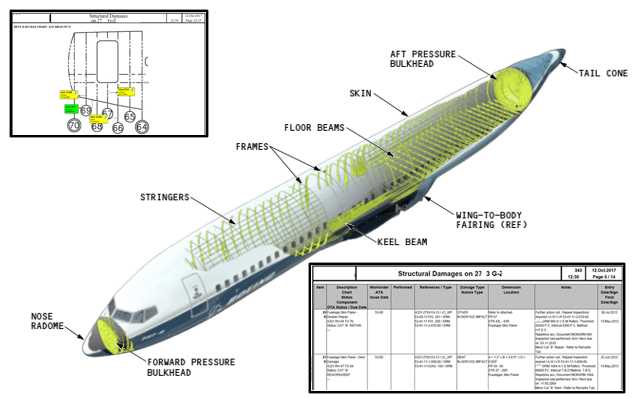
This section delves into the essential aspects of maintaining the integrity and functionality of aircraft structures. Proper attention to these elements ensures the safety and reliability of aviation operations. By adhering to systematic practices, professionals can effectively manage various challenges that arise in the field of aeronautical engineering.
Addressing the needs of aircraft frameworks involves a comprehensive understanding of materials, techniques, and the specific requirements dictated by different aircraft models. The importance of regular evaluations and appropriate interventions cannot be overstated. Such diligence not only prolongs the lifespan of the aircraft but also contributes to overall operational efficiency.
Moreover, the guidance provided within this section is designed to equip aviation specialists with the knowledge necessary to execute their duties proficiently. Emphasizing a methodical approach, this resource serves as a vital tool for ensuring compliance with industry standards and enhancing the overall safety of air travel.
The stability and reliability of any built environment depend on the soundness of its foundational elements. Ensuring that these components remain intact is crucial for safety, functionality, and longevity. A robust framework supports not only the physical load but also withstands various external pressures, contributing to the overall resilience of the structure.
Maintaining this foundational soundness involves regular assessments and timely interventions to address any vulnerabilities. The following table outlines key factors that highlight the significance of maintaining integrity in engineering constructs:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Safety | A sound structure minimizes the risk of failure, protecting occupants and users. |
| Longevity | Regular maintenance prolongs the lifespan of the construction, ensuring it serves its purpose effectively over time. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Preventive measures can save significant costs associated with major repairs or replacements. |
| Compliance | Adhering to established guidelines and standards promotes legal compliance and reduces liability risks. |
| Performance | Well-maintained frameworks enhance overall performance, supporting their intended functions without compromise. |
Key Components of the Manual
This section outlines the essential elements found in comprehensive guidelines for addressing issues related to aviation structures. These components are crucial for ensuring safe and effective interventions, providing users with the necessary information to understand and implement corrective measures efficiently.
Detailed Procedures and Protocols
One of the primary aspects includes step-by-step instructions that guide technicians through various processes. These procedures cover everything from preliminary assessments to final inspections, ensuring a systematic approach to each task. Clear illustrations and diagrams often accompany these steps, enhancing understanding and execution.
Material Specifications and Standards
Another critical element consists of specifications regarding materials and standards to be adhered to during the process. This information ensures that all components meet safety regulations and performance criteria. By following these guidelines, technicians can maintain the integrity and longevity of the structures they work on.
Common Types of Structural Repairs
When it comes to maintaining the integrity of a building or vehicle, various interventions are often necessary to address different forms of damage. These actions not only enhance safety but also ensure longevity and performance. Understanding the common methods of addressing these issues can aid in effective decision-making and resource allocation.
1. Cracking and Fractures: One of the most prevalent issues encountered is the occurrence of cracks in various components. These may arise from environmental stressors or material fatigue. Repair techniques typically involve filling the gaps with suitable compounds to restore strength and prevent further deterioration.
2. Corrosion Mitigation: Over time, materials such as metals can suffer from corrosion, leading to weakened sections. Treatments may include applying protective coatings or replacing severely affected parts to enhance resilience against future deterioration.
