
This section provides essential insights into the upkeep of a classic agricultural vehicle. Understanding the intricacies of machinery is vital for ensuring longevity and optimal performance. By delving into systematic approaches, operators can significantly enhance the reliability of their equipment.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various techniques and strategies aimed at troubleshooting common issues and conducting necessary interventions. Each aspect will be addressed meticulously, enabling users to gain confidence in handling their machinery effectively.
From routine checks to more detailed interventions, this resource aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to maintain peak operational standards. Emphasizing practical tips and preventive measures, you will learn how to safeguard your investment and keep your equipment running smoothly for years to come.

This section aims to provide an in-depth understanding of a classic agricultural vehicle, focusing on its design, functionality, and significance in farming history. The exploration of this vehicle encompasses its mechanical components, operational principles, and the common issues faced by users.
Overview of the Tractor
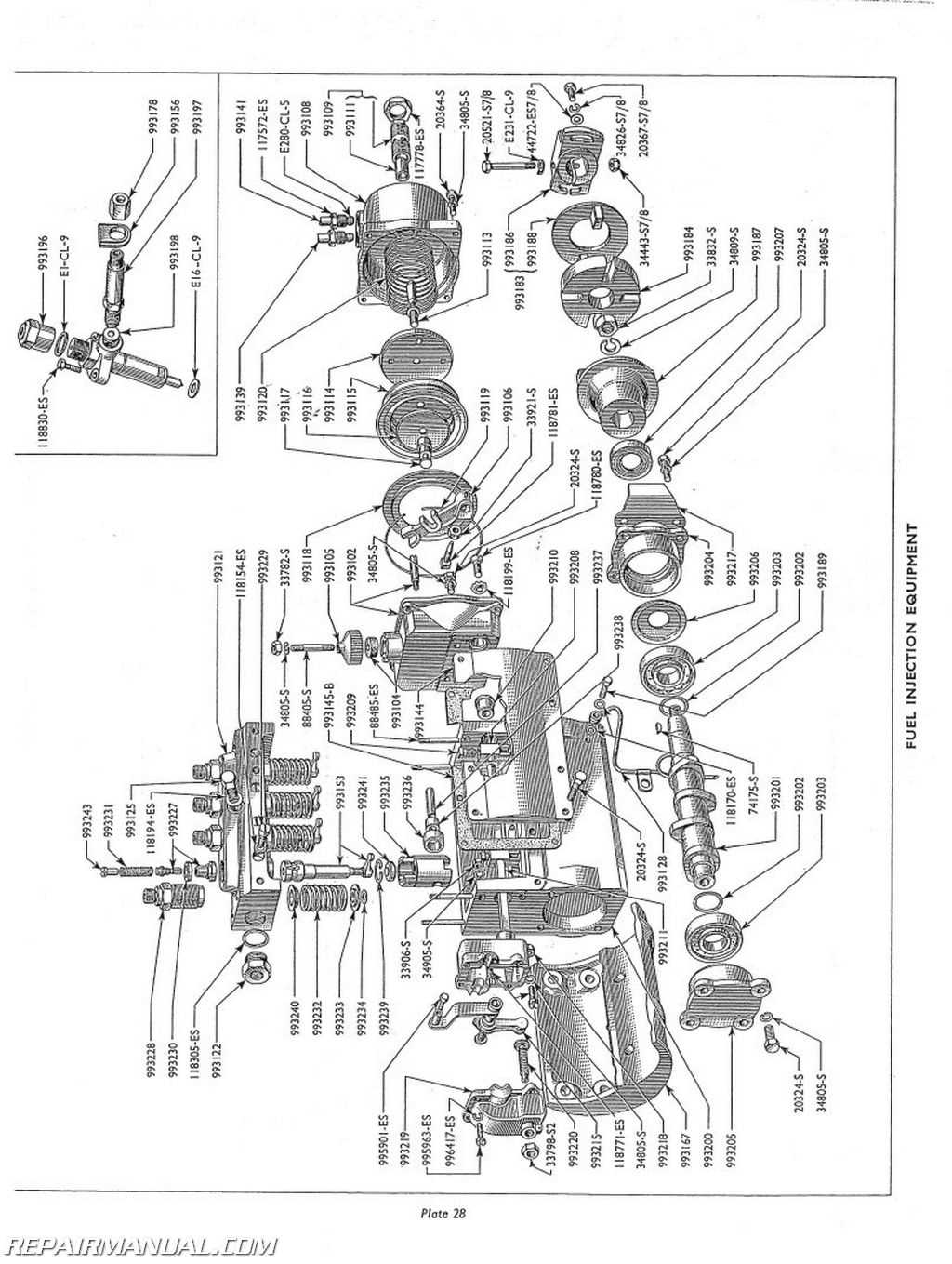
The machine is renowned for its robust construction and reliable performance in various agricultural tasks. Originally designed to meet the needs of farmers, it has become a staple in many farming operations.
- Durable engineering for extended use
- Versatile applications in farming
- Economical fuel consumption
Key Components and Features

