
In the realm of outdoor equipment, understanding the intricacies of engine upkeep is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This section delves into the fundamental practices and techniques necessary for addressing common issues encountered with small engines. By following these guidelines, users can effectively troubleshoot and resolve various challenges that may arise.
Detailed instructions and systematic approaches will be provided to empower users to perform necessary tasks with confidence. From routine inspections to more complex interventions, a thorough understanding of each component’s functionality is crucial. This knowledge not only aids in problem-solving but also enhances the overall efficiency of the machinery.
Furthermore, maintaining equipment in peak condition can prevent potential breakdowns, saving time and resources in the long run. This guide aims to equip users with the insights required to tackle maintenance tasks effectively, ensuring that engines operate smoothly and reliably throughout their lifespan.
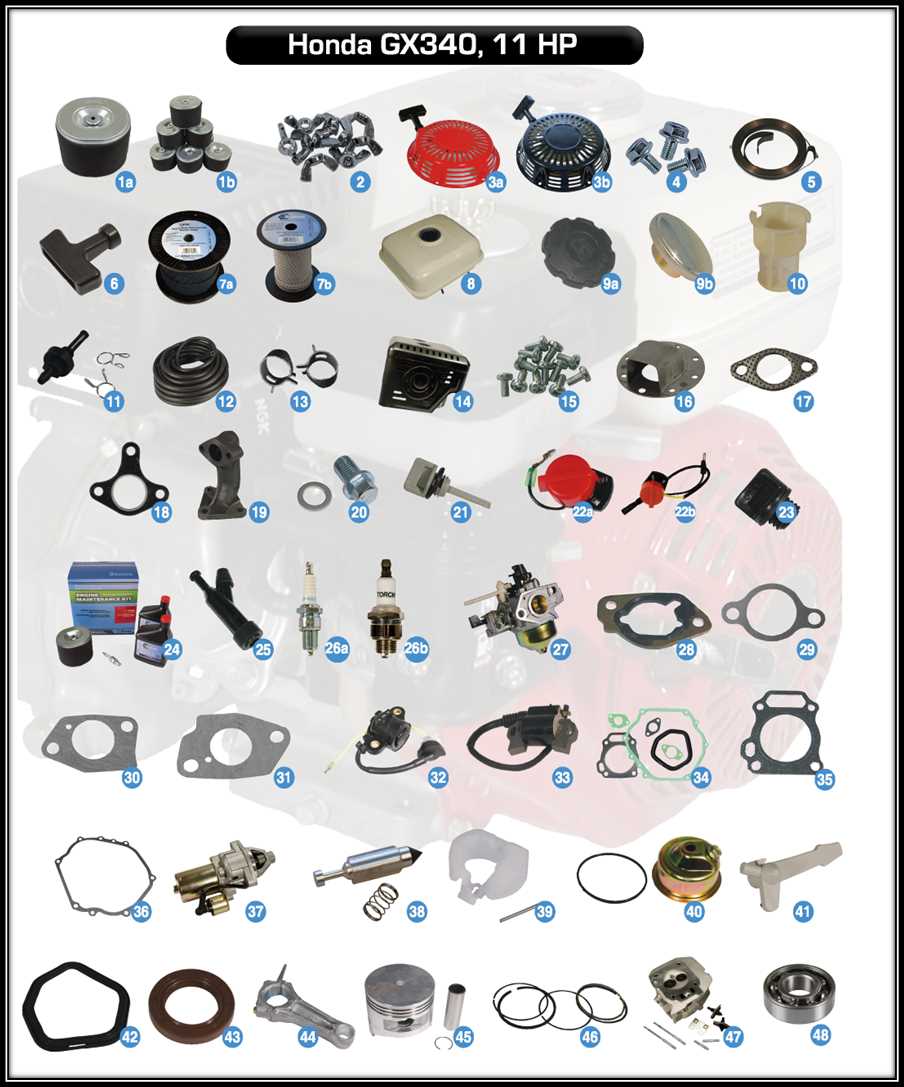
Understanding Honda GX340 Engine Components

