
Effective upkeep of small engines is crucial for ensuring longevity and optimal performance. Understanding the intricacies of these power units not only enhances their efficiency but also reduces the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns. This section delves into essential practices that can empower owners to tackle common issues with confidence.
Detailed instructions provide a valuable resource for anyone looking to enhance their mechanical skills. Whether you are a seasoned technician or a novice enthusiast, having access to structured guidance can significantly simplify the troubleshooting process. This ensures that your equipment remains in peak condition, ready to tackle any task.
In addition, regular maintenance plays a pivotal role in extending the lifespan of your machinery. By familiarizing yourself with fundamental components and their functions, you can more effectively diagnose problems and perform necessary adjustments. This proactive approach not only saves time and money but also cultivates a deeper appreciation for the mechanics behind your tools.
Understanding the Briggs & Stratton Manual
Grasping the intricacies of the technical documentation for small engines can significantly enhance your maintenance and troubleshooting skills. These comprehensive guides serve as essential resources, providing detailed instructions on assembly, disassembly, and servicing of various engine components. A clear understanding of this documentation empowers users to perform efficient diagnostics and repairs, ultimately prolonging the lifespan of their equipment.
Key Sections of the Document

The documentation typically includes several vital sections that users should familiarize themselves with. Each part contributes to a holistic understanding of the engine’s operation and care requirements.
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Introduction | An overview of the engine type and its applications. |
| Specifications | Technical details and performance metrics that define the engine. |
| Maintenance Procedures | Step-by-step guidelines for routine checks and upkeep. |
| Troubleshooting | Common issues and solutions to restore functionality. |
| Parts List | A detailed inventory of components, including part numbers. |
Importance of Familiarity

Becoming acquainted with this technical literature not only aids in immediate problem resolution but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the machinery’s design and functionality. Regular consultation of the guide can lead to improved performance and efficiency, ensuring that your equipment remains in optimal condition for years to come.
Common Issues with Small Engines

Small engines are widely used in various applications, from lawnmowers to generators. However, they can encounter several frequent problems that affect their performance and longevity. Understanding these issues is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
Frequent Problems

- Fuel System Issues:
- Contaminated fuel can lead to poor combustion.
- Clogged fuel filters restrict flow, resulting in engine stalling.
- Starting Difficulties:
- Worn spark plugs can hinder ignition.
- Low battery charge may prevent starting in electric models.
- Overheating:
- Blocked air filters reduce airflow and cooling efficiency.
- Lack of proper oil levels can lead to excessive heat generation.
Maintenance Tips

- Regularly check and replace fuel as needed.
- Inspect and clean air filters to ensure optimal airflow.
- Monitor oil levels and change it according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Replace spark plugs periodically to maintain proper ignition.
Essential Tools for Engine Repair

