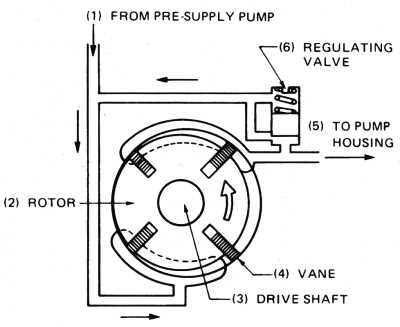
Ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of essential machinery requires a thorough understanding of their intricate components and operational principles. This section aims to equip users with the knowledge necessary to address common issues and maintain peak efficiency in their equipment.
With an emphasis on practical insights and step-by-step instructions, this guide delves into various aspects of upkeep, focusing on identifying faults, implementing solutions, and performing regular assessments. Emphasizing the importance of proactive care, it highlights techniques that can prevent potential breakdowns and extend the lifespan of the machinery.
By mastering these skills, users can cultivate a more effective working environment, reducing downtime and enhancing productivity. A well-maintained system not only saves time but also contributes to overall operational excellence, making it crucial for anyone involved in the management of these vital tools.
VE Pump Overview
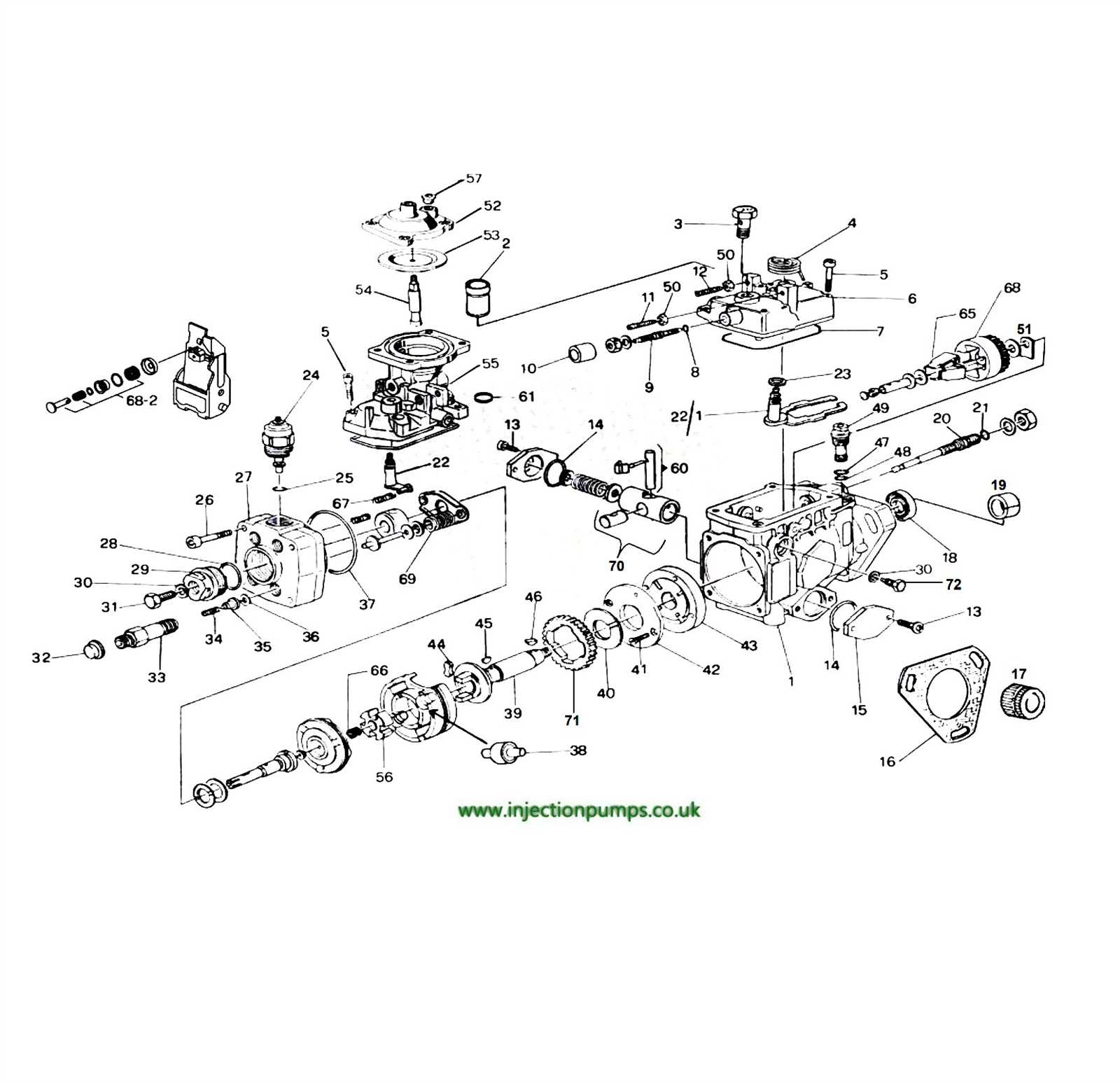
This section provides an insightful exploration of a vital component widely utilized in various automotive applications. Understanding its functionalities and features is crucial for those involved in maintenance and optimization of vehicle performance.
