
In the realm of compact construction machinery, understanding the intricacies of operation and upkeep is essential for optimal performance. This section provides valuable insights into the processes that ensure these machines remain in peak condition, helping operators maximize efficiency and longevity.
Comprehending the various components and systems within these excavators is crucial. Knowledge of proper handling techniques, troubleshooting, and periodic assessments empowers users to address potential issues before they escalate. This guidance promotes a proactive approach to maintaining machinery, fostering a culture of diligence among operators.
By adhering to systematic procedures for upkeep, operators can minimize downtime and enhance productivity. This resource serves as a comprehensive reference, equipping users with the necessary tools to navigate the challenges associated with machinery maintenance effectively.
Overview of Bobcat 325 Specifications

This section provides a comprehensive look at the key features and technical details of the compact excavator, highlighting its capabilities and performance metrics.
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Engine Power | 25.5 HP |
| Operating Weight | 2,610 lbs |
| Digging Depth | 7.5 ft |
| Max Reach | 12.2 ft |
| Width | 39.5 in |
| Height | 85 in |
The above specifications illustrate the robustness and efficiency of this compact model, making it suitable for a range of construction and landscaping applications.
Common Issues with Bobcat 325

When operating compact machinery, users often encounter various challenges that can affect performance and efficiency. Understanding these common problems can help operators maintain their equipment effectively and minimize downtime.
Hydraulic System Malfunctions
One frequent issue arises from the hydraulic system, which is crucial for various functions. Problems may include leaks or inconsistent pressure, leading to reduced functionality. Regular inspection and timely maintenance are essential to prevent serious complications.
Electrical Component Failures

Another area of concern involves electrical components. Operators might experience faulty connections or malfunctioning sensors, which can lead to operational disruptions. Ensuring that wiring is intact and connections are secure can mitigate these electrical issues.
Step-by-Step Repair Procedures
This section provides a comprehensive approach to addressing common issues encountered with compact machinery. Detailed instructions ensure that users can systematically tackle each problem, enhancing the efficiency and longevity of the equipment.
Preparation and Safety Measures
Before beginning any work, it is crucial to follow essential safety protocols to protect yourself and the machinery:
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves and goggles.
- Ensure the machine is turned off and securely parked on a level surface.
- Disconnect the battery to prevent any accidental starts during maintenance.
Common Issues and Solutions

Below are steps to resolve frequent complications:
- Hydraulic Fluid Leakage:
- Identify the source of the leak by inspecting hydraulic hoses and connections.
- Replace any damaged hoses and ensure all fittings are tight.
- Engine Starting Problems:
- Check the battery for charge; replace if necessary.
- Inspect the starter and ignition system for any faults.
- Overheating:
- Examine the coolant levels and top up if low.
- Clean the radiator and ensure airflow is not obstructed.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity

Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring the extended lifespan of machinery. By following a few fundamental practices, operators can enhance performance and minimize the likelihood of costly repairs. Consistent attention to detail in maintenance routines will contribute significantly to the efficiency and reliability of equipment.
Firstly, it is crucial to conduct routine inspections to identify any signs of wear or potential issues before they escalate. This includes checking fluid levels, examining hoses for leaks, and ensuring that all components are functioning correctly. Keeping an eye on these aspects can prevent unexpected breakdowns and prolong the life of the machinery.
Secondly, adhering to the recommended lubrication schedule is vital. Proper lubrication reduces friction between moving parts, which helps to prevent overheating and excessive wear. Utilizing high-quality lubricants suited for the specific equipment will further enhance performance and reliability.
Additionally, ensuring that air filters are clean and replaced as needed is an important factor in maintaining optimal engine performance. Clogged filters can restrict airflow, leading to reduced efficiency and increased fuel consumption. Regularly cleaning or replacing these filters helps maintain peak operational capacity.
Lastly, storing the equipment in a sheltered location when not in use can protect it from the elements. Exposure to harsh weather conditions can accelerate wear and tear. Providing a suitable environment will significantly aid in preserving the machinery’s integrity over time.
Essential Tools for Bobcat Repairs

