
Ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your power tools is essential for achieving optimal performance in various projects. This section provides essential insights into the upkeep and troubleshooting of commonly used devices, focusing on common issues that users may encounter over time.
From understanding the key components to recognizing signs of wear and malfunction, this guide aims to equip users with the knowledge necessary for effective maintenance. With a systematic approach, even those new to these tools can confidently tackle issues that arise during use.
Whether you’re looking to enhance the functionality of your equipment or simply address minor concerns, this resource offers practical advice to help you navigate the complexities of tool maintenance. By following the outlined steps, users can ensure their devices operate smoothly and reliably, extending their useful life.
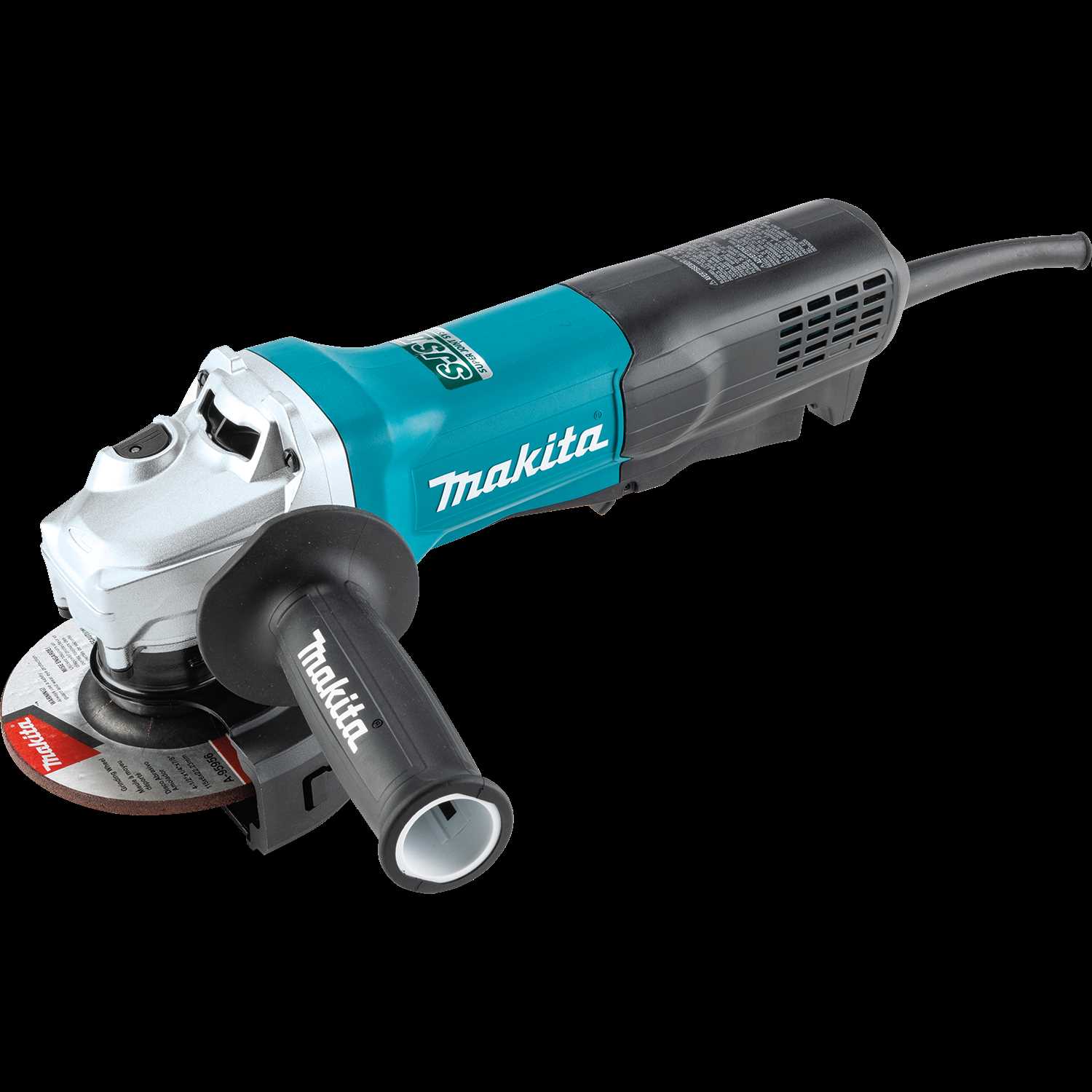
Overview of Makita Angle Grinders
This section provides insight into a popular category of power tools designed for a variety of cutting, grinding, and polishing tasks. These devices are favored for their durability and efficiency, making them essential for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts.
These tools typically feature a powerful motor and a range of attachments, allowing users to perform various applications with ease. Understanding their key components and functionalities is crucial for maximizing performance and ensuring safety during operation.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Motor Power | Varies by model, typically ranges from 500 to 2000 watts for efficient operation. |
| Speed Settings | Often equipped with variable speed controls to adapt to different materials and tasks. |
| Disc Size | Commonly available in sizes ranging from 4 to 9 inches, allowing for flexibility in usage. |
| Weight | Lightweight designs enhance maneuverability, while heavier models provide stability during use. |
| Safety Features | Many models include protective guards, ergonomic handles, and safety switches to reduce risks. |
Common Issues and Symptoms
This section focuses on typical problems that can arise with power tools and their corresponding indicators. Recognizing these signs early can help in addressing issues efficiently and preventing further complications.