Functionality and Design
The design of this system emphasizes efficiency and precision. It operates by managing the fuel flow, ensuring optimal combustion and power output. The intricate engineering behind its construction allows for adaptability across different engine types, highlighting its versatility.
Common Issues and Solutions

Over time, this device may encounter several challenges, such as wear and tear or improper calibration. Recognizing these issues early can significantly enhance performance and longevity. Regular diagnostics and adjustments are recommended to maintain peak functionality, ensuring the system operates smoothly.
Common Issues with Bosch VE Pumps
This section explores typical problems associated with a specific type of fuel delivery system. Understanding these challenges is crucial for efficient operation and longevity of the equipment.
Frequent Problems
- Fuel Leakage: A common issue often manifests as wet spots around the unit, indicating compromised seals or fittings.
- Inconsistent Performance: Erratic engine behavior can stem from inadequate fuel delivery, leading to power loss or stalling.
- Noise Levels: Unusual sounds may suggest internal wear or misalignment, requiring immediate attention.
Diagnosis Steps
- Visual Inspection: Check for any signs of leaks or physical damage to the components.
- Fuel Quality Check: Ensure that the fuel being used is free from contaminants.
- Pressure Testing: Use appropriate tools to assess the system’s pressure, ensuring it meets manufacturer specifications.
Tools Required for Repairs
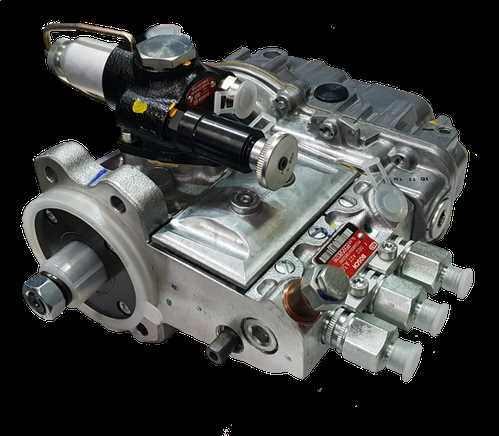

When undertaking maintenance tasks on complex machinery, having the right equipment is essential. Proper tools not only facilitate efficient work but also ensure safety and precision during the process. This section will outline the essential instruments and apparatus needed to successfully perform maintenance operations.
Basic Hand Tools
Every technician should have a set of fundamental hand tools at their disposal. This includes screwdrivers of various sizes, wrenches, pliers, and a reliable hammer. These items are critical for loosening and tightening components, as well as for making adjustments as needed.
Specialized Equipment
In addition to standard tools, certain specialized equipment may be required for more intricate tasks. This can include torque wrenches for precise tightening, multimeters for electrical diagnostics, and pressure gauges for checking system performance. Having these advanced tools readily available will enhance the effectiveness of the service work and ensure optimal functionality.
Step-by-Step Disassembly Process
This section outlines a detailed approach to systematically dismantling the device, ensuring that each component is carefully handled and documented. Following these steps will help in reassembling the unit effectively, minimizing the risk of damage to any parts.
Preparation Phase

- Gather all necessary tools: wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers.
- Organize a clean workspace to avoid losing small components.
- Ensure you have a container for screws and small parts.
- Familiarize yourself with the assembly layout for reference during reassembly.
Disassembly Steps
- Disconnect the power supply and any attached hoses or connections.
- Remove external casing by unscrewing all securing fasteners.
- Carefully detach any electronic components, noting their positions and connections.
- Proceed to take off internal components sequentially, starting from the top or a designated end.
- Place each part in the organized container, labeling them as necessary.
- Inspect each component for wear or damage as you remove it.
Following this structured process will ensure that disassembly is conducted safely and efficiently, allowing for a smooth transition to maintenance or refurbishment tasks.
Inspecting Pump Components
Ensuring optimal performance of a hydraulic system involves thorough examination of its various elements. Regular assessments help in identifying wear, damage, or inefficiencies that could affect overall functionality. This process is crucial for maintaining reliability and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
When examining the individual parts, focus on the following key areas:
- Seals and Gaskets: Look for signs of deterioration or leaks, which can lead to fluid loss.