3. Load Redistribution: In certain cases, modifications to load-bearing elements may be necessary to redistribute forces more evenly. This can involve adding reinforcements or altering the design to improve stability and safety.
4. Joint Sealing: Sealing joints and connections is crucial to prevent moisture infiltration, which can lead to further damage. Employing appropriate sealants can significantly enhance durability and protect against environmental factors.
5. Surface Treatments: Applying various surface treatments can help improve the performance and appearance of components. These methods may include coatings that enhance resistance to wear, weathering, or chemical exposure.
Addressing these common challenges with the right approaches ensures that the overall structure remains functional and safe over time.
Materials Used in Repairs
Choosing appropriate materials plays a vital role in ensuring the resilience and safety of components that undergo maintenance. The selection is driven by a need for durability, compatibility, and performance under various operational conditions. These materials must meet specific criteria to support long-term functionality and withstand environmental challenges.
Metals and Alloys
High-strength metals and alloys, such as aluminum and titanium, are frequently chosen for their lightweight properties and excellent resistance to stress and fatigue. These metals offer a balance between strength and weight, making them ideal for parts that require both durability and minimal mass. Titanium, for instance, provides impressive corrosion resistance, which is essential for enduring exposure to moisture and varying temperatures.
Composite Materials
Advanced composite materials, including carbon fiber and fiberglass, have gained popularity due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and flexibility in design. Composites offer advantages such as reduced weight without compromising stability. Their ability to withstand dynamic forces while remaining lightweight contributes significantly to performance, especially in areas exposed to vibration and high-speed forces.
Step-by-Step Repair Procedures
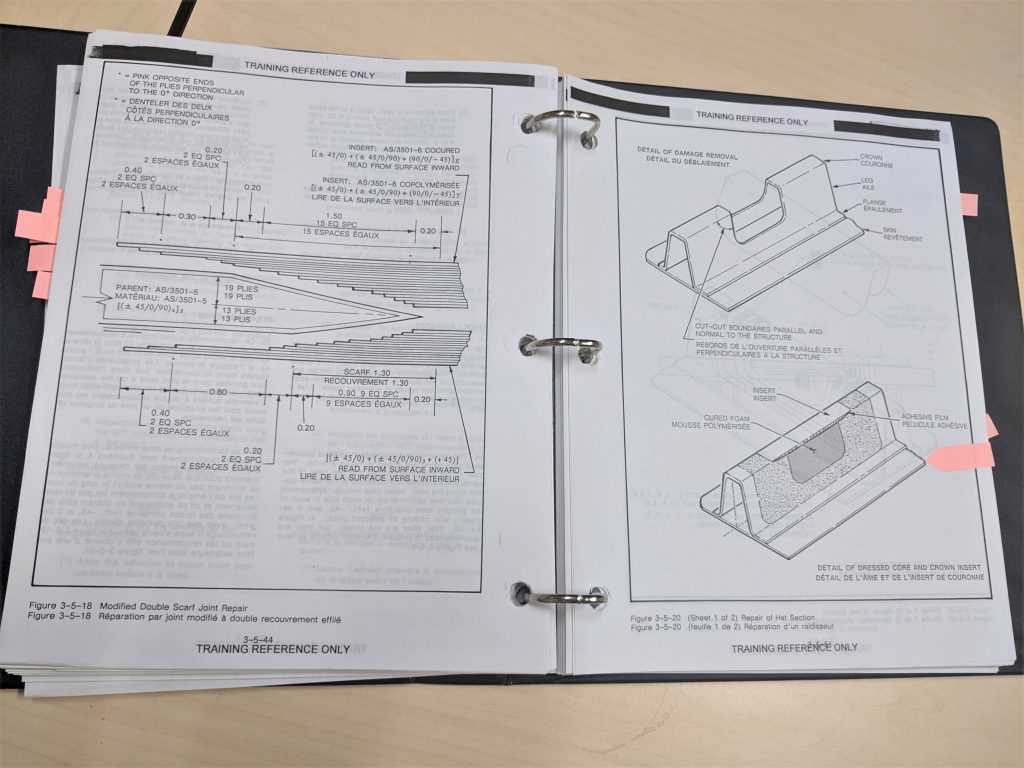
This section provides a detailed sequence of actions aimed at restoring components to their optimal function. Following these guidelines ensures that all necessary processes are carried out systematically and with precision, enhancing both safety and performance.