This section explores the essential parts that constitute a small four-stroke power unit commonly used in various applications. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall functionality, contributing to the engine’s performance and reliability.
Core Parts of the Engine
The primary components include the cylinder, where the combustion process occurs, and the piston, which translates the energy generated into mechanical motion. Additionally, the crankshaft converts this linear movement into rotational force, powering connected machinery effectively.
Supporting Mechanisms

Supporting parts such as the camshaft and valves regulate the air-fuel mixture intake and exhaust gas expulsion, ensuring optimal performance. The ignition system ignites the mixture, initiating the power cycle, while the lubrication system maintains efficient operation and minimizes wear on moving parts.
Common Issues with Honda GX340

Engines of this type are known for their durability and efficiency, yet they can experience several recurring problems. Understanding these common concerns can help users maintain performance and extend the lifespan of the unit.
Fuel-Related Problems

- Fuel Contamination: Impurities in the fuel can lead to poor combustion, resulting in reduced power output and increased emissions.
- Clogged Fuel Filters: Over time, filters may become blocked, restricting fuel flow and causing the engine to stall or run inefficiently.
Starting Difficulties
- Dead Battery: A weak or dead battery can prevent the engine from starting, requiring regular checks and maintenance.
- Faulty Spark Plug: Worn or damaged spark plugs can hinder ignition, making it essential to inspect and replace them as needed.
Step-by-Step Maintenance Guide

This section offers a comprehensive approach to keeping your engine in optimal condition. Regular upkeep not only enhances performance but also prolongs the lifespan of your equipment. Following a structured routine can prevent unexpected failures and ensure reliability during operation.
1. Check Oil Levels: Regularly inspect the oil level and quality. Ensure that the oil is clean and within the recommended range. If it’s dark or gritty, consider changing it.
2. Clean or Replace Air Filter: A clean air filter is vital for efficient airflow. Remove the filter, clean it with compressed air, or replace it if it’s excessively dirty.
3. Inspect Spark Plug: Examine the spark plug for wear and carbon buildup. Clean or replace it as necessary to ensure proper ignition.
4. Examine Fuel System: Inspect fuel lines for cracks or leaks. Ensure the fuel filter is clean, and replace it if needed. Use fresh fuel to avoid complications.
5. Tighten Fasteners: Periodically check all bolts and screws for tightness. Vibration during operation can loosen components, so ensure everything is secure.
6. Clean Exterior: Keep the exterior clean to prevent debris buildup. Use a soft brush or cloth to wipe down surfaces regularly.
7. Store Properly: When not in use, store the unit in a dry and sheltered location. Consider using a cover to protect it from dust and moisture.
Tools Needed for Repairs
When undertaking maintenance tasks for small engines, having the right equipment is essential for achieving optimal results. Proper tools not only facilitate efficient work but also ensure safety and longevity of the machinery. This section outlines the essential instruments required to perform various tasks effectively.
A comprehensive toolkit should include basic hand tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers, which are indispensable for disassembly and reassembly. Additionally, specialized tools like torque wrenches and feeler gauges may be necessary to maintain precise specifications. Having a reliable socket set can significantly speed up the process, allowing for quick changes and adjustments.
For cleaning and inspection, items like brushes, cloths, and solvents play a vital role in maintaining engine performance. Safety gear, including gloves and goggles, should not be overlooked to protect the user during the maintenance process. Overall, ensuring that all necessary equipment is on hand will lead to a smoother and more efficient working experience.
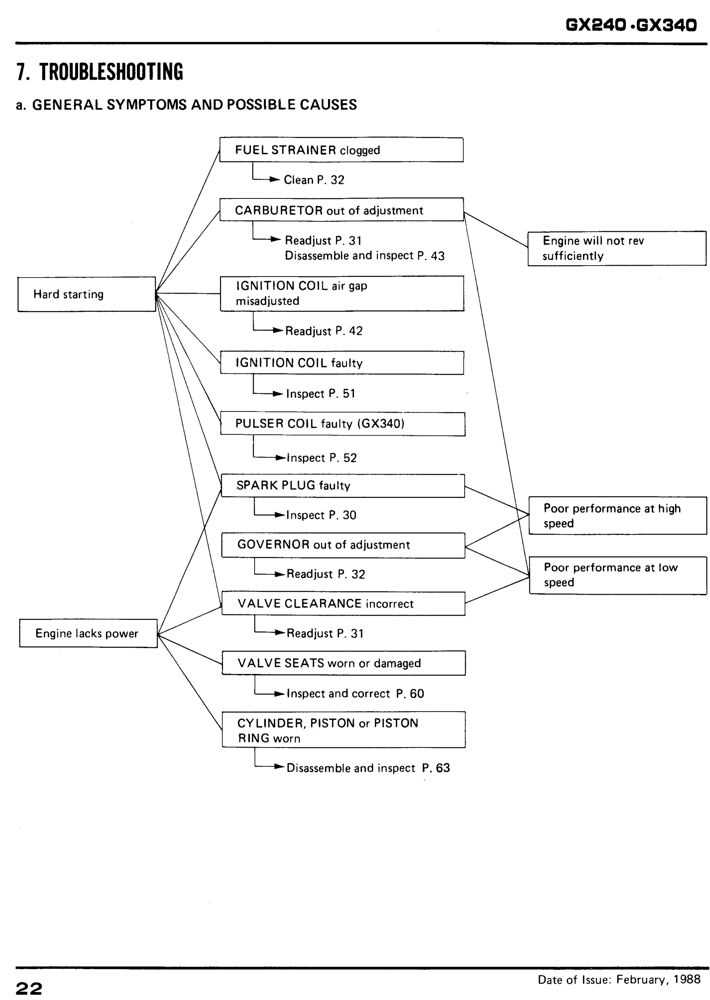
Troubleshooting Engine Performance Problems