- Housing: Inspect for cracks, corrosion, or any structural integrity issues that may compromise performance.
- Rotors and Vanes: Check for wear and tear, ensuring they move freely and efficiently within the assembly.
- Bearings: Assess for smooth operation; any grinding noises or rough movement may indicate the need for replacement.
- Inlet and Outlet Ports: Ensure these passages are clear of obstructions and free from any debris that could impede flow.
Following a systematic approach during inspections can lead to timely interventions, preventing more significant issues down the line. Regular maintenance not only promotes efficiency but also contributes to safer operational conditions.
Replacing Worn-Out Seals
Over time, components in various systems may experience wear and tear, leading to diminished performance and potential leaks. Addressing these issues promptly is essential for maintaining efficiency and prolonging the lifespan of the equipment. One crucial aspect of this maintenance involves replacing the seals that have become degraded or damaged.
Identifying the signs of worn-out seals is the first step in the process. Common indicators include:
- Visible cracks or splits in the seal material
- Leaks or fluid accumulation around the area
- Unusual noises during operation
- Inconsistent performance or pressure fluctuations
Once you have determined that the seals need replacing, follow these general steps to ensure a successful replacement:
- Turn off the system and disconnect any power sources to prevent accidents.
- Carefully disassemble the component to access the seals, taking care to note the arrangement of parts for reassembly.
- Remove the old seals, ensuring that all remnants are cleared from the seating area to allow for a proper fit of the new seals.
- Install the new seals, making sure they are aligned correctly and seated securely.
- Reassemble the component, double-checking that all parts are in their original positions.
- Reconnect any power sources and test the system for leaks or irregularities.
By following these steps, you can effectively replace worn seals and restore the functionality of your equipment. Regular inspections and timely maintenance can prevent more significant issues down the line, ensuring reliable operation for years to come.
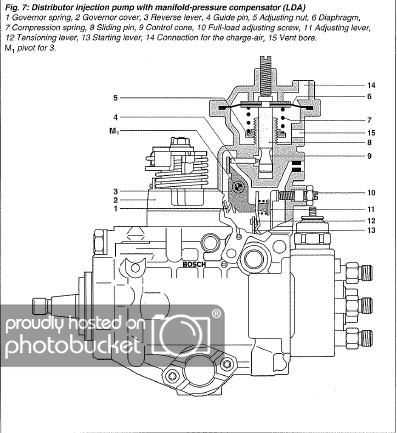
Adjusting Fuel Delivery Settings
Proper calibration of fuel flow is crucial for optimal engine performance. Adjustments to these settings can significantly influence efficiency, power output, and emissions. Understanding the nuances of fuel delivery allows for precise modifications that cater to specific operational needs.
Understanding the System

Before making any adjustments, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the components involved in fuel distribution. Each element plays a vital role in ensuring the correct amount of fuel reaches the engine. Anomalies in this system can lead to performance issues or increased fuel consumption.
Adjustment Procedure
To initiate the adjustment process, start by assessing the current settings. Use a calibrated measuring tool to determine the existing fuel flow rates. After obtaining a baseline, you can proceed to modify the settings. Turn the adjustment screws or knobs gently, making small increments to avoid drastic changes. Monitor the engine’s response closely, as immediate feedback is essential for achieving the desired performance. After adjustments, always conduct a thorough test to ensure that the modifications yield the intended results.
Note: It’s advisable to consult relevant specifications and guidelines throughout the adjustment process to maintain safety and efficiency.
Reassembling the Bosch VE Pump
The process of putting together this specific fuel injection device requires precision and attention to detail. Each component must be carefully positioned to ensure optimal functionality. Proper alignment and secure fastening are crucial to avoid any operational issues once the unit is back in service.
Before starting, gather all necessary tools and ensure that the work area is clean and organized. It’s essential to follow a systematic approach, beginning with the main housing. Inspect all seals and gaskets for wear, replacing them as needed to maintain integrity.
As you reinsert the internal components, pay close attention to the order and orientation. Reference diagrams, if available, to confirm correct placement. After assembling the core elements, ensure that all connections are tight and that there are no obstructions that could hinder performance.
Once the assembly is complete, perform a thorough inspection. Check for any signs of misalignment or looseness. A final review will help guarantee that the unit is ready for testing and eventual operation.
Testing After Repairs
Once maintenance work has been completed, it is crucial to ensure that the system functions effectively and reliably. This phase involves a series of evaluations designed to verify that all components operate as intended and meet performance standards. Proper testing not only identifies any remaining issues but also confirms the success of the interventions made.
