
Understanding the complexities involved in the upkeep of specialized machinery is essential for optimal performance. This section provides insights into the various components that contribute to the functionality of elevating systems, ensuring safety and efficiency in their operation.
Effective handling of these mechanisms requires knowledge of both routine procedures and advanced techniques. By familiarizing oneself with the intricacies of assembly and potential issues, operators can significantly enhance the longevity and reliability of the equipment.
This resource aims to equip users with essential information, enabling them to address common challenges and perform necessary adjustments. With the right approach, maintaining such systems can be both manageable and rewarding.
This section aims to elucidate the intricate mechanisms and functionalities of specific elevation systems employed in various settings. By examining the core components and their interactions, one can gain insights into the operational principles that underpin these structures.
Key Components of Elevation Systems
- Hydraulic Cylinders: These units provide the necessary force for movement.
- Control Valves: Responsible for regulating the flow of fluid within the system.
- Power Units: These are crucial for generating the energy required for operation.
- Safety Mechanisms: Essential features designed to ensure user protection during use.
Operational Principles

- The system initiates movement through the activation of power units.
- Fluid is directed via control valves to hydraulic cylinders, creating lift.
- Safety mechanisms engage automatically to prevent accidents during operation.
- Upon completion, the system reverses the process, lowering the structure safely.
Common Issues with Rotary Lifts
When it comes to hydraulic platforms, several frequent complications can arise, impacting their performance and safety. Understanding these common challenges is essential for effective maintenance and ensuring optimal functionality.
1. Hydraulic Fluid Leaks
One of the most prevalent issues involves fluid escaping from the system. This can lead to decreased efficiency and potential hazards. Key factors contributing to this problem include:
- Worn seals or gaskets
- Punctured hoses
- Corroded fittings
2. Electrical Failures

Another critical concern is related to the electrical components that control the operation of the platform. Failures in this area can halt functionality entirely. Common causes include:
- Damaged wiring
- Faulty switches
- Malfunctioning control units
Essential Tools for Repairs
Having the right equipment is crucial for effectively addressing issues and ensuring longevity in operation. A well-equipped toolkit not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes potential risks during maintenance tasks. Below are some key implements that are indispensable for successful troubleshooting and upkeep.
Basic Hand Tools
Essential hand tools form the foundation of any maintenance kit. Items such as wrenches, pliers, and screwdrivers are vital for various tasks. These instruments allow for adjustments and disassembly of components, facilitating quick fixes and thorough inspections.
Specialized Equipment
In addition to standard hand tools, certain specialized instruments may be required for specific tasks. This could include torque wrenches for precise fastening, multimeters for electrical diagnostics, and hydraulic jacks for lifting heavy parts. Utilizing these tailored devices ensures that all aspects of maintenance can be addressed effectively.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
This section provides a systematic approach to identifying and resolving common issues encountered during operation. By following these outlined procedures, users can efficiently pinpoint the source of the problem and implement corrective actions.
Begin by observing the situation carefully, noting any unusual signs or behaviors. Use the table below to guide your diagnostic process.
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment does not activate | Power supply issue | Check power connections and fuses |
| Unexpected noises during operation | Mechanical obstruction | Inspect for debris and clear any blockages |
| Inconsistent performance | Wear on components | Examine parts for signs of deterioration and replace if necessary |
| Error messages displayed | Faulty sensors | Reset the system and check sensor connections |
By diligently working through this guide, users can enhance the longevity and effectiveness of their equipment.
Maintenance Practices for Longevity

Ensuring the durability of equipment involves implementing systematic care and attention to detail. Adopting a proactive approach to upkeep can significantly extend the lifespan of mechanical systems, minimizing the likelihood of unexpected failures and costly repairs.
Regular Inspections
Conducting frequent evaluations is crucial. Visual checks for wear and tear, as well as functional assessments, help identify potential issues early. This practice not only enhances safety but also contributes to optimal performance.
Lubrication and Cleaning
Proper lubrication is essential for reducing friction and preventing rust. Regularly cleaning components removes debris and contaminants that could impede functionality. Establishing a routine schedule for these tasks will ensure that systems operate smoothly and efficiently.
Electrical Components Overview
This section provides a comprehensive look at essential electrical parts found within various lifting systems. Understanding these elements is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety during operations.
Power Supply Units are fundamental as they convert electrical energy into usable power, supplying the necessary voltage to various components. Regular checks can prevent unexpected failures.
Control Panels serve as the command center, allowing operators to manage functions and monitor the system’s status. They integrate user-friendly interfaces with advanced diagnostics to streamline operation.
Sensors play a pivotal role in enhancing safety and efficiency. These devices monitor different parameters and provide real-time feedback, enabling prompt responses to any irregularities.
Lastly, Wiring Harnesses are critical for connecting all components, ensuring seamless communication within the system. Proper installation and maintenance are vital to avoid electrical malfunctions.
Hydraulic Systems Explained

Hydraulic systems are essential mechanisms that utilize the principles of fluid dynamics to transfer force and motion. These systems leverage incompressible fluids to enable smooth operation and enhance efficiency in various applications. Understanding the fundamentals of these systems can provide insight into their effective implementation and maintenance.
Key Components of Hydraulic Systems
- Fluid Reservoir: A container that stores the hydraulic fluid required for operation.
- Pump: A device that generates flow by converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy.
- Actuator: An element that converts hydraulic energy back into mechanical motion.
- Valves: Components that control the direction and flow of the hydraulic fluid.
Advantages of Hydraulic Systems

- High Power-to-Weight Ratio: These systems can transmit significant force without large machinery.
- Smooth Operation: Hydraulic mechanisms allow for gradual and controlled movements.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications, from machinery to automotive systems.
Safety Protocols During Repairs