Addressing issues related to engine efficiency is essential for maintaining optimal performance. This section provides guidance on identifying and resolving common complications that can lead to decreased functionality. Understanding these problems can significantly enhance the reliability and lifespan of the machinery.
Common Symptoms and Causes
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Poor acceleration | Clogged air filter or fuel line |
| Rough idling | Incorrect fuel mixture or spark plug issues |
| Overheating | Low coolant levels or radiator blockage |
| Excessive smoke | Oil leak or fuel contamination |
Diagnostic Steps
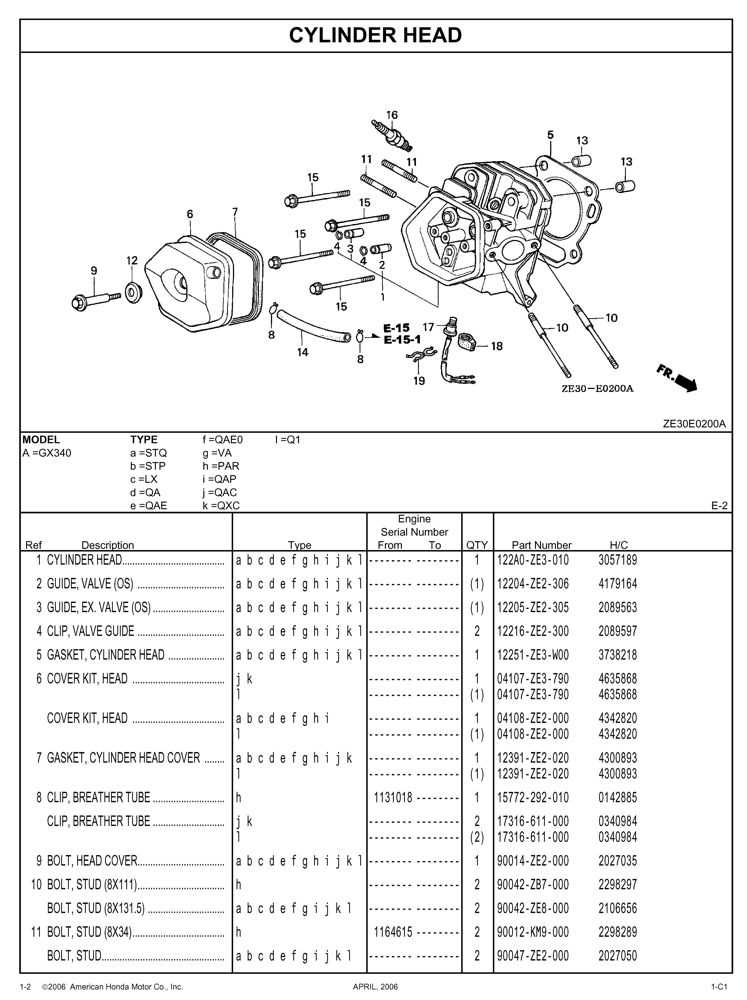
To effectively troubleshoot performance issues, follow these steps: first, conduct a visual inspection of the engine components for any obvious signs of damage or wear. Next, check fluid levels and replace any filters that appear dirty. Finally, consult the specifications to ensure all settings are correct, and perform any necessary adjustments to restore optimal operation.
Fuel System Inspection Techniques

