
Understanding the intricacies of machinery is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This section provides essential insights into the upkeep of specific models, highlighting key aspects that contribute to their functionality. Proper maintenance techniques are vital for preventing breakdowns and ensuring smooth operation in various conditions.
When facing operational issues, it becomes imperative to diagnose problems accurately. By delving into systematic approaches, users can identify faults and apply effective solutions. This guide offers practical steps and detailed instructions to navigate challenges effectively, empowering users to take control of their equipment’s maintenance.
Equipped with knowledge and resources, operators can enhance their experience and maximize efficiency. Emphasizing routine checks and timely interventions, this document serves as a valuable reference for anyone seeking to improve their understanding of machine care. The aim is to foster confidence in handling machinery and to promote proactive measures for optimal performance.
Overview of Case 1845C
This section provides a comprehensive look at a specific model of compact construction equipment known for its versatility and efficiency. Designed to perform a variety of tasks, this machine is equipped with powerful features that enhance its operational capabilities, making it suitable for various work environments.
Key Features

Notable attributes include robust performance specifications, user-friendly controls, and a durable build that withstands rigorous use. The equipment excels in maneuverability, allowing operators to navigate tight spaces with ease. Additionally, it is designed for straightforward maintenance, ensuring minimal downtime during operations.
Specifications Table
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Engine Type | Diesel |
| Horsepower | 65 HP |
| Operating Weight | 6,000 lbs |
| Lift Capacity | 1,500 lbs |
| Dimensions | Length: 132 in, Width: 53 in |
Common Issues and Symptoms
Understanding frequent problems and their manifestations is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Identifying these symptoms early can prevent further complications and ensure efficient operation.
Mechanical Problems

