
Ensuring the longevity and safety of light aviation vehicles requires a thorough understanding of their design and assembly principles. This guide offers insights into the processes necessary for maintaining the integrity of an aircraft’s body, focusing on common issues and effective solutions. A well-documented approach is essential for both novice and experienced technicians alike.
In this resource, we delve into various techniques and methodologies that facilitate the restoration and enhancement of the airframe. From assessing damage to implementing effective strategies for reinforcement, each section provides detailed information aimed at preserving optimal performance and safety standards. By adhering to established guidelines, practitioners can ensure their aircraft remains in peak condition.
The importance of regular evaluations cannot be overstated. Through systematic inspections and precise interventions, potential hazards can be identified and addressed proactively. This not only safeguards the craft but also enhances the confidence of its operators and passengers. Emphasizing best practices in maintenance lays the foundation for a robust aviation experience.
Cessna 150 Overview

This section provides a comprehensive introduction to a popular light aircraft model, known for its reliability and ease of handling. Designed primarily for training and personal use, it combines efficiency with performance, making it an ideal choice for both novice and experienced pilots.
Features of this aircraft include a high-wing configuration, which enhances stability and visibility. Its compact design allows for maneuverability in various environments, contributing to its reputation as an excellent trainer. Additionally, the aircraft is powered by a modest engine, providing a balance between power and fuel efficiency.
The interior space is tailored for comfort, accommodating two occupants with adequate legroom and visibility. Instrumentation is straightforward, allowing for easy navigation and operation, thus reducing the learning curve for new aviators.
Overall, this aircraft serves as a cornerstone in the realm of general aviation, exemplifying what is achievable in light aviation design and functionality.
Importance of Structural Repair Manuals
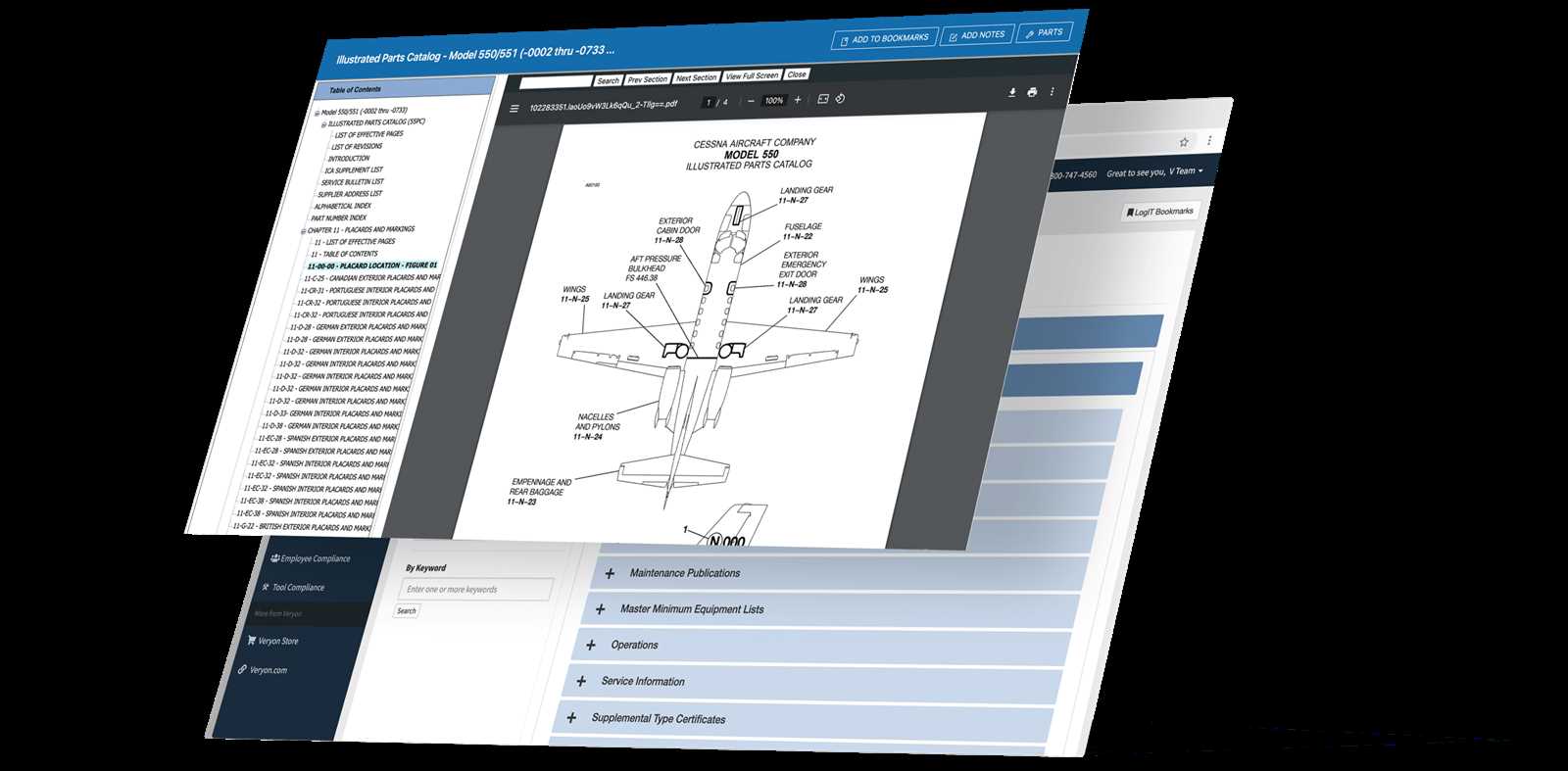
Guidelines for maintaining and restoring aircraft integrity play a crucial role in ensuring safety and longevity. These resources serve as essential tools for professionals, providing detailed instructions and best practices that are vital in the aviation industry.
- Safety Assurance: Following established protocols minimizes risks associated with air travel.
- Consistency in Work: Standardized procedures help maintain uniformity across various repair projects.
- Training Resource: New technicians benefit from comprehensive documentation that aids in skill development.
Moreover, having access to these documents enhances the efficiency of restoration tasks, enabling technicians to quickly locate necessary information and apply the correct methods. This leads to:
- Reduced downtime during maintenance.
- Improved quality of work through adherence to industry standards.
- Enhanced communication among team members through a shared understanding of processes.
In summary, well-structured guidelines are indispensable for maintaining aircraft, ensuring that all repair activities are executed with precision and care.
Common Issues in Cessna 150