Evaluating the fuel system is essential for maintaining optimal performance and reliability. Effective examination methods can help identify issues before they escalate, ensuring smooth operation and longevity of the equipment. This section outlines several practical approaches to assessing the fuel delivery mechanisms and components.
Visual Inspection

Begin with a thorough visual examination of the fuel system components. Check for any signs of wear, leaks, or damage in the fuel lines, connectors, and filters. Ensure that all connections are secure and free from corrosion. Pay special attention to the condition of the fuel tank, as any rust or contaminants can significantly impact functionality.
Functional Testing
After completing the visual check, proceed with functional tests to evaluate system performance. Start by inspecting the fuel pump’s operation. Listen for unusual sounds that may indicate malfunction. Additionally, measure fuel pressure with a gauge to verify that it meets manufacturer specifications. If the pressure is outside the recommended range, further investigation into the pump and filter may be necessary.
Oil Change and Recommendations

Regular maintenance of the engine’s lubrication system is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Replacing the oil at appropriate intervals ensures that the internal components remain well-lubricated, reducing wear and tear and enhancing efficiency. Below are some key points to consider when performing an oil change.
It is advisable to utilize high-quality engine oil that meets the required specifications. The type of oil you choose can significantly affect the engine’s functionality and life span. Always refer to the specific viscosity grade recommended for best results.
| Aspect | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Oil Type | Synthetic or High-Quality Conventional |
| Viscosity Grade | SAE 10W-30 or as specified |
| Change Interval | Every 50 hours of operation |
| Filter Replacement | With every oil change |
Ensure that the engine is warm before draining the oil, as this allows for better flow and removal of contaminants. Always dispose of used oil properly to protect the environment.
Electrical System Diagnostics