Maintaining and restoring small engines requires a specific set of instruments to ensure effective and efficient service. The right equipment not only facilitates the process but also enhances the quality of the work performed. Below are key tools that every enthusiast should consider having in their arsenal.
Basic Hand Tools
- Wrenches: Adjustable and fixed wrenches are essential for loosening and tightening bolts.
- Screwdrivers: A variety of screwdrivers, including Phillips and flathead, are necessary for accessing different components.
- Pliers: Needle-nose and slip-joint pliers are useful for gripping and twisting various parts.
- Socket Set: A comprehensive socket set allows for easier work with fasteners in tight spaces.
Specialized Equipment
- Torque Wrench: Ensures that bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Compression Tester: Assesses the condition of the engine’s internal components by measuring cylinder pressure.
- Fuel System Cleaner: Helps to maintain the fuel system and improve engine performance.
- Digital Multimeter: Essential for diagnosing electrical issues and testing components.
Having these tools readily available can significantly enhance the ability to troubleshoot and restore engine functionality effectively. Investing in quality instruments not only saves time but also ensures better outcomes in maintenance tasks.
Step-by-Step Repair Guide Overview
This section provides a comprehensive approach to addressing issues with small engine equipment. Following a structured process not only enhances efficiency but also ensures a thorough understanding of each component’s functionality. This guide is designed to assist users in diagnosing problems, performing maintenance, and restoring optimal performance.
Key Phases of the Process
- Diagnosis: Identify the symptoms and determine the root cause of the issue.
- Preparation: Gather the necessary tools and replacement parts to facilitate the task.
- Disassembly: Carefully dismantle the engine components, taking note of their arrangement.
- Inspection: Examine each part for wear and damage, ensuring that all components meet operational standards.
- Replacement: Substitute any faulty parts with new or refurbished components.
- Reassembly: Put the engine back together, following the initial disassembly order.
- Testing: Conduct a thorough check to confirm that the engine operates smoothly and effectively.
Safety Precautions
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment.
- Ensure the equipment is powered off and disconnected before starting any work.
- Keep work areas clean and organized to prevent accidents.
Maintaining Your Engine’s Performance
To ensure the optimal functioning of your engine, regular upkeep is essential. This involves a series of practices aimed at enhancing efficiency and prolonging lifespan. By following a systematic approach, you can avoid common issues and keep your machine running smoothly.
Key maintenance tasks include monitoring fluid levels, replacing filters, and checking for any signs of wear. Implementing these measures will not only improve performance but also reduce the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns.
| Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Change | Every 25 hours | Replace old oil with fresh to ensure smooth operation. |
| Air Filter Check | Monthly | Inspect and clean or replace the air filter to maintain airflow. |
| Spark Plug Inspection | Every 100 hours | Check for wear and replace if necessary for efficient ignition. |
| Fuel Stabilization | As needed | Use stabilizers to prevent fuel degradation during storage. |
By adhering to these guidelines, you can significantly enhance your engine’s reliability and performance over time. Regular attention to these details ensures that your equipment remains in peak condition, ready for any task you undertake.
Identifying Engine Components and Parts

Understanding the various elements that make up an engine is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Each component plays a specific role in the overall functionality, and recognizing these parts can simplify any work required on the machine.
Main Components
- Cylinder: The chamber where fuel and air mix and ignite, creating power.
- Piston: Moves up and down within the cylinder, converting fuel energy into mechanical energy.
- Crankshaft: Transfers the piston’s linear motion into rotational motion to drive the machine.
- Valves: Regulate the intake of air-fuel mixture and the exhaust of combustion gases.
- Spark Plug: Ignites the air-fuel mixture, initiating combustion.
Supporting Elements

