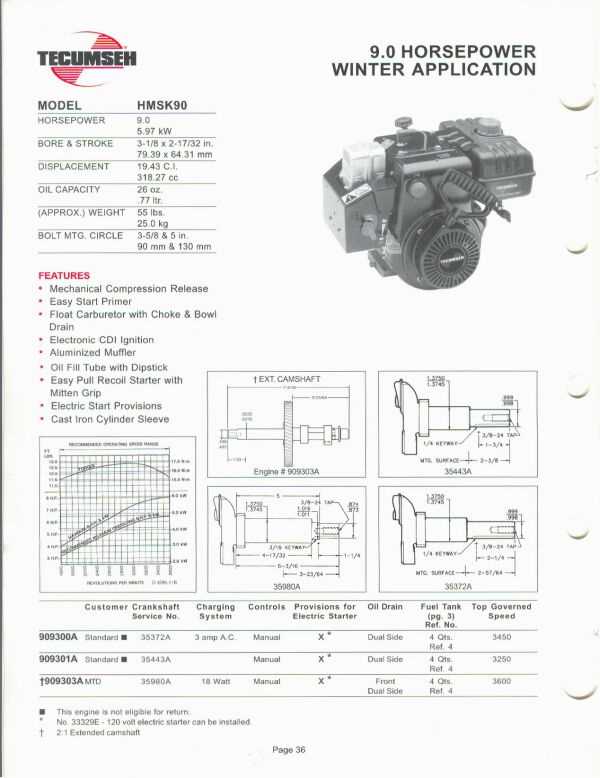
Maintaining small engines is essential for ensuring their longevity and optimal performance. This guide delves into the intricacies of servicing a specific type of engine, providing detailed insights and step-by-step procedures for tackling common issues. Whether you’re a seasoned technician or a novice enthusiast, this resource will enhance your understanding and skills.
Engines are intricate machines that require regular attention to keep them running smoothly. From troubleshooting to reassembling components, each phase of maintenance is crucial. This article highlights the fundamental techniques and practices necessary for effective upkeep, focusing on practical tips that simplify complex tasks.
By following the instructions outlined here, users can effectively address various challenges encountered during engine maintenance. With a clear focus on hands-on methods, this guide aims to empower individuals to take charge of their machinery, fostering a deeper connection between operator and engine.
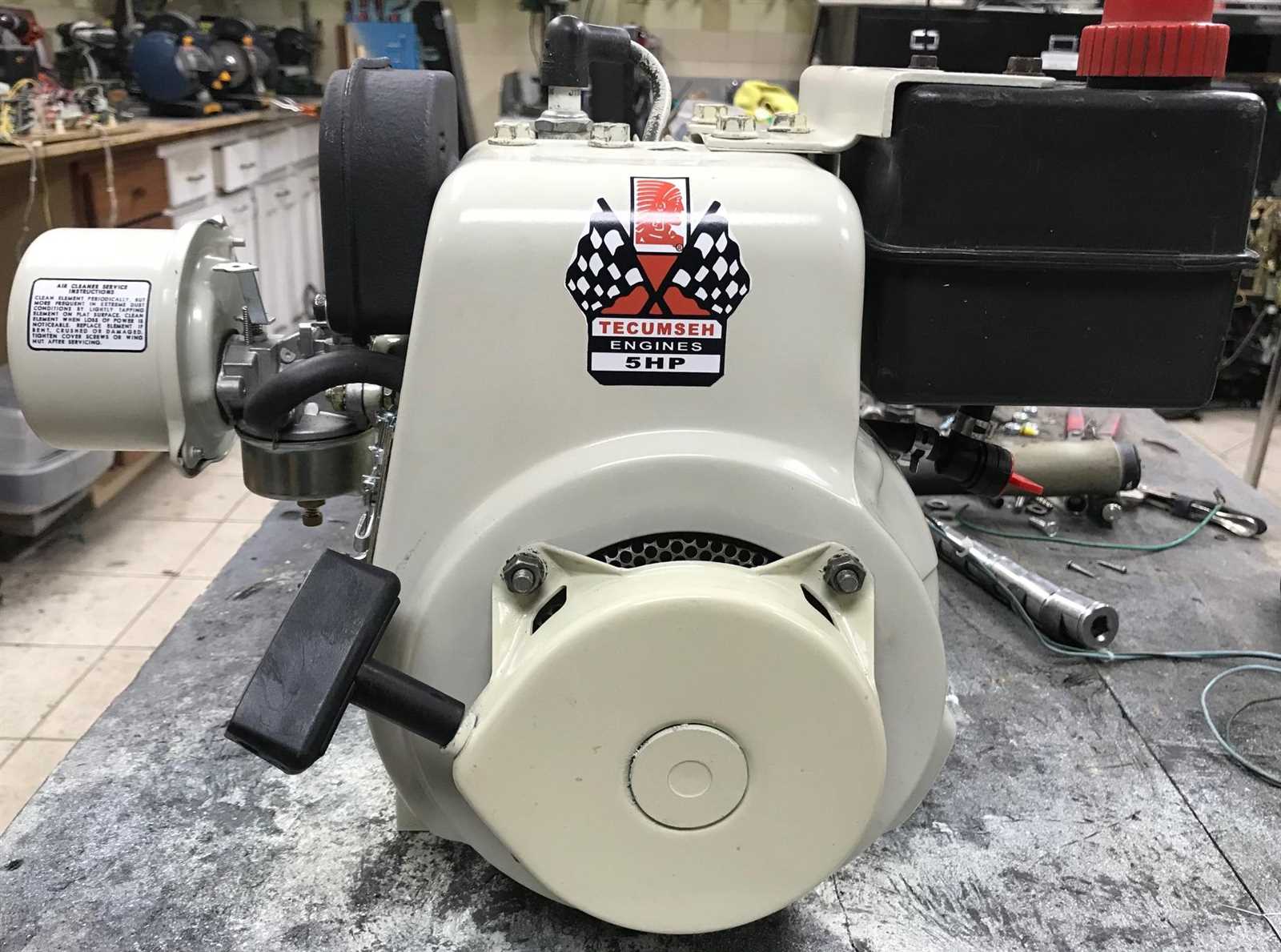
Engine Overview