The effective functioning of an electrical system is crucial for the overall performance of any engine. Diagnosing issues within this system requires a systematic approach, enabling the identification of faults that may affect operation. This section outlines the essential steps and tools necessary for thorough electrical diagnostics.
Key Components to Inspect
- Battery condition and connections
- Wiring integrity and insulation
- Fuse functionality
- Electrical components such as solenoids and relays
- Grounding points and their resistance
Diagnostic Procedures
- Begin with a visual inspection of all electrical components.
- Utilize a multimeter to check voltage levels at various points in the system.
- Test continuity in wires and connections to identify breaks or shorts.
- Examine the battery for proper charge and terminal cleanliness.
- Confirm the operation of switches and relays by manually activating them.
By following these guidelines, one can effectively troubleshoot and resolve electrical issues, ensuring optimal performance and reliability of the engine.
Replacing the Air Filter
Maintaining optimal performance in your engine requires regular attention to various components, including the air filtration system. Ensuring that the air filter is clean and functioning effectively can enhance efficiency and prolong the life of the machine.
Tools and Materials Needed
Before beginning the process, gather the necessary tools and materials. You will need a new air filter, a screwdriver, and possibly a pair of gloves for cleanliness. Having everything on hand will streamline the replacement procedure.
Step-by-Step Replacement Process
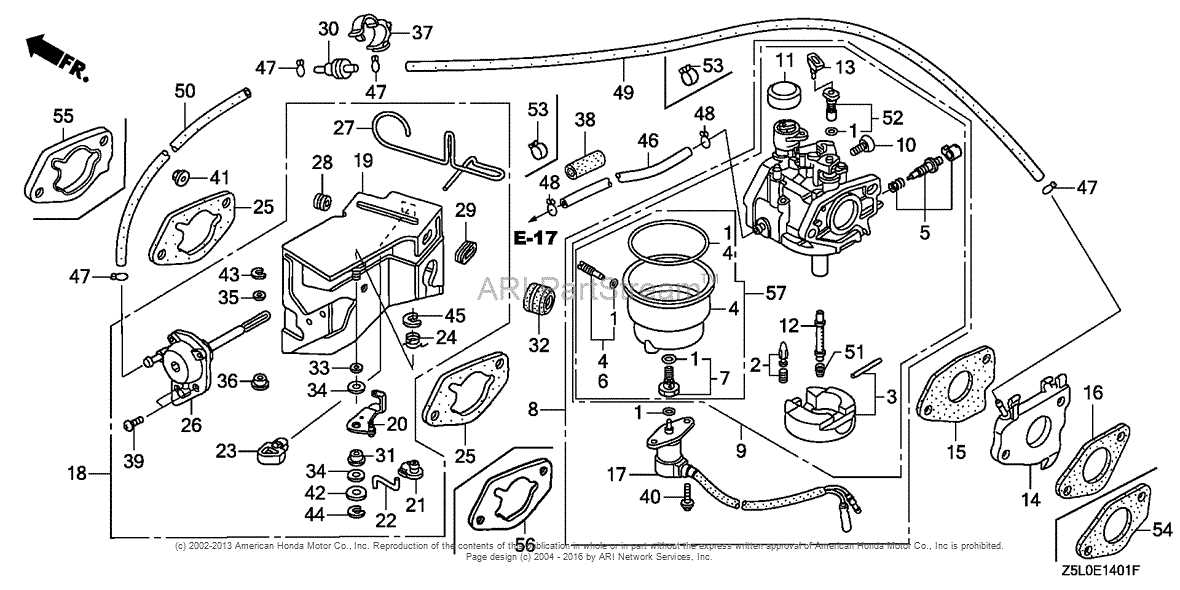
Start by turning off the engine and allowing it to cool down. Locate the air filter cover, which is typically secured by screws. Carefully remove the screws and lift off the cover to access the filter. Take out the old filter, inspecting it for any damage or excessive dirt. Replace it with the new filter, ensuring it fits snugly in place. Finally, reattach the cover and secure it with screws, making sure everything is tight to prevent any debris from entering the engine.
Contacting Professional Repair Services

When faced with mechanical challenges, seeking assistance from experts can ensure optimal performance and longevity of your equipment. Engaging professionals allows for a thorough assessment and the application of specialized knowledge, which can be crucial for effective troubleshooting.
Before reaching out, it is advisable to gather relevant information about the issue at hand. This may include details about the machine’s model, symptoms observed, and any previous maintenance performed. Providing this information can significantly enhance the efficiency of the diagnostic process.
While searching for qualified technicians, consider their experience and reputation within the industry. Reviews and recommendations from previous clients can offer insights into the quality of service and reliability you can expect. Additionally, verify that the service providers possess the necessary certifications and training to handle your specific model.
After identifying potential candidates, don’t hesitate to inquire about their availability and pricing structures. Clear communication regarding the anticipated costs and timeframes for service can help manage expectations and ensure a smooth process. Ultimately, enlisting the help of skilled professionals can lead to effective solutions and peace of mind.