1. Assessment of Damage: Begin by thoroughly inspecting the affected area, identifying any visible wear, cracks, or deformation. Record findings to ensure a comprehensive approach in subsequent steps.
2. Preparation: Gather required tools and materials, ensuring they meet quality standards. Prepare the workspace by cleaning the surrounding surfaces to prevent contamination during the work.
3. Removal of Affected Parts: Carefully detach any components that need replacement or reinforcement. Use appropriate techniques to avoid additional damage, paying attention to fastenings and joints.
4. Restoration of Surface Integrity: Address any inconsistencies on the surface by cleaning, sanding, or buffing as needed. This step ensures that new materials will bond effectively and aligns with overall system requirements.
5. Application of Reinforcements: Position reinforcement elements precisely according to specifications. Secure them using recommended tools and techniques, ensuring stability and durability.
6. Final Testing and Adjustment: Perform a thorough check on the restored components to verify their function and alignment. Make any necessary ad
Inspection and Evaluation Techniques
Inspection and evaluation play a crucial role in maintaining the longevity and performance of various structures. Proper techniques are essential for identifying any signs of wear, material fatigue, or potential issues that could compromise safety and effectiveness. By applying systematic approaches, evaluators can detect irregularities early, allowing for timely interventions that prevent further degradation.
Visual Examination Methods
Visual inspection remains one of the most straightforward yet effective approaches for identifying surface-level irregularities. Inspectors often use tools such as magnifying glasses or portable lights to enhance visibility, which helps in spotting cracks, corrosion, or other signs of wear. This preliminary assessment provides a baseline for further, more detailed analysis.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools
For in-depth evaluations, advanced diagnostic tools come into play. Ultrasonic testing, radiography, and other non-destructive methods allow evaluators to penetrate deeper layers, revealing hidden issues without damaging the surface. These techniques are invaluable for detecting weaknesses that may not be visible during a standard visual examination, ensuring comprehensive assessment and accurate maintenance planning.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Understanding the regulatory framework is essential to ensure that all maintenance procedures meet the highest safety standards. Complying with these guidelines not only promotes operational safety but also enhances the longevity and reliability of all components.
- Documentation Standards: Accurate records of inspections, modifications, and routine checks must be maintained to ensure consistency and accountability across all levels of service.
- Material Approval: All materials used in maintenance should be pre-approved by relevant authorities to confirm their quality and suitability for specific tasks.
- Personnel Certification: Only certified personnel are authorized to perform assessments and technical adjustments, ensuring qualified oversight at each step of the process.
- Periodic Reviews: Scheduled reviews and updates to compliance guidelines are critical to adapt to evolving regulations and ensure continuous alignment with current standards.
Adhering to these requirements minimizes risks and establishes a robust foundation for effective oversight and quality assurance. Compliance with such standards also contributes to the broader goals of safety and reliability in all m
Understanding Repair Limitations

In any technical field, there are specific guidelines and boundaries that dictate how adjustments or improvements can be made to ensure safe and optimal performance. Knowing these boundaries helps avoid modifications that could compromise integrity, safety, or functionality.
Several factors define the boundaries for feasible modifications:
- Material Suitability: Every material has its own strength, flexibility, and wear resistance. Alterations must respect these properties to prevent premature degradation.
- Design Consistency: Adjustments should harmonize with the original design, maintaining balance and load distribution.
- Operational Safety: Changes must adhere to safety requirements, especially in contexts with high safety standards and rigorous inspection routines.
Limitations also vary depending on the complexity and purpose of the original system. Minor adjustments might be allowed, but more complex alterations require thorough analysis and testing:
- Evaluate potential impact on connected parts.