- Unusual Noises:
- Grinding or rattling sounds may indicate loose components.
- High-pitched whines could suggest bearing wear.
- Overheating:
- Excessive heat often results from prolonged use or insufficient ventilation.
- Smelling burnt rubber may signal internal damage.
- Loss of Power:
- Sudden drops in performance can be due to worn brushes.
- Inconsistent speed may result from electrical issues.
- Vibration:
- Increased vibrations can indicate imbalance or misalignment.
- Shaking during operation might suggest a damaged component.
- Difficulty Starting:
- Issues with ignition can stem from faulty switches or electrical connections.
- Tools that require excessive effort to start may have internal failures.
Monitoring these signs can lead to timely interventions, ensuring the longevity and functionality of the equipment.
Essential Tools for Repair
When tackling maintenance tasks for power tools, having the right equipment is crucial for effective and efficient work. Proper tools ensure that every component can be accessed and adjusted with ease, promoting a smooth workflow.
Here are some of the fundamental items you should consider having on hand:
- Screwdrivers: A set of various types and sizes, including flathead and Phillips, is essential for loosening or tightening screws.
- Wrenches: Both adjustable and fixed wrenches are important for handling nuts and bolts of different sizes.
- Pliers: Needle-nose and slip-joint pliers are useful for gripping, twisting, and cutting wires.
- Hex keys: These tools are necessary for tightening or loosening hex screws found in many devices.
- Multimeter: This instrument is vital for diagnosing electrical issues and ensuring proper function.
- Replacement parts: Keeping a stock of commonly worn components can save time and facilitate quicker fixes.
Having these essential tools ready will significantly enhance your ability to perform maintenance tasks with confidence and precision.
Step-by-Step Disassembly Guide
This section provides a comprehensive approach to dismantling your tool effectively and safely. Following these steps will help you understand the internal components and facilitate any necessary maintenance or troubleshooting.
Preparation
- Ensure the device is unplugged and has completely cooled down.
- Gather essential tools: screwdrivers, pliers, and a soft cloth.
- Clear a workspace to organize parts as you remove them.
Disassembly Steps
- Start by removing the outer casing screws using a screwdriver.
- Carefully detach the casing to expose the internal components.
- Identify and disconnect the power wires; take note of their positions for reassembly.
- Remove any additional screws holding internal parts in place.
- Gently extract the motor assembly, ensuring not to damage any connections.
- Inspect the gears and bearings, cleaning any debris if necessary.
By following these steps, you can effectively access the inner workings of your tool, making future maintenance and repairs more manageable.
Identifying Replacement Parts
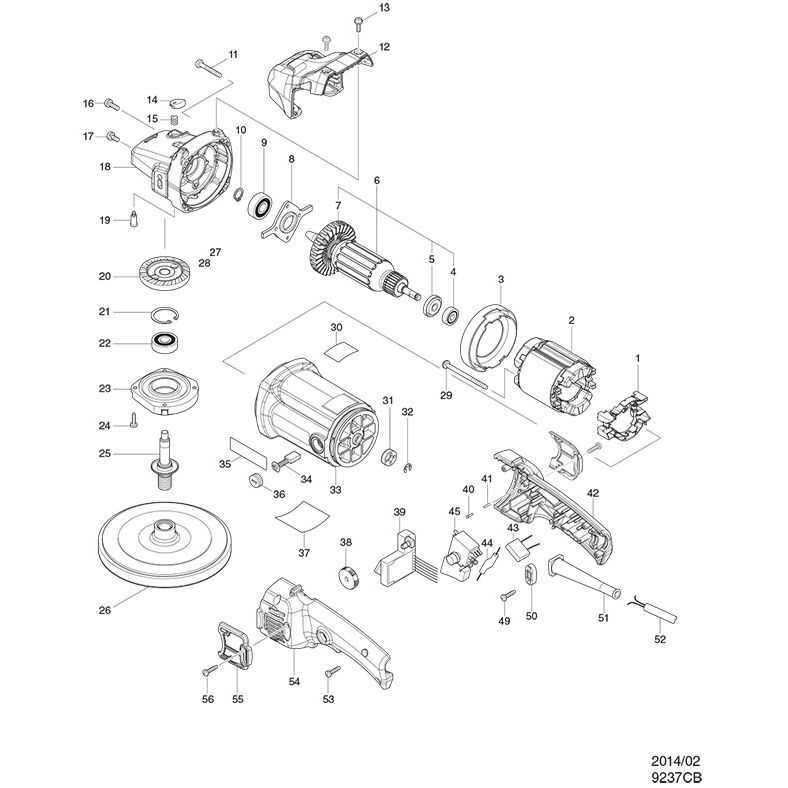
Understanding how to pinpoint the necessary components for maintenance is crucial for efficient operation. This section provides guidance on recognizing essential elements that may require substitution, ensuring optimal functionality of your equipment.