Every aircraft has its own set of challenges that can arise during operation and maintenance. Identifying these frequent problems is crucial for ensuring safety and longevity. This section explores the typical concerns associated with a particular model, providing insights into common areas that may require attention.
Structural Concerns
One of the primary issues often observed relates to the airframe integrity. Regular inspections can reveal signs of wear or damage that might compromise performance. Monitoring these aspects is essential for the continued airworthiness of the aircraft.
Mechanical Failures
Another area of concern involves mechanical components that can fail over time. This includes the engine, control surfaces, and landing gear systems. Understanding the failure modes of these parts can help in proactive maintenance and mitigate potential hazards.
| Issue | Description | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion | Oxidation of metal surfaces, affecting strength. | Regular cleaning and application of protective coatings. |
| Engine Overheating | Inadequate cooling leading to engine failure. | Routine checks of cooling systems and engine timing. |
| Control Surface Wear | Degradation of hinges and attachment points. | Frequent inspections and timely replacement of parts. |
| Landing Gear Malfunctions | Issues with deployment or retraction mechanisms. | Regular system checks and lubrication of moving parts. |
Materials Used in Aircraft Repair
The choice of materials for aviation maintenance is crucial for ensuring safety, performance, and longevity of the aircraft. Various substances are employed to address different components and structures, each selected for its unique properties and benefits. Understanding these materials helps in achieving effective solutions for any issues that may arise during the life cycle of an aircraft.
Common Materials
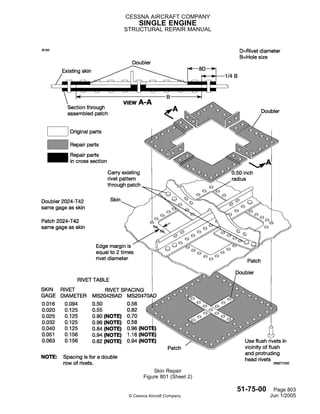
Metal alloys, such as aluminum and titanium, are widely used due to their strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion. Composites, including carbon fiber and fiberglass, provide lightweight alternatives that enhance fuel efficiency and structural integrity. Additionally, specialty adhesives and sealants play a vital role in bonding components while maintaining flexibility and durability.
Selection Criteria