- Fuel Tank: Stores the fuel required for operation.
- Air Filter: Cleans the air entering the engine, ensuring optimal performance.
- Oil Filter: Removes contaminants from the engine oil, prolonging the life of the engine.
- Cooling System: Maintains optimal operating temperatures, preventing overheating.
- Starter Motor: Initiates the engine’s operation by turning the crankshaft.
Familiarity with these components not only aids in recognizing potential issues but also enhances the overall efficiency of the engine. Each part’s proper function is critical for the longevity and performance of the equipment.
Safety Precautions During Repairs
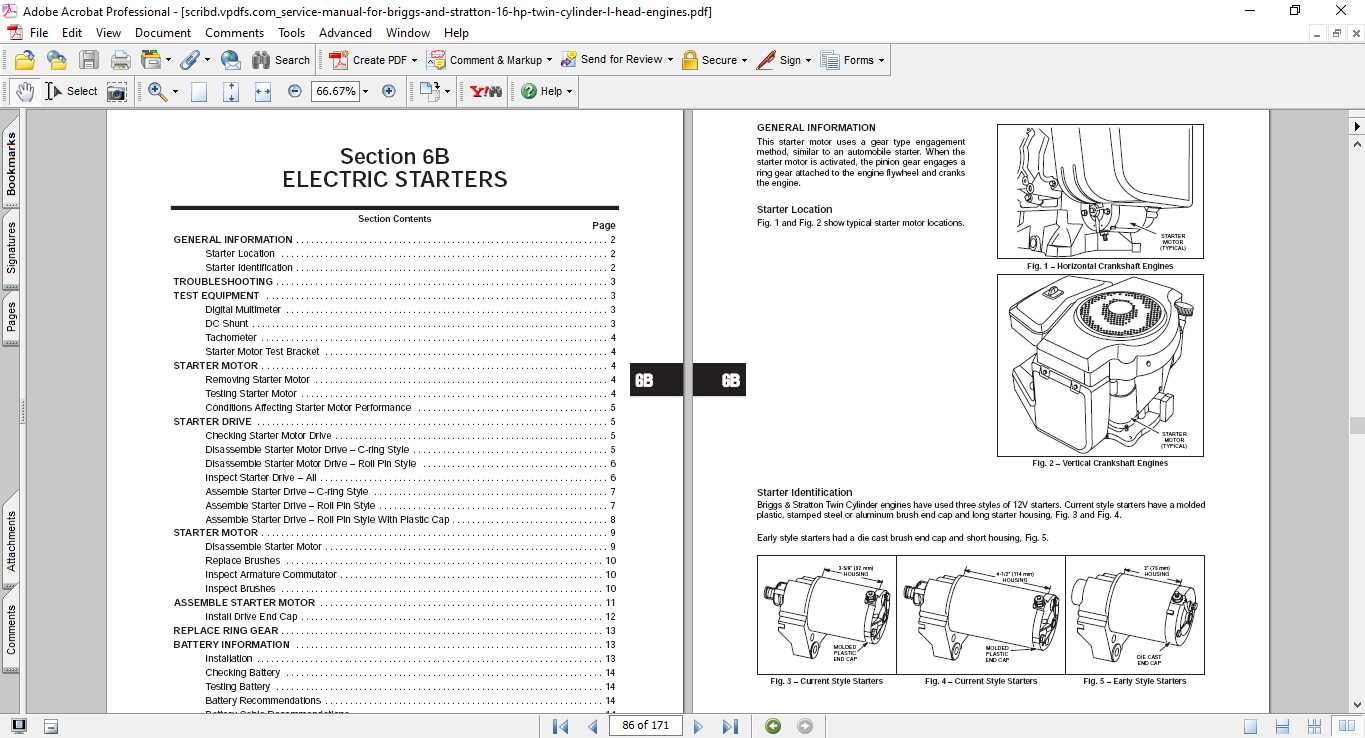
Ensuring safety during maintenance tasks is essential to prevent accidents and injuries. Proper precautions not only protect the individual performing the work but also safeguard the equipment being serviced. Familiarity with safety measures is crucial for a smooth and efficient process.
Personal Protective Equipment

Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is vital. This includes gloves, goggles, and sturdy footwear to shield against potential hazards. Gloves help prevent cuts and abrasions, while goggles protect the eyes from debris and chemicals. Always opt for closed-toe shoes that provide stability and support during tasks.
Work Environment Considerations