The initial step in this process typically involves a visual inspection to check for any obvious signs of malfunction or improper assembly. Following this, operational tests should be conducted under various conditions to assess performance metrics. Monitoring parameters such as pressure, flow rate, and temperature will provide valuable insights into the overall functionality.
In addition to these evaluations, it is beneficial to compare the system’s performance with manufacturer specifications. This comparison helps to highlight any discrepancies that may indicate further adjustments are necessary. Furthermore, conducting a series of stress tests can reveal how well the unit copes under increased demand, ensuring it can handle real-world scenarios effectively.
Finally, documenting all test results is essential for future reference and accountability. This documentation not only serves as a record of the current state of the system but also assists in troubleshooting any potential issues that may arise later. By following a comprehensive testing protocol, one can ensure that the equipment operates smoothly and efficiently, prolonging its lifespan and maintaining its reliability.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
Ensuring the durability and efficiency of your equipment requires regular attention and care. By implementing a few key practices, you can significantly extend its lifespan and maintain optimal performance over time. This section outlines essential strategies to keep your system in peak condition.
Routine Inspections
Conducting periodic evaluations is vital for identifying potential issues before they escalate. Regular checks help you monitor the condition of components and ensure everything is functioning as intended.
Cleaning Procedures
Accumulation of dirt and debris can lead to decreased efficiency and operational problems. Establish a routine cleaning schedule to remove contaminants and maintain clear pathways for fluids.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Monthly | Check for leaks or wear. |
| Deep Cleaning | Quarterly | Use appropriate cleaning agents. |
| Lubrication | Every 6 months | Follow manufacturer’s recommendations. |
| Parts Replacement | As needed | Replace worn or damaged components promptly. |
Signs Your Pump Needs Attention
Recognizing the early indicators that a fluid-moving device requires servicing is crucial for maintaining its efficiency and longevity. By being vigilant about changes in performance, you can prevent more significant issues and costly replacements down the line.
Common Symptoms
- Unusual Noises: If you hear grinding, whining, or rattling sounds, it may indicate internal wear or loose components.
- Leaking Fluids: Puddles or damp spots around the unit can signal a seal failure or a crack in the casing.
- Decreased Performance: A noticeable drop in fluid delivery or pressure can point to blockages or mechanical failures.
- Increased Energy Consumption: If the system is drawing more power than usual, it may be struggling to operate effectively.
When to Seek Help
- If you observe multiple symptoms listed above.
- When routine maintenance does not resolve performance issues.
- As soon as you notice unusual vibrations or overheating.
- If there are frequent system shutdowns or interruptions.
Timely action can help avoid further damage, ensuring smooth operation and extending the life of your equipment.
Understanding Pump Specifications
Grasping the details of fluid transfer devices is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Each model comes with its unique set of characteristics, which dictate how effectively it can operate under various conditions. By familiarizing yourself with these traits, you can make informed choices tailored to specific applications.
Specifications often include key metrics that outline the device’s capabilities and limitations. These indicators help in selecting the right unit for your needs, ensuring that it meets the demands of the system it is integrated into.
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Flow Rate | The volume of fluid that can be moved in a given time, typically measured in liters per minute or gallons per minute. |
| Pressure Rating | The maximum pressure that the unit can withstand, often expressed in bar or psi. |
| Power Consumption | The amount of energy required to operate the unit, usually indicated in watts or horsepower. |
| Material Composition | The types of materials used in construction, which can affect durability and compatibility with various fluids. |
| Temperature Range | The range of temperatures within which the device can operate safely and effectively. |
Understanding these specifications enables you to select the most suitable device for your requirements, ensuring reliable and efficient operation over time.
Frequently Asked Repair Questions
This section aims to address common inquiries related to maintenance and troubleshooting of various equipment. Whether you are dealing with issues related to performance or need guidance on specific components, you will find valuable insights here.
What are the signs that my equipment needs attention?
Common indicators include unusual noises, leaks, decreased efficiency, or warning lights. Regular monitoring can help identify these issues early.
How can I perform basic diagnostics?
Begin by checking for visible wear, ensuring all connections are secure, and verifying that power sources are functioning correctly. Consult relevant specifications for detailed guidance.
What tools do I need for minor adjustments?
A basic toolkit including screwdrivers, wrenches, and pliers is essential. Additionally, having a multimeter can help diagnose electrical issues.
Are there any common mistakes to avoid?
Avoid over-tightening screws, using incorrect parts, or neglecting to follow safety protocols. These can lead to further complications or damage.
When should I seek professional assistance?
If you encounter persistent problems despite troubleshooting or if complex repairs are necessary, it is advisable to consult a qualified technician for expert support.