Common Components to Consider
- Motor Assembly
- Switch Mechanism
- Housing and Protective Covers
- Power Cord
- Grinding Discs
Steps for Identification
- Review the original documentation for part specifications.
- Examine the current components for any wear or damage.
- Utilize online resources or local suppliers for part numbers.
- Consult with professionals if uncertain about compatibility.
Electrical Troubleshooting Techniques
This section provides essential methods for diagnosing electrical issues in power tools. Understanding the underlying principles of electrical systems is crucial for effectively identifying and resolving problems. Proper troubleshooting techniques can save time and ensure optimal functionality of the equipment.
Begin with a systematic approach to isolate the problem. Follow these steps:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Check the power source to ensure that the device is receiving electricity. |
| 2 | Inspect the power cord and plug for any visible damage or wear. |
| 3 | Test switches and controls for functionality using a multimeter. |
| 4 | Examine internal components for signs of overheating or shorts. |
| 5 | Replace any faulty parts and reassemble the tool for testing. |
Using these techniques will aid in effectively diagnosing and resolving electrical malfunctions, ensuring the tool operates efficiently.
Motor Maintenance and Care
Proper upkeep of the motor is essential for optimal performance and longevity of power tools. Regular maintenance not only enhances efficiency but also prevents potential malfunctions. By adhering to a few simple practices, users can ensure their devices remain in peak condition.
Regular Cleaning
Cleaning the motor regularly is crucial to eliminate dust and debris that can impede functionality. It is recommended to use a soft brush or a vacuum to remove any buildup from the exterior and air vents. Ensure the device is unplugged before starting this process to avoid accidents.
Lubrication and Inspections

Periodic lubrication of moving parts contributes significantly to smooth operation. Apply the appropriate lubricant as specified in the user guide, paying special attention to bearings and gears. Additionally, perform inspections for any signs of wear or damage. Promptly addressing minor issues can prevent more serious problems down the line.
Reassembling the Angle Grinder
Reassembling a power tool requires careful attention to detail and an understanding of its components. This process ensures that all parts fit together correctly and function as intended, contributing to optimal performance. It is essential to follow a systematic approach to avoid mistakes and ensure longevity.
Steps to Follow
Begin by gathering all the components and tools necessary for assembly. Start with the base and work your way up, securing each piece in its designated place. Pay close attention to any screws or clips, ensuring they are tightened appropriately to maintain structural integrity. Always consult any available diagrams to guide the arrangement of parts.
Final Checks
Once the tool is reassembled, conduct a thorough inspection. Check for any loose fittings or misaligned pieces, which could impact functionality. Test the tool in a safe environment to ensure everything operates smoothly before putting it back into regular use. Proper reassembly is crucial for both safety and efficiency.
Testing After Repair
Once maintenance or modifications have been completed, it is crucial to ensure that the tool functions correctly. This process involves a series of evaluations to verify that all components operate as intended and that safety standards are upheld. Conducting these assessments not only guarantees performance but also extends the lifespan of the equipment.
Initial Functionality Check
Begin by connecting the device to a power source and inspecting for any unusual sounds or vibrations. Activate the tool and observe its behavior during operation. This initial assessment is vital for identifying any immediate issues that may arise from the recent adjustments.
Performance Evaluation
Next, conduct a comprehensive performance evaluation by using the tool under normal working conditions. Monitor its efficiency and effectiveness while performing tasks. Look for consistent power delivery and check for any signs of overheating or instability. Documenting these findings will help in future troubleshooting and maintenance efforts.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Regular upkeep is essential to ensure the longevity and efficient operation of your power tools. By incorporating simple practices into your routine, you can prevent potential issues and enhance performance. Taking proactive measures can save time and costs associated with unexpected failures.
Begin with thorough cleaning after each use to remove dust and debris. Pay special attention to ventilation openings to prevent overheating. Inspect the device for any signs of wear or damage, including cables and connectors. Replacing worn parts promptly can prevent further complications.
Lubrication is key for smooth functionality. Ensure that moving parts are adequately greased according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Additionally, check and replace any worn-out brushes or accessories to maintain optimal performance.
Finally, store your equipment in a dry, protected area to avoid moisture damage. Keeping tools organized and accessible not only promotes safety but also encourages regular use and maintenance. Following these guidelines will contribute to the reliable operation of your equipment for years to come.
Resources for Further Assistance
When faced with challenges related to tool maintenance or malfunction, accessing reliable information is essential. Various resources are available to guide users through troubleshooting processes, ensuring that tools are returned to optimal working conditions efficiently.
Online Communities and Forums
Engaging with online communities can be incredibly beneficial. Websites dedicated to tool enthusiasts often host forums where users share their experiences, solutions, and advice. These platforms allow individuals to ask specific questions and receive guidance from those with similar interests and expertise.
Instructional Videos and Tutorials
Many users find visual aids particularly helpful. Numerous video platforms offer a wealth of tutorials that demonstrate troubleshooting techniques and maintenance procedures. Watching experienced individuals tackle similar issues can provide valuable insights and boost confidence in handling repairs.