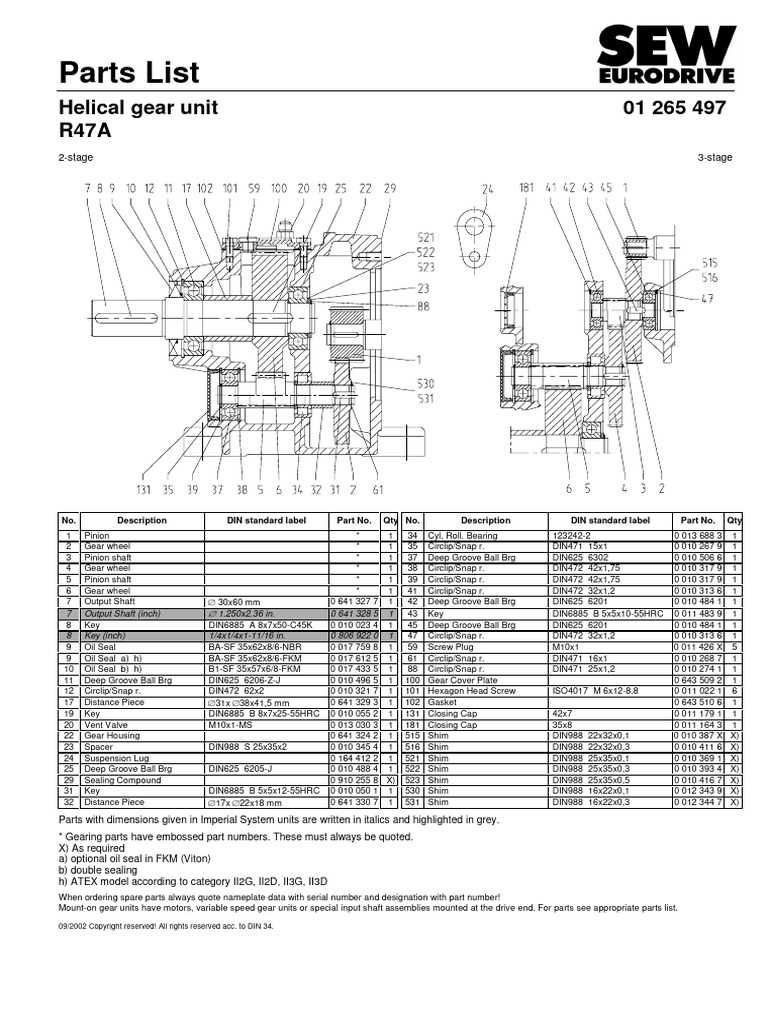
Identifying Gearbox Components
Understanding the various elements of a transmission system is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Each part plays a vital role in ensuring smooth operation, and recognizing them can aid in identifying issues or planning for repairs.
Key Elements to Recognize
Familiarity with the primary sections, such as the casing, input shaft, and output shaft, is essential. These components interact to transmit power efficiently, making their identification paramount for any diagnostic process.