When selecting materials, factors such as weight, strength, environmental resistance, and cost are considered. Each component’s specific function and the operational conditions it will face are essential in determining the most suitable option. Regular evaluation and adherence to industry standards ensure that the materials used remain reliable and effective throughout the aircraft’s operational life.
Step-by-Step Repair Procedures
This section outlines the essential processes for addressing and restoring aircraft components to ensure optimal performance and safety. Each phase is designed to provide clear guidance, enabling technicians to systematically approach any issues that may arise during maintenance or refurbishment.
| Step | Description | Tools Required |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Inspect the affected area thoroughly for any signs of damage or wear. | Flashlight, Inspection mirror |
| 2 | Document findings with photographs and notes for reference. | Camera, Notepad |
| 3 | Remove any necessary components to access the damaged section. | Wrenches, Screwdrivers |
| 4 | Clean the area to remove debris and contaminants. | Cleaning solution, Rags |
| 5 | Evaluate the extent of the damage and determine the appropriate course of action. | Measuring tools, Reference guidelines |
| 6 | Apply necessary patches or reinforcements as dictated by the assessment. | Adhesive, Patching material |
| 7 | Allow for curing or setting time as specified in the product instructions. | Timer, Environmental controls |
| 8 | Reassemble any components removed during the initial steps. | Wrenches, Screwdrivers |
| 9 | Conduct a final inspection to ensure all work meets safety standards. | Checklists, Inspection tools |
| 10 | Document the completed work and update maintenance records. | Computer, Maintenance logs |
Safety Protocols for Repairs

When undertaking any maintenance work on aircraft, it is crucial to adhere to established safety measures to ensure the well-being of personnel and the integrity of the craft. These guidelines are designed to mitigate risks associated with maintenance tasks and create a secure working environment.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is essential. Technicians should wear appropriate gear such as gloves, goggles, and ear protection to shield against potential hazards. Ensuring that all members of the team are equipped with the right PPE fosters a culture of safety and vigilance.
Moreover, workspace organization plays a vital role in accident prevention. A clutter-free area reduces the chances of tripping or misplacing tools, which can lead to unintended injuries. Clearly labeled storage for tools and materials can enhance efficiency and minimize risks.
It is also imperative to conduct risk assessments before initiating any tasks. Identifying potential hazards associated with specific procedures allows technicians to implement necessary precautions. Regular training sessions can reinforce safety protocols and keep the team updated on best practices.
Lastly, emergency preparedness cannot be overlooked. Having a clear plan for responding to accidents or injuries ensures that help can be summoned quickly. Familiarity with emergency procedures and access to first aid kits contribute to a safer workplace.
Tools Required for Structural Work
Performing maintenance or modifications on aircraft requires a specific set of instruments to ensure safety and precision. Each tool plays a crucial role in the effective execution of tasks, from minor adjustments to significant alterations. Below is a list of essential equipment needed for these operations.
- Hand Tools
- Wrenches
- Screwdrivers
- Pliers
- Files
- Hammers
- Power Tools
- Drills
- Grinders
- Sanders
- Measurement Instruments
- Calipers
- Tape measures
- Levels
- Fastening Equipment
- Riveters
- Screw guns
- Clamps
- Safety Gear
- Safety glasses
- Gloves
- Ear protection
Utilizing the correct tools not only enhances the quality of work but also minimizes the risk of accidents. Therefore, ensuring that all necessary equipment is available and in good condition is paramount for effective operations.
Maintenance Checks for Cessna 150
Regular assessments are crucial for ensuring the longevity and safety of any aircraft. These inspections help identify wear and tear, enabling timely interventions that prevent more significant issues down the line. Establishing a routine for these evaluations is essential for maintaining airworthiness and operational efficiency.
Pre-Flight Inspections
Before every flight, it is vital to conduct thorough checks to verify the aircraft’s readiness. This includes examining the exterior for any visible damage, ensuring that all control surfaces are functioning correctly, and checking fluid levels such as oil and fuel. Safety is paramount, and pre-flight evaluations play a significant role in mitigating risks associated with airborne activities.
Scheduled Maintenance