- Consider the effect on overall functionality and longevity.
- Follow set guidelines to ensure every adjustment meets quality standards.
By underst
Case Studies of Successful Repairs
This section provides an overview of various instances where damaged components were successfully restored to optimal performance. Through practical examples, readers gain insights into effective methodologies and techniques applied to achieve long-term durability and functionality in complex systems.
Aircraft Frame Restoration

In one notable case, technicians addressed extensive wear on critical sections of an airframe. Using innovative reinforcement techniques and advanced materials, they extended the lifespan of the component. The project highlighted both the importance of precise assessment before intervention and the effectiveness of modern tools in achieving a seamless finish, minimizing the need for further interventions.
Wing Reassembly Techniques
Another example involves a complex wing reassembly project where high precision was essential for alignment and load-bearing restoration. Engineers adopted specialized joining techniques that improved aerodynamic efficiency while adhering to strict safety protocols. This case underscored the advantages of blending traditional craftsmanship with cutting-edge technology to restore original performance standards.
Challenges in Structural Repairs
Performing restoration work on complex frameworks involves numerous hurdles, each requiring precise assessment and specialized approaches. Overcoming these difficulties demands a careful balance between maintaining safety standards and implementing efficient, lasting solutions. To address the most common obstacles, teams rely on both traditional methods and evolving technologies that adapt to the structure’s unique characteristics and wear conditions.
Common Restoration Obstacles
Key challenges often arise from structural age, material fatigue, and environmental impacts. Materials can degrade differently based on exposure, leading to various levels of damage that demand individualized approaches. Assessing these factors accurately is essential to determine appropriate solutions that extend longevity without compromising stability.
Technological Innovations and Their Impact
Recent advancements in diagnostic tools and restoration materials have enabled a more precise approach to challenges in restoration work. Enhanced imaging systems, for instance, allow for detailed inspection and analysis, revealing hidden issues and aiding in more accurate restoration plans. Furthermore, new materials provide better resilience, helping to counter the effects of aging a
Tools and Equipment for Repairs
Performing effective restorations requires a selection of reliable tools and devices designed to handle a variety of tasks. Each instrument plays a critical role, whether it is measuring, cutting, aligning, or fastening. The right equipment ensures both precision and efficiency in tasks, reducing downtime and enhancing safety.
Essential Instruments
Core instruments include various measurement tools like calipers and gauges for accurate dimensions, alongside cutting tools such as saws and shears for reshaping materials. Drills and rivet guns are essential for assembly, while torque wrenches allow precise fastening. When working with these devices, understanding their functionality and upkeep is key to maintaining high-quality results.
Specialized Equipment

For certain projects, specialized devices may be necessary. Hydraulic presses, for example, are invaluable for tasks that require controlled force, and ultrasonic testers provide a non-destructive way to inspect materials. Heat guns and welding devices are commonly used for joining or reshaping, depending on the materials involved. Utilizing these specialized tools helps achieve consistent and durable outcomes.
| Tool Category | Examples | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
Measurement Tools
Future Trends in Structural Maintenance
The landscape of maintenance for complex systems is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and data-driven approaches. Emerging trends are shaping how teams approach longevity, safety, and performance enhancements in key components, focusing on predictive methods and minimizing downtime. Predictive Analytics and Monitoring Systems
One significant development is the integration of predictive analytics and advanced monitoring systems. By harnessing real-time data, these tools provide insights that enable early detection of potential issues, allowing teams to address concerns before they impact functionality. This trend emphasizes proactive measures over reactive solutions, ultimately extending the lifespan of essential assets. Automation and AI-Driven AssessmentsAutomation and AI are becoming core to maintenance strategies, enabling faster, more accurate assessments. Automated inspections, often performed by drones or robotic systems, help in identifying areas that need attention without human intervention. These intelligent solutions reduce inspection times and offer detailed analyses, empowering teams to make informed decisions based on precise data. |