Understanding the main components of the vehicle is crucial for effective operation and maintenance. Each part plays a vital role in ensuring the smooth functioning of the machine.
- Engine: The heart of the tractor, responsible for power generation.
- Transmission: Facilitates the transfer of power to the wheels.
- Hydraulics: Essential for lifting and operating various implements.
By familiarizing oneself with these elements, operators can enhance their experience and troubleshoot issues more effectively.
Key Features of the Fordson Major

This section explores the standout attributes of a well-known agricultural vehicle, highlighting its practical advantages and design elements that make it a preferred choice among farmers and enthusiasts. The focus will be on its operational efficiency, durability, and versatility, showcasing why it remains a significant player in the world of farming machinery.
Robust Engine Performance
The powerhouse of this vehicle is its highly efficient engine, delivering substantial torque and horsepower. This robust performance allows for effective handling of various tasks, whether in plowing, hauling, or other demanding operations. Fuel efficiency is another notable aspect, ensuring that users can accomplish more with less, making it economically viable for long-term use.
User-Friendly Design

Comfort and ease of use are prioritized in the design of this machine. The intuitive controls and layout allow operators to navigate with minimal effort. Adjustable seating and ergonomic features enhance user comfort during extended periods of operation, reducing fatigue. Additionally, the vehicle’s compact dimensions enable maneuverability in tight spaces, which is essential for various agricultural settings.
Common Issues and Solutions

This section addresses frequent challenges faced by users and offers effective strategies for resolution. Understanding these problems can enhance the overall experience and prolong the lifespan of your equipment.
Engine Overheating: One common issue is overheating, which may result from inadequate coolant levels or a malfunctioning thermostat. Regularly check coolant levels and ensure the thermostat is functioning properly to maintain optimal engine temperature.
Starting Difficulties: If the machinery is hard to start, it may be due to a weak battery or fuel delivery issues. Inspect the battery condition and connections, and ensure that fuel lines are clear and free of obstructions.
Unusual Noises: Unwanted sounds during operation can indicate problems with components such as belts or bearings. Regularly inspect these parts for wear and tear, and replace them as necessary to prevent further damage.
Hydraulic System Failure: Issues in the hydraulic system often stem from leaks or low fluid levels. Regularly check for leaks and maintain proper fluid levels to ensure smooth operation.
Transmission Slipping: If the transmission is slipping, it may be due to low fluid levels or worn clutches. Regular fluid checks and timely maintenance can help address these issues before they escalate.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity

Ensuring the extended lifespan of machinery requires consistent attention and care. By following a few essential practices, operators can significantly enhance the durability and performance of their equipment. Regular maintenance not only prevents unexpected breakdowns but also optimizes efficiency, ultimately saving time and resources.
Here are some crucial guidelines to follow:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Inspections | Conduct frequent checks to identify wear and tear early, addressing issues before they escalate. |
| Fluid Levels | Keep all fluid levels, such as oil and coolant, at optimal levels to ensure smooth operation and prevent overheating. |
| Cleaning | Regularly clean the exterior and interior components to remove dirt and debris, which can hinder performance. |
| Lubrication | Apply lubricant to moving parts to reduce friction and wear, extending the life of essential components. |
| Battery Care | Check battery connections and charge levels to ensure reliable starts and efficient power supply. |
Implementing these strategies can lead to better performance and a longer operational life for your machinery. Prioritizing regular upkeep creates a more reliable and efficient work environment.
Step-by-Step Repair Procedures