In addition to daily inspections, adherence to a systematic maintenance schedule is necessary. These periodic checks involve a more in-depth review of critical components, including the engine, electrical systems, and avionics. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines during these evaluations ensures that any underlying issues are addressed promptly, thereby extending the aircraft’s operational lifespan. Regular maintenance not only enhances safety but also improves performance efficiency.
Understanding Aircraft Fatigue
Aircraft experience repetitive stress over time, leading to gradual degradation of materials and structures. This phenomenon, known as fatigue, is a critical consideration in aviation safety and maintenance. Understanding how fatigue develops and manifests is essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of aircraft components.
Causes of Fatigue
Fatigue arises from a variety of factors, including cyclical loading, environmental conditions, and material properties. Repeated flexing and bending can create micro-cracks within the materials, which may eventually lead to failure if not addressed. Additionally, temperature variations and exposure to corrosive elements can exacerbate the fatigue process, making regular inspections vital.
Recognizing Fatigue Symptoms

Identifying early signs of fatigue is crucial for maintaining airworthiness. Common indicators include visible cracks, unusual noises during operation, and changes in handling characteristics. Timely detection allows for appropriate interventions, such as component replacement or further examination, ultimately enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
Impact of Environmental Factors
The longevity and integrity of aviation structures are significantly influenced by various environmental conditions. Elements such as temperature fluctuations, humidity, and exposure to corrosive substances can all affect materials over time, leading to potential vulnerabilities that must be addressed.
Temperature plays a critical role in the performance of materials used in aircraft construction. Extreme heat can cause thermal expansion, while cold temperatures may lead to contraction. These variations can create stress points, ultimately impacting the overall stability of the airframe.
Humidity is another vital factor that can lead to degradation, particularly in materials that are susceptible to moisture absorption. High humidity levels can promote the growth of mold and mildew, while also accelerating corrosion processes, especially in metallic components.
Exposure to pollutants and other corrosive agents can exacerbate material fatigue. Aircraft that operate in industrial areas or near saltwater may experience accelerated wear due to the harsh chemical environments, necessitating more frequent inspections and maintenance.
Understanding and mitigating the effects of these environmental factors is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of aviation systems. Proper design considerations and regular assessments can help in maintaining structural integrity over the lifespan of the aircraft.
Regulatory Standards for Repairs

Adhering to established guidelines is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance in maintenance activities. These frameworks provide a foundation for quality assurance and risk management throughout the process.
Key standards include:
- Federal Aviation Regulations (FAR): Essential rules governing aviation safety.
- Advisory Circulars (AC): Recommendations and best practices for maintenance procedures.
- Manufacturer Specifications: Detailed requirements from the aircraft maker that outline acceptable methods and materials.
Compliance with these regulations not only safeguards the aircraft’s integrity but also enhances operational efficiency.
Training for Aircraft Technicians
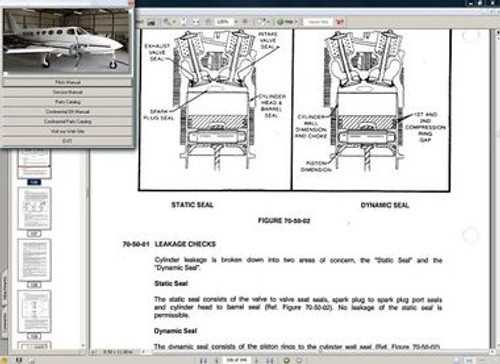
The journey to becoming a skilled aircraft technician involves a comprehensive educational framework that encompasses both theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This training is essential to ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance within the aviation industry.
Programs typically integrate classroom instruction with hands-on workshops, allowing trainees to gain familiarity with various aircraft systems and components. Key areas of focus include aerodynamics, propulsion systems, and electronic navigation. Through this blend of learning methods, students develop the critical thinking and problem-solving skills necessary for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Moreover, industry certifications play a crucial role in validating the competencies of aspiring technicians. These credentials often require passing rigorous examinations and completing a specified number of practical hours, reinforcing the importance of real-world application in the training process. Continuous education and staying updated with technological advancements are also emphasized, ensuring technicians remain proficient in an ever-evolving field.