Importance of Component Familiarity
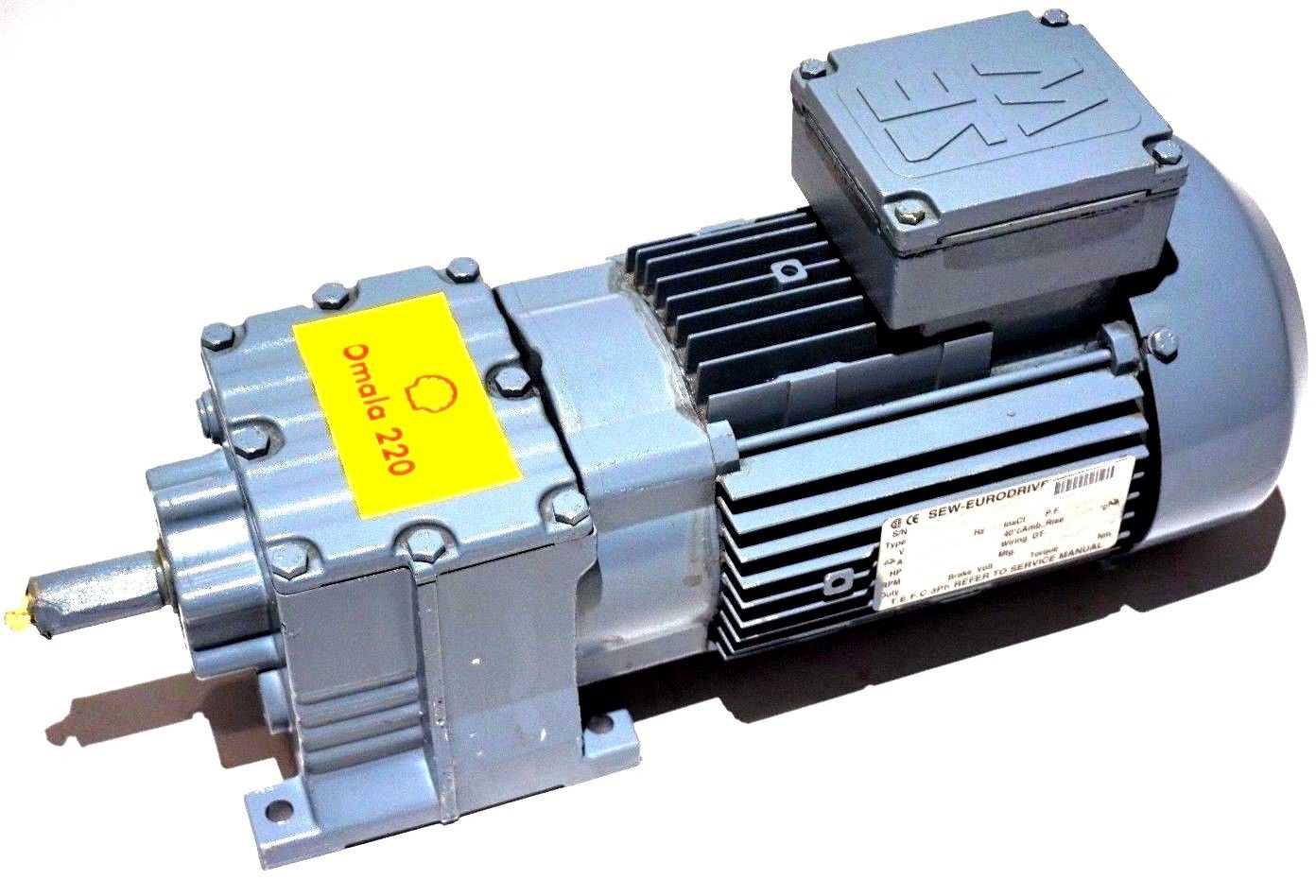
Knowing the specific functions and locations of these parts not only simplifies maintenance tasks but also enhances the understanding of the entire mechanism’s operation. This knowledge ultimately contributes to better performance and longevity of the system.
Disassembling the Gearbox Safely
Taking apart complex machinery requires careful attention to detail and adherence to safety protocols. Proper techniques ensure not only the longevity of components but also the well-being of the technician involved in the process.
Before beginning disassembly, follow these essential steps:
- Ensure the equipment is powered down and disconnected from any electrical sources.
- Gather all necessary tools and safety gear, including gloves and goggles.
- Document the assembly for easier reassembly later.
During disassembly, keep these guidelines in mind:
- Work in a clean, organized space to avoid losing small parts.
- Label components as they are removed to streamline the reassembly process.
- Use proper techniques to avoid damaging parts, especially seals and bearings.
Finally, always follow manufacturer-specific guidelines to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Replacing Worn-Out Parts

Maintaining the efficiency of mechanical systems often involves the timely substitution of components that have deteriorated over time. This process not only ensures optimal performance but also extends the lifespan of the entire assembly. Identifying the right moment to replace these elements is crucial for avoiding larger issues in the future.
Identifying Worn Components

Regular inspections can help detect signs of wear, such as unusual noises, vibrations, or performance declines. Key indicators include:
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Noise | Unusual sounds may indicate internal damage or misalignment. |
| Vibration | Excessive vibration can signal imbalanced or worn parts. |
| Performance Drop | Decreased efficiency often points to failing elements. |
Replacement Process
Once worn components are identified, follow a systematic approach for replacement. This involves safely disassembling the unit, removing the old parts, and installing new ones. Ensure that all replacements meet the specified standards to maintain compatibility and functionality.