This section provides a comprehensive guide to effective maintenance and troubleshooting techniques for your equipment. The following instructions are designed to enhance your understanding of the processes involved, ensuring that you can tackle any challenges with confidence.
1. Preparation: Before beginning any work, gather all necessary tools and materials. Ensure you have a clean and organized workspace to facilitate the process.
2. Safety First: Always prioritize safety. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and follow standard safety protocols to avoid accidents.
3. Assessment: Conduct a thorough evaluation of the system. Identify any issues that need addressing and make a list of components that require attention.
4. Disassembly: Carefully take apart the necessary parts, keeping track of each component. Document the disassembly process to aid reassembly later.
5. Inspection: Examine all parts for wear, damage, or corrosion. Replace any defective components to ensure optimal functionality.
6. Cleaning: Clean all parts thoroughly using appropriate solvents or cleaning agents. Remove dirt and debris to prevent future issues.
7. Reassembly: Reassemble the components according to the documentation. Ensure each part is correctly positioned and secured.
8. Testing: After reassembly, conduct tests to verify that the system operates as expected. Monitor for any irregularities during the operation.
9. Final Checks: Perform a final inspection to ensure all tools are removed from the workspace, and everything is in order before concluding the process.
Following these detailed procedures will not only enhance your skills but also contribute to the longevity and efficiency of your machinery.
Tools Required for Repairs

When undertaking maintenance or restoration tasks, having the right equipment is essential for ensuring efficiency and effectiveness. This section outlines the necessary instruments and devices needed for successful troubleshooting and fixing various issues.
Essential Instruments
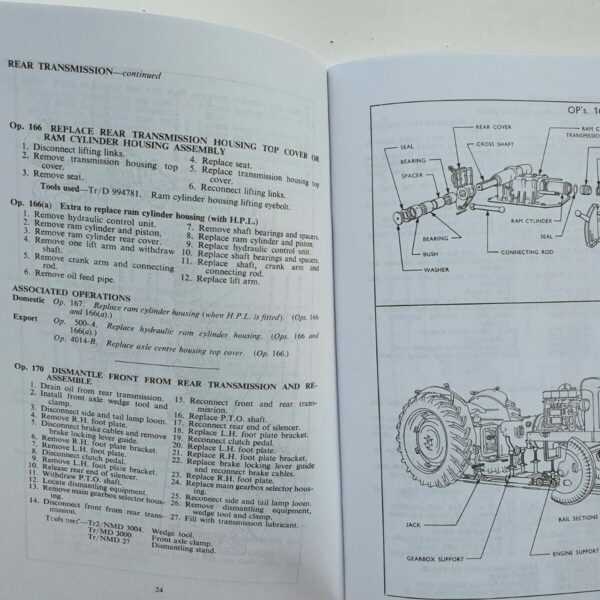
- Wrenches of various sizes
- Socket set with ratchet
- Screwdrivers (flathead and Phillips)
- Pliers (needle-nose and standard)
- Torque wrench for precise fittings
Specialized Equipment

- Multimeter for electrical diagnostics
- Compression tester for engine assessments
- Oil filter wrench for easy access
- Jack and jack stands for lifting
- Diagnostic scanner for troubleshooting
Gathering these tools will facilitate a smoother process, enabling effective identification and resolution of mechanical problems. Ensuring proper equipment is on hand before starting any project can save time and enhance overall productivity.
Engine Overhaul Instructions

This section provides detailed guidance on the process of rebuilding the engine to restore its optimal performance. Proper maintenance and thorough understanding of the engine’s components are essential for successful completion of this task.
Before starting the overhaul, ensure you have the necessary tools and a clean workspace. Follow these steps to achieve a successful engine refurbishment:
- Preparation:
- Gather all required tools and parts.
- Disconnect the battery and drain all fluids.
- Label all wires and hoses for easy reinstallation.
- Disassembly:
- Remove the engine from the chassis.
- Carefully take apart the engine components, including the cylinder head, pistons, and crankshaft.
- Inspect each part for wear or damage.
- Cleaning:
- Clean all components using a suitable solvent.
- Remove any carbon deposits and old gasket material.
- Check for cleanliness before reassembly.
- Reassembly:
- Replace any worn or damaged parts with new ones.
- Follow the specified torque settings for bolts.
- Reinstall the components in reverse order of disassembly.
- Testing:
- Reconnect the battery and refill fluids.
- Start the engine and monitor for unusual sounds or leaks.
- Allow the engine to run for a short period and check for proper operation.
By adhering to these instructions, you can effectively overhaul the engine, ensuring it runs efficiently for many more miles.
Electrical System Troubleshooting
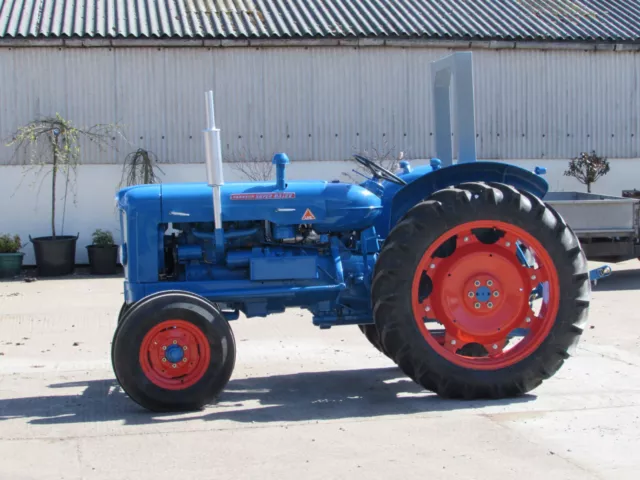