To maintain and restore compact construction machinery, having the right equipment is crucial. Proper tools not only enhance efficiency but also ensure safety during maintenance tasks. This section outlines the key instruments necessary for effective service and upkeep of these machines.
Basic Hand Tools
- Wrenches: Adjustable and socket wrenches are essential for loosening and tightening bolts.
- Screwdrivers: A variety of flathead and Phillips screwdrivers are required for different fasteners.
- Pliers: Needle-nose and slip-joint pliers assist in gripping and manipulating components.
- Hammers: A claw hammer or rubber mallet can help with assembly and disassembly tasks.
Specialized Equipment
- Diagnostic Tools: Electronic diagnostic devices help identify issues within the machinery.
- Hydraulic Jacks: These are essential for lifting heavy components safely.
- Torque Wrench: Ensures that bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Grease Gun: Used for lubricating moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
Having these tools readily available will streamline the maintenance process and enhance the longevity of your machinery. Investing in quality equipment is an important step toward effective service.
Safety Guidelines During Repairs

Ensuring a secure environment while conducting maintenance is essential for both the technician and the machinery involved. Adhering to safety protocols minimizes risks and enhances the overall efficiency of the task at hand.
Before commencing any service, it is crucial to familiarize yourself with the equipment’s specifications and functions. This understanding allows for better decision-making and reduces the likelihood of accidents. Always utilize personal protective equipment, such as gloves, safety goggles, and hard hats, to safeguard against potential hazards.
Ensure that the workspace is well-ventilated and free from clutter, which can lead to slips, trips, or falls. Disconnect power sources and relieve any stored energy from hydraulic systems before beginning work. This precaution prevents unexpected movement or discharge during the process.
Always use the appropriate tools for each task. Utilizing the wrong tools can lead to equipment damage or personal injury. Additionally, keep all tools organized and within reach to avoid unnecessary movements that could result in accidents.
In case of any uncertainty regarding a procedure, consult available resources or seek assistance from a knowledgeable individual. It is better to take extra time to clarify instructions than to risk injury or damage due to guesswork. Prioritizing safety not only protects individuals but also prolongs the lifespan of the equipment.
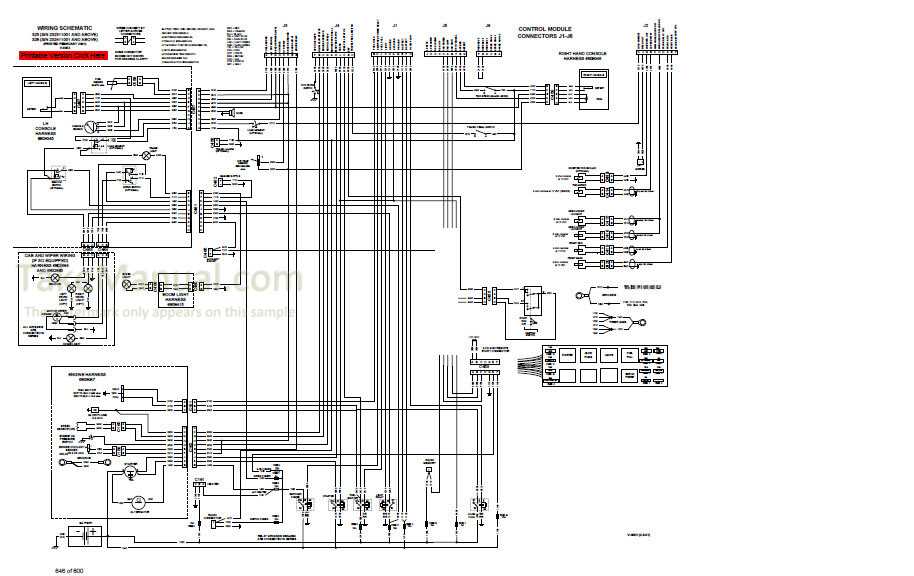
Troubleshooting Electrical Problems
Addressing issues related to electrical systems can be challenging yet essential for maintaining optimal functionality. This section provides guidance on identifying and resolving common electrical malfunctions that may arise in your machinery.
To effectively troubleshoot electrical difficulties, follow these general steps:
- Visual Inspection: Begin by examining the wiring and connectors for any visible signs of wear or damage. Look for:
- Cuts or frayed wires
- Corroded terminals
- Loose connections
- Battery voltage levels
- Fuse integrity
- Switch operation
- Relays
- Sensors
- Motors
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can systematically identify and rectify electrical issues, ensuring the reliability and performance of your machinery.
Hydraulic System Maintenance Practices
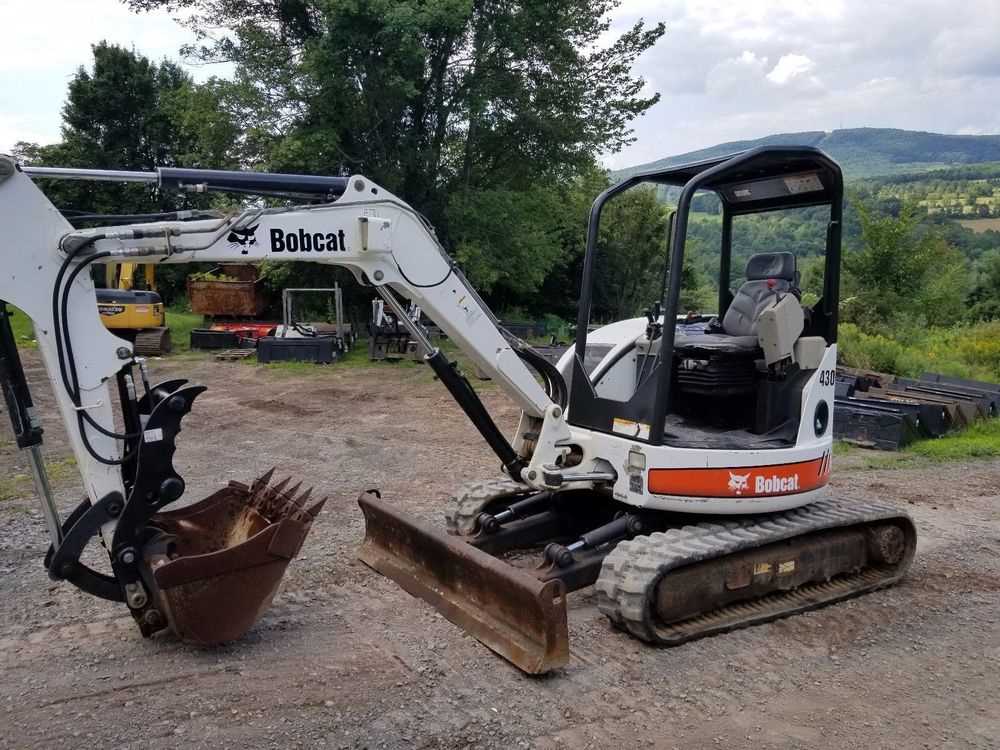