Reassembling the Gearbox Correctly
Proper assembly of mechanical components is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Attention to detail during the reassembly process can prevent future complications and enhance overall efficiency. Each part must be positioned accurately and secured firmly to maintain the integrity of the system.
First and foremost, it is essential to clean all components thoroughly before starting the assembly. Any remnants of lubricants or debris can interfere with the proper fit of parts. Utilize appropriate cleaning agents and tools to ensure all surfaces are pristine.
Next, refer to your documentation to understand the correct sequence of assembly. Following the designated order minimizes the risk of misalignment and ensures that all elements fit together seamlessly. Pay special attention to any alignment marks or guides that indicate how parts should be oriented.
When placing components back together, apply the correct torque specifications to fasteners. This prevents over-tightening, which can cause damage, and under-tightening, which can lead to component failure. Use a calibrated torque wrench to achieve the desired settings.
Finally, conduct a thorough inspection after reassembly. Check for any unusual noises or movement when the system is powered on. A careful review will help identify potential issues early, ensuring reliable operation for years to come.
Testing Gearbox Functionality

Assessing the operational effectiveness of mechanical transmission systems is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This process involves a series of systematic evaluations to identify any discrepancies or inefficiencies. By conducting thorough tests, users can preemptively address issues, thereby enhancing reliability and performance.
Initial Inspection

Before performing any functional tests, it is important to conduct a visual examination. This helps in identifying any obvious signs of wear or damage. Key areas to inspect include:
- Seals and gaskets for leaks
- Mounting hardware for looseness
- Exterior for cracks or corrosion
Functional Testing Procedures
Once the initial inspection is complete, follow these procedures to evaluate performance:
- Connect the unit to a suitable power source.
- Gradually increase the load while monitoring vibrations.
- Check the operating temperature to ensure it remains within acceptable limits.
- Listen for unusual noises that may indicate internal issues.
- Evaluate the output torque to verify it meets specifications.
Regular testing and monitoring are essential practices that contribute to the efficiency and lifespan of mechanical transmission systems. By adhering to these guidelines, users can maintain peak operational performance and prevent costly breakdowns.
Safety Precautions During Repairs
Ensuring a secure working environment is crucial when performing maintenance tasks on mechanical devices. Adhering to safety guidelines not only protects the individual carrying out the work but also prevents damage to equipment and promotes overall efficiency. This section highlights essential measures to consider before and during the maintenance process.
Personal Protective Equipment
Wearing appropriate personal protective gear is vital. This includes safety goggles, gloves, and sturdy footwear to shield against potential hazards such as flying debris or heavy components. Additionally, using ear protection can help minimize noise-related risks in high-decibel environments.
Workplace Organization
Keeping the workspace clean and organized contributes significantly to safety. Ensure that all tools and materials are stored properly to prevent trips and falls. Adequate lighting should also be maintained to facilitate visibility, reducing the likelihood of accidents during the procedure.
When to Seek Professional Help
Knowing when to consult an expert can save time, resources, and prevent further complications. Certain issues require specialized knowledge and experience that may go beyond general understanding. Recognizing the signs that indicate professional intervention is necessary can ensure that systems operate efficiently and safely.
Consider seeking assistance in the following situations:
| Situation | Reason |
|---|---|
| Persistent Malfunctions | If problems recur despite troubleshooting, expert analysis may identify underlying causes. |
| Complex Installations | When new systems are being integrated, professional guidance can ensure proper alignment and functionality. |
| Safety Concerns | Any issues posing safety risks should be addressed immediately by trained personnel. |
| Lack of Tools or Skills | Inadequate equipment or expertise to carry out the work effectively warrants professional help. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adhering to industry standards often requires expert knowledge to avoid legal or operational issues. |
Making the decision to involve a specialist can lead to better outcomes and prolong the lifespan of equipment, ensuring that operations remain smooth and effective.