This section aims to guide you through diagnosing and resolving issues related to the electrical components of your vehicle. Understanding the fundamentals of the electrical system is crucial for identifying faults and ensuring optimal performance.
Begin by checking the following key areas:
- Battery Condition: Inspect for signs of corrosion or loose connections. Ensure that the battery is fully charged.
- Circuit Integrity: Examine wiring for damage, fraying, or breaks that could disrupt the flow of electricity.
- Fuses: Check for blown fuses that may indicate an overload or short circuit in the system.
- Ground Connections: Ensure that all ground points are clean and securely connected to prevent electrical faults.
If problems persist, follow these troubleshooting steps:
- Test the battery voltage using a multimeter. A reading below the recommended level indicates the need for replacement or recharging.
- Verify the operation of switches and relays by checking for continuity and function.
- Inspect the alternator output to ensure it is charging the battery effectively.
- Utilize a wiring diagram to trace circuits and locate potential issues.
Document your findings and repairs to create a reference for future maintenance and troubleshooting efforts. Regular checks can help prevent electrical failures and extend the life of your vehicle’s components.
Hydraulic System Maintenance Guide

Maintaining the hydraulic system is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of your machinery. Regular checks and servicing can prevent breakdowns and enhance efficiency, making it crucial for operators to understand the basic maintenance practices involved.
Regular Inspection Procedures
Routine inspections should be conducted to identify any signs of wear or potential issues. This includes checking for leaks, assessing the condition of hoses, and ensuring that fluid levels are adequate. Here is a simple checklist for effective inspection:
| Inspection Item | Frequency | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Level Check | Weekly | Top up if low |
| Hose Condition | Monthly | Replace if damaged |
| Filter Status | Every 500 hours | Clean or replace |
Fluid Maintenance Tips

Proper management of hydraulic fluid is vital for system performance. Ensure to use the correct type of fluid recommended for your equipment. Additionally, it’s important to replace the fluid at intervals specified by the manufacturer to prevent contamination and maintain hydraulic efficiency.
Bodywork and Aesthetic Repairs
Maintaining the exterior of your vehicle is essential for both functionality and visual appeal. This section focuses on techniques and approaches to enhance the overall appearance and integrity of the vehicle’s body. Addressing issues such as dents, scratches, and corrosion not only improves aesthetics but also helps in preserving the underlying structure.
Identifying Damage: The first step in any aesthetic enhancement process is to thoroughly inspect the bodywork for any imperfections. Look for signs of wear, including minor dents and paint chips, which can be addressed with appropriate methods.
Repair Techniques: Various techniques can be employed to restore the bodywork. For shallow dents, paintless dent removal is often effective, preserving the original finish. Scratches can be treated using a combination of sanding and repainting to blend seamlessly with the surrounding area. For more severe damage, it may be necessary to replace panels entirely.
Protection Measures: To prevent future damage, consider applying a protective coating or wax. This not only enhances the shine but also acts as a barrier against environmental factors. Regular washing and maintenance routines will further extend the life of the exterior surfaces.
By focusing on bodywork and aesthetic improvements, you ensure that your vehicle remains in excellent condition, contributing to both its value and your driving enjoyment.
Safety Precautions During Repairs

Ensuring safety while performing maintenance on machinery is crucial for both the technician and the equipment. Proper precautions help prevent accidents and injuries, promoting a secure working environment.
Before starting any service, consider the following guidelines:
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and steel-toed boots.
- Ensure the work area is clean and free of obstacles to avoid tripping hazards.
- Disconnect the power source and secure the machine to prevent unintended movement.
- Keep all tools organized and within reach to minimize distractions and enhance efficiency.
Additionally, it is important to:
- Read all relevant documentation to understand the specific requirements for the task at hand.
- Be aware of your surroundings, including other personnel and potential hazards.
- Communicate clearly with team members regarding tasks and responsibilities.
By adhering to these safety measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and ensure a smooth maintenance process.