Regular upkeep of hydraulic systems is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Proper care not only enhances efficiency but also prevents costly breakdowns. Adopting systematic maintenance routines can significantly extend the lifespan of hydraulic components and improve overall functionality.
Fluid Levels and Quality: Monitoring hydraulic fluid levels is crucial. Ensure that the fluid is at the recommended level to avoid air contamination and overheating. Regularly check the fluid’s condition, as contamination can lead to severe damage. If the fluid appears dirty or has a foul odor, it should be replaced promptly.
Filter Maintenance: Filters play a vital role in keeping the hydraulic system clean. Regularly inspect and replace filters as necessary to prevent dirt and debris from entering the system. A clean filter reduces wear on components and maintains fluid integrity.
Inspecting Hoses and Fittings: Regularly examine hoses and fittings for any signs of wear, leaks, or damage. Look for cracks, bulges, or fraying that could compromise performance. Promptly address any issues to prevent fluid loss and maintain system integrity.
System Testing: Conduct routine tests on the hydraulic system to ensure all components are functioning correctly. Monitor pressure levels and performance metrics to identify any abnormalities early. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions before significant issues arise.
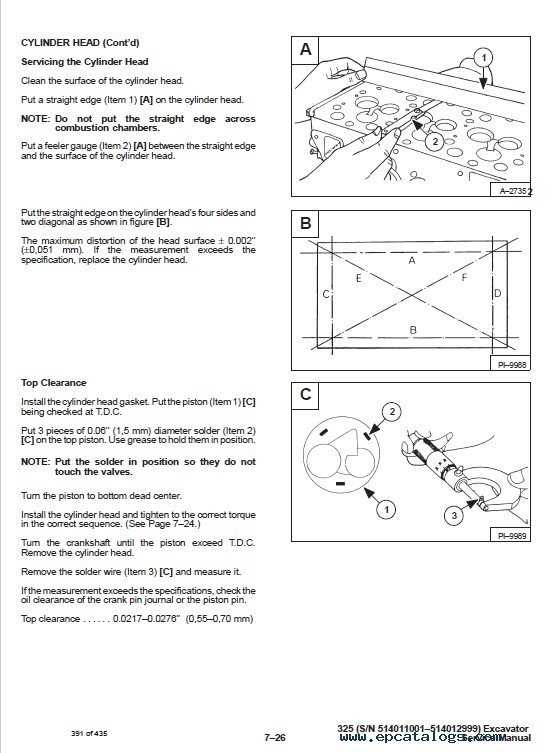
Engine Overhaul: A Complete Guide