- Unusual Noises: Grinding or squeaking sounds often indicate wear in moving parts.
- Vibration: Excessive shaking can signal imbalances or loose components.
- Fluid Leaks: Any leakage may point to damaged seals or hoses.
Operational Issues
- Difficulty Starting: Issues with ignition can arise from battery or electrical faults.
- Loss of Power: Inadequate performance may result from fuel delivery or air intake problems.
- Overheating: Elevated temperatures could indicate coolant failures or obstructions in airflow.
Monitoring these signs closely allows for timely interventions and prolonged functionality.
Essential Tools for Repair
Having the right instruments is crucial for effectively addressing issues with machinery. A well-equipped toolkit not only simplifies the process but also enhances efficiency and accuracy during maintenance tasks. Familiarity with various tools ensures that challenges can be tackled swiftly and safely.
Basic Hand Tools
Start with a selection of basic hand tools, including wrenches, pliers, and screwdrivers. These items are fundamental for disassembling components and making adjustments. Ensure you have various sizes to accommodate different fasteners and fittings.
Diagnostic Equipment
Invest in diagnostic tools to identify problems accurately. A multimeter can measure voltage, current, and resistance, while a pressure gauge can assess hydraulic systems. These instruments are invaluable for troubleshooting and ensuring optimal performance.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
This section provides a comprehensive approach to diagnosing issues in your equipment. By following a systematic method, you can identify problems efficiently and implement solutions effectively.
1. Initial Assessment: Begin by observing any unusual sounds, vibrations, or performance issues. Take note of any error codes or warning lights that may appear on the display.
2. Visual Inspection: Conduct a thorough visual examination of the unit. Check for any loose connections, damaged components, or signs of wear. Pay special attention to wiring and hydraulic lines for leaks or breaks.
3. Functional Testing: Test all operational features systematically. Start with the primary functions, and then move to secondary systems. This will help pinpoint the source of the malfunction.
4. Consult the Documentation: Refer to the relevant technical documentation for guidance on specifications and troubleshooting steps specific to your model. This information can provide valuable insights into common issues.
5. Isolate the Problem: If the issue persists, isolate each component. Disconnect or deactivate non-essential systems to determine whether the problem is localized or more widespread.
6. Implement Solutions: Once the source of the problem is identified, apply the necessary repairs or adjustments. Ensure that any replacement parts meet the required specifications for compatibility.
7. Final Testing: After making repairs, conduct a final test of the unit. Confirm that all functions operate as intended and that no new issues have emerged during the process.
By following these steps, you can effectively troubleshoot and restore your equipment to optimal performance.
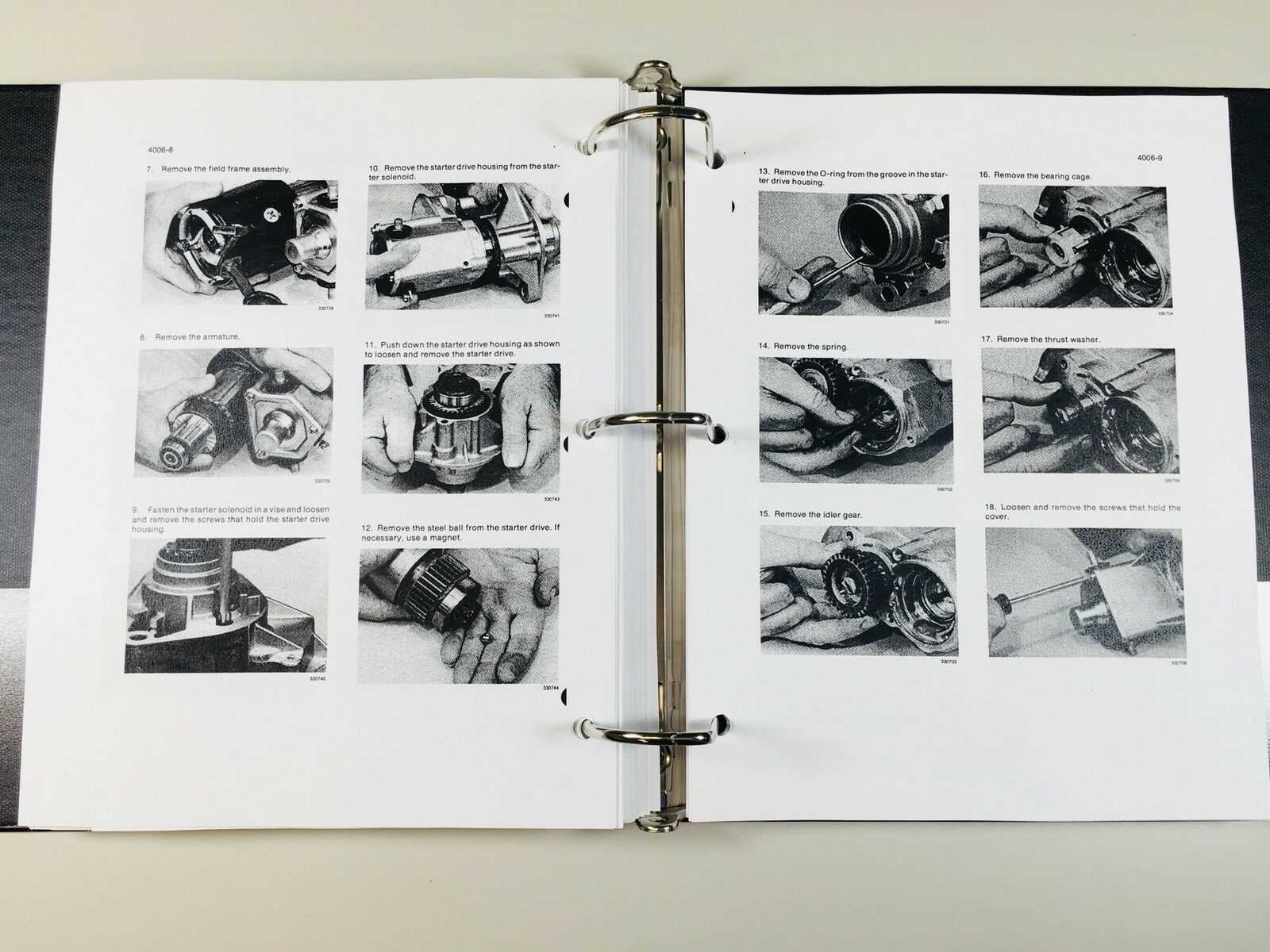
Engine Maintenance Techniques
Effective upkeep of an engine is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Employing a range of practices can help ensure that the machinery runs smoothly and efficiently. Regular attention to vital components not only prevents failures but also enhances overall functionality.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Oil Changes | Frequent replacement of engine lubricant to reduce friction and wear. |
| Air Filter Inspection | Checking and replacing air filters to maintain optimal airflow and prevent debris entry. |
| Coolant Level Monitoring | Ensuring appropriate coolant levels to prevent overheating and maintain temperature regulation. |
| Fuel System Maintenance | Regular cleaning and checking of the fuel system to enhance combustion efficiency. |
Hydraulic System Diagnostics
The hydraulic system is essential for optimal performance and functionality in various machinery. Effective diagnostics are crucial for identifying issues that may hinder operation. This section provides insights into methods and tools for evaluating the hydraulic components, ensuring they function correctly and efficiently.
When diagnosing the hydraulic system, consider the following key aspects:
- Fluid Quality: Check for contamination, such as dirt or water, that could affect performance.
- Pressure Levels: Monitor the pressure readings to ensure they are within specified limits.
- Leaking Components: Inspect hoses and connections for signs of leakage, which can lead to system failures.
- Actuator Functionality: Assess cylinders and motors for proper operation and response to controls.
Utilizing the right diagnostic tools can significantly enhance the accuracy of evaluations:
- Pressure gauges to monitor system pressure.
- Flow meters to measure the fluid flow rate.
- Leak detection kits to identify and address any leaks effectively.
- Diagnostic software for analyzing electronic control systems, if applicable.
By systematically addressing these elements, operators can ensure the hydraulic system remains in peak condition, minimizing downtime and enhancing productivity.
Electrical System Checks
Ensuring the integrity of the electrical components is crucial for optimal performance. Regular inspections help identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring smooth operation. This section outlines key procedures for evaluating the electrical setup, focusing on essential tests and troubleshooting steps.
Visual Inspection
Begin with a thorough visual assessment of wiring and connections. Look for signs of wear, fraying, or corrosion on terminals. Ensure that all connections are secure and free from moisture, as these factors can lead to electrical failures.
Testing Voltage and Continuity
Utilize a multimeter to measure voltage levels across various components. Confirm that readings align with manufacturer specifications. Additionally, perform continuity tests on wires to ensure they are intact and functioning correctly. This step is vital for diagnosing issues related to power delivery and grounding.
Replacing Major Components
When dealing with machinery, the replacement of significant parts can be essential for restoring optimal functionality. This process not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of the equipment. Understanding the steps involved in component replacement is crucial for effective maintenance and operation.
Common Components to Replace
Several key elements may require attention over time. Here’s a list of frequently replaced parts:
| Component | Symptoms of Failure | Replacement Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Pump | Reduced power, unusual noises | 1. Disconnect power supply. 2. Remove old pump. 3. Install new pump and reconnect. |
| Engine | Excessive smoke, loss of power | 1. Drain fluids. 2. Detach engine components. 3. Replace with a new engine. |
| Transmission | Slipping gears, erratic shifting | 1. Remove drive shafts. 2. Unbolt transmission. 3. Install the new unit. |
Conclusion
Addressing component issues promptly ensures that equipment operates efficiently. Regular inspections and timely replacements are key to minimizing downtime and preventing further damage.
Safety Precautions During Repairs