Maintaining a clean and organized workspace is equally important. Clutter can lead to slips and falls, so keeping tools and materials neatly arranged minimizes risks. Additionally, ensure adequate ventilation if working with any chemicals or fuels to avoid inhalation of harmful fumes. Taking these steps can greatly enhance safety and efficiency during your tasks.
Troubleshooting Engine Starting Problems
When facing difficulties with engine ignition, it is essential to identify potential issues that may prevent proper starting. Several factors can contribute to this problem, ranging from fuel supply to electrical connections. A systematic approach to diagnosing these issues can lead to effective solutions and restore functionality.
Check Fuel Supply: Ensure that the fuel tank is filled with fresh gasoline. Old or contaminated fuel can hinder the ignition process. Inspect the fuel lines for any blockages or leaks that may restrict fuel flow.
Examine the Battery: A weak or dead battery is a common culprit in starting failures. Test the battery voltage and connections to confirm they are secure and corrosion-free. If necessary, recharge or replace the battery to ensure adequate power.
Inspect the Spark Plug: A faulty spark plug can impede engine starting. Remove the spark plug and examine it for wear, carbon buildup, or damage. Cleaning or replacing the spark plug can significantly improve ignition performance.
Evaluate Electrical Components: Check the ignition switch, fuses, and wiring for any signs of damage. Faulty electrical components can disrupt the starting sequence, so ensure all connections are intact and functional.
Assess Air Intake: A blocked air filter can restrict airflow, affecting the combustion process. Clean or replace the air filter to promote optimal engine performance and facilitate easier starting.
By systematically addressing these areas, you can effectively troubleshoot starting issues and enhance the reliability of your engine. Regular maintenance and timely interventions are key to preventing future problems.
Importance of Regular Maintenance Checks
Conducting routine inspections and upkeep is essential for ensuring the longevity and efficiency of equipment. Regular checks help identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems, allowing for timely interventions that can save both time and money. By prioritizing maintenance, users can enhance the performance and reliability of their machines.
Benefits of Consistent Maintenance
One of the primary advantages of regular upkeep is improved performance. Equipment that is well-maintained operates more smoothly and efficiently, reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns. Additionally, consistent checks can lead to increased safety, as potential hazards can be addressed proactively. This not only protects the user but also extends the lifespan of the machinery.
Cost-Effectiveness of Routine Checks
Investing time and resources in periodic inspections can result in significant cost savings in the long run. By preventing major repairs and enhancing fuel efficiency, users can minimize operational costs. Moreover, maintaining equipment in optimal condition helps preserve its resale value, making it a wise financial decision for any owner.
In conclusion, regular maintenance checks are vital for the effective operation and longevity of machinery. They not only ensure safety and performance but also contribute to overall cost savings, making them an indispensable practice for all users.
How to Replace Common Engine Parts
Maintaining an engine often requires the replacement of various components to ensure optimal performance. This guide outlines the essential steps involved in swapping out frequently needed parts, helping you keep your machinery running smoothly.
Identifying Parts for Replacement
Before beginning any replacement process, it’s crucial to identify which components need attention. Common parts that may require replacement include:
- Air filter
- Fuel filter
- Spark plug
- Oil filter
- Battery
Steps for Replacing Parts

Follow these general steps to replace the parts effectively:
- Gather Tools: Collect necessary tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and replacement parts.
- Disconnect Power: Ensure that the engine is off and disconnected from any power source.
- Remove Old Part: Carefully detach the component, paying attention to any fasteners or connections.
- Install New Part: Position the new part in place and secure it properly.
- Reconnect Power: Once everything is securely in place, reconnect the power source and test the engine.
By following these steps, you can effectively manage part replacements and enhance the longevity of your engine.
Using Diagrams in the Repair Process
Visual aids play a crucial role in the maintenance and restoration of machinery, enhancing understanding and efficiency. Diagrams offer a clear representation of components and their interconnections, simplifying complex tasks and guiding users through procedures.
| Type of Diagram | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Schematic Diagrams | Illustrate electrical connections and flow of energy. |
| Exploded Views | Show individual parts and their arrangement in assemblies. |
| Flowcharts | Outline step-by-step processes for troubleshooting. |
By utilizing these graphical representations, individuals can delve into intricate tasks with confidence, ultimately achieving successful outcomes in their projects.
Finding Replacement Parts for Your Engine
Locating the right components for your engine is essential for maintaining its performance and longevity. Whether you’re working on a lawn mower, generator, or other small engine equipment, sourcing high-quality parts can significantly impact the reliability of your machinery.
Here are some effective strategies to find the necessary components:
- Manufacturer Websites: Start by visiting the official websites of engine manufacturers. They often provide a comprehensive list of parts and compatibility information.
- Authorized Dealers: Contact local dealers or service centers that specialize in your engine brand. They can offer original parts and expert advice.
- Online Retailers: Utilize trusted e-commerce platforms that specialize in engine components. Read customer reviews to ensure quality.
- Forums and Community Groups: Join online communities related to small engines. Members often share tips on where to find reliable parts.
When searching for components, it’s crucial to verify that they match the specifications of your engine. This will help avoid compatibility issues and ensure optimal performance.
Finally, consider purchasing spare parts in bulk, especially if they are prone to wear and tear. This proactive approach can save you time and money in the long run.