Revitalizing an engine is a crucial process that can significantly enhance the performance and longevity of machinery. This comprehensive guide provides insights into the essential steps and considerations involved in an engine rebuild, ensuring optimal functionality and efficiency.
Preparation is the foundation of a successful overhaul. Before beginning, it is vital to gather all necessary tools and materials. Create a clean and organized workspace to facilitate the disassembly and reassembly processes. Familiarizing yourself with the engine’s specifications and components will greatly aid in the overall undertaking.
During the disassembly phase, it is essential to methodically remove parts while taking care to document the arrangement and condition of each component. This will prove invaluable during reassembly. Pay particular attention to the state of critical elements such as pistons, valves, and gaskets, as their integrity directly affects performance.
Once disassembled, cleaning each part thoroughly is imperative. Utilize appropriate cleaning agents and methods to remove deposits and contaminants. Inspect all components for wear and damage, and replace any that do not meet the required standards. This step ensures that the engine operates smoothly and reliably upon reassembly.
After cleaning, it’s time to focus on reassembly. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure correct torque specifications and alignment of parts. Attention to detail during this phase is crucial, as improper assembly can lead to future issues. Be sure to utilize new gaskets and seals to prevent leaks and maintain optimal performance.
Finally, once reassembly is complete, conduct thorough testing to verify the engine’s performance. Monitor for any irregularities or leaks and make necessary adjustments. A well-executed overhaul not only revitalizes machinery but also contributes to its efficient operation for years to come.
Parts Replacement and Upgrades
Maintaining equipment functionality and enhancing performance often involves the strategic replacement of components and the integration of modern upgrades. This process not only ensures optimal operation but also prolongs the lifespan of machinery. Understanding the essential elements of this practice can greatly assist operators in making informed decisions regarding their equipment.
Identifying Components for Replacement

Before initiating the replacement process, it is crucial to identify which parts are worn or underperforming. Regular inspections can reveal components that may need attention. Commonly replaced elements include hydraulic filters, tracks, and engine components. Monitoring these parts can prevent unexpected breakdowns and maintain efficiency.
Upgrading for Enhanced Performance

In addition to replacements, upgrading certain features can lead to significant improvements in functionality. Modern alternatives may offer better durability and efficiency. Upgrades might include enhanced hydraulic systems, advanced control panels, or improved safety features. Investing in these enhancements can provide a competitive edge in performance.
| Part Type | Replacement Interval | Potential Upgrades |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Filter | Every 500 hours | High-efficiency filters |
| Tracks | Every 1,000 hours | Rubber tracks with better traction |
| Engine Oil | Every 250 hours | Synthetic oils for improved performance |
| Control Panel | As needed | Digital display panels with diagnostics |