Ensuring safety is paramount when conducting maintenance on machinery. Adhering to essential guidelines can prevent accidents and protect both the technician and the equipment involved. Understanding potential hazards and implementing appropriate measures is crucial for a successful and secure working environment.
Before beginning any servicing tasks, familiarize yourself with the equipment’s specifications and operational protocols. Always wear personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and sturdy footwear to minimize the risk of injury.
| Precaution | Description |
|---|---|
| Disconnect Power | Always ensure that the power source is disconnected before starting any maintenance work. |
| Use Proper Tools | Utilize the correct tools for each task to avoid damaging components or causing injury. |
| Maintain Workspace | Keep the workspace organized and free of obstructions to prevent accidents. |
| Follow Procedures | Adhere strictly to the outlined procedures to ensure tasks are performed safely. |
| Have Emergency Plan | Be prepared with an emergency plan, including access to first aid and emergency contacts. |
Recommended Replacement Parts

Maintaining optimal performance of your equipment often requires timely updates to certain components. Selecting quality substitutes can enhance functionality and extend the lifespan of the machine. This section outlines essential elements to consider when seeking replacements, ensuring smooth operation and reliability.
Essential Components
When replacing parts, it is vital to focus on key components that frequently wear out or fail. These include hydraulic seals, filters, and belts, which are crucial for maintaining efficiency and safety. Investing in high-quality replacements can prevent unnecessary downtime and costly repairs.
Quality Substitutes
Opting for durable alternatives from reputable manufacturers is advisable. This not only guarantees compatibility but also enhances the overall performance of the machine. Below is a list of commonly recommended components for replacement:
| Part Type | Description | Recommended Brand |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Seal | Prevents leaks and maintains fluid integrity. | Brand A |
| Oil Filter | Removes impurities from the hydraulic fluid. | Brand B |
| Belt | Ensures proper movement and function of machinery. | Brand C |
Cost Estimation for Repairs
Understanding the financial implications of maintenance and fixes is essential for effective budgeting. Accurately assessing costs involves considering various factors, such as parts, labor, and any potential downtime. This section provides insights into estimating expenses associated with equipment servicing.
Factors Influencing Cost
Several elements play a crucial role in determining overall expenses. Parts required for replacements often vary in price, depending on availability and brand. Labor costs can fluctuate based on technician expertise and regional market rates. Additionally, unforeseen complications during the servicing process may lead to increased expenses.
Estimating Total Expenses
To arrive at a comprehensive estimate, it is beneficial to gather quotes from multiple sources for parts and services. Creating a detailed list of necessary components, along with their respective prices, can facilitate accurate calculations. Always allocate a portion of the budget for unexpected issues that may arise during the process, ensuring financial preparedness.
Maintenance Schedule for Longevity
Establishing a consistent maintenance routine is essential for ensuring the durability and optimal performance of machinery. Regular checks and timely interventions can significantly extend the lifespan of equipment, preventing unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs.
Recommended Maintenance Activities

Implement the following tasks at specified intervals to maintain peak functionality:
| Activity | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Check fluid levels | Weekly |
| Inspect filters | Monthly |
| Grease moving parts | Every 500 hours |
| Examine electrical connections | Quarterly |
| Perform full system diagnostics | Annually |
Tips for Effective Maintenance
Adhering to the outlined schedule enhances reliability. Additionally, keeping a maintenance log helps track completed tasks and schedule future activities efficiently.