Ensuring a secure environment during maintenance activities is crucial for the safety of personnel and equipment. Adhering to established guidelines minimizes risks and promotes a culture of caution.
Prior to beginning any maintenance work, it is essential to assess the workspace for potential hazards. This includes verifying that the area is well-lit, free from clutter, and that all necessary safety equipment is readily available. Proper personal protective gear should be worn at all times, including gloves, helmets, and safety glasses.
Before initiating any procedures, a thorough understanding of the equipment involved is vital. Familiarize yourself with the operational aspects and identify emergency shutdown mechanisms. Collaborating with team members can enhance safety; communicate effectively about tasks and responsibilities to ensure everyone is aware of their roles.
During the maintenance process, maintain a clear focus on the task at hand. Avoid distractions and take regular breaks to prevent fatigue. Regularly inspect tools for wear and damage, ensuring they are in optimal condition to avoid accidents.
Lastly, always follow the specific guidelines provided by the manufacturer or regulatory bodies. Staying informed about the latest safety standards and practices helps cultivate a safer working environment for all.
Identifying Wear and Tear Signs

Recognizing the indicators of deterioration is crucial for maintaining optimal functionality and safety. Regular inspection can help detect issues before they escalate, ensuring longevity and efficiency.
Here are some common signs to look for:
- Visible Cracks: Inspect surfaces for any fractures that may compromise structural integrity.
- Unusual Noises: Listen for grinding, squeaking, or rattling sounds during operation, which may signal internal problems.
- Fluid Leaks: Check for any fluids pooling beneath components, indicating potential leakage that requires attention.
- Irregular Movement: Observe any jerky or inconsistent motion, which can suggest worn parts or misalignment.
- Excessive Heat: Monitor temperature during use; overheating may indicate friction or resistance issues.
By keeping an eye on these aspects, you can proactively address wear and prolong the lifespan of your equipment.
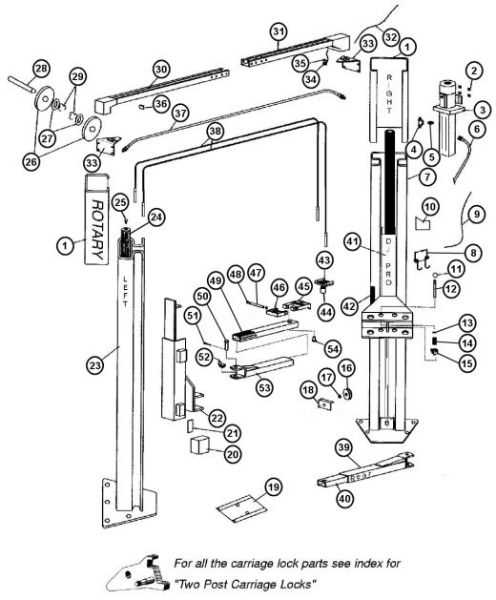
Parts Replacement Procedures
This section outlines the essential steps and guidelines for exchanging components within the equipment. Proper adherence to these instructions ensures optimal performance and longevity of the system, reducing the likelihood of future issues.
Preparation Steps

Before commencing the replacement process, ensure the following preparations are made:
- Gather all necessary tools and replacement parts.
- Review the specifications for each component to be replaced.
- Ensure a safe working environment, including proper lighting and clearance.
Replacement Steps
Follow these systematic procedures for replacing the specified parts:
| Component | Replacement Steps |
|---|---|
| Hydraulic Cylinder |
1. Disconnect the hydraulic lines. 2. Remove securing bolts. 3. Extract the old cylinder and insert the new one. 4. Reconnect the hydraulic lines and secure everything. |
| Control Panel |
1. Disconnect power supply. 2. Unscrew the panel from its mounting. 3. Disconnect the wiring harness. 4. Connect the new panel and secure it in place. |
| Safety Sensors |
1. Disconnect the sensors from the power source. 2. Remove the mounting brackets. 3. Install the new sensors and secure them. 4. Reconnect to the power source. |
Documentation and Record Keeping
Maintaining accurate and thorough records is essential for effective maintenance and servicing of equipment. Proper documentation not only ensures compliance with industry standards but also facilitates timely repairs and performance assessments. A well-organized system for recording activities helps in tracking the history of interventions, parts used, and inspections carried out.
Importance of Accurate Records
Keeping precise documentation serves multiple purposes, including aiding in the identification of recurring issues, optimizing maintenance schedules, and enhancing safety protocols. Detailed records also provide valuable insights for future enhancements and troubleshooting, making them an integral part of any service operation.
Recommended Record-Keeping Practices
To ensure effective documentation, consider the following practices:
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Consistent Format | Utilize a uniform template for all entries to streamline information retrieval. |
| Timely Updates | Document all activities immediately after they occur to avoid missing critical details. |
| Digital Solutions | Adopt electronic record-keeping systems for easier access and improved data management. |
| Regular Reviews | Conduct periodic audits of records to ensure accuracy and completeness. |
Best Practices for User Training
Effective training is essential for ensuring users are well-equipped to operate complex equipment safely and efficiently. A comprehensive approach not only enhances proficiency but also minimizes the risk of accidents and equipment damage. Implementing structured learning techniques can significantly improve the overall experience for users.
To achieve optimal results in training, consider the following guidelines:
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Hands-On Training | Engage users in practical exercises that mimic real-world scenarios to build confidence and skill. |
| Structured Curriculum | Develop a clear and organized training program that covers all necessary topics systematically. |
| Assessment and Feedback | Regularly evaluate user performance and provide constructive feedback to identify areas for improvement. |
| Safety Protocols | Emphasize the importance of adhering to safety guidelines to protect users and maintain equipment integrity. |
| Continuous Learning | Encourage ongoing education through workshops and refresher courses to keep skills up to date. |