This section provides a comprehensive insight into a specific model of small engine known for its reliability and versatility. Often utilized in various applications, this power unit has garnered attention for its efficiency and ease of maintenance, making it a preferred choice among enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Key Features

- Compact design suitable for tight spaces
- Lightweight construction for enhanced portability
- Robust performance ideal for diverse tasks
- Easy starting mechanism that simplifies operation
Specifications

- Cylinder configuration: Single-cylinder
- Displacement: Approximately 5 horsepower
- Cooling system: Air-cooled for efficient heat management
- Fuel type: Typically operates on regular gasoline
This engine type stands out for its user-friendly design and adaptability across various equipment, ensuring it remains a valuable asset in both residential and commercial settings.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
When dealing with small engines, users often encounter a range of typical challenges that can hinder performance. Understanding these common problems and their solutions is essential for maintaining optimal functionality. This section will address frequent issues and provide guidance on how to troubleshoot effectively.
Starting Difficulties
One of the most prevalent concerns is difficulty in starting the engine. This issue may stem from various sources, such as insufficient fuel supply, clogged air filters, or malfunctioning spark plugs. To diagnose the problem, check the fuel level and ensure that the fuel is fresh. Inspect the air filter for debris and clean or replace it if necessary. Lastly, examine the spark plug for wear or carbon buildup, and replace it if needed.
Overheating
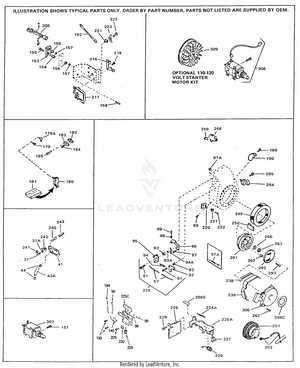
Overheating can lead to severe engine damage if not addressed promptly. Common causes include blocked cooling fins, low oil levels, or a malfunctioning cooling system. To troubleshoot overheating, start by inspecting the cooling fins for dirt or debris that could obstruct airflow. Verify the oil level and top it off if necessary. If the issue persists, check the cooling system for any leaks or failures that may require further attention.
Essential Tools for Repairs

When undertaking maintenance tasks, having the right equipment is crucial for efficiency and effectiveness. A well-equipped toolkit not only simplifies the process but also enhances the quality of the work being performed. Below is a list of fundamental instruments that can make a significant difference during service activities.
- Wrenches: Adjustable and fixed wrenches are essential for loosening and tightening various nuts and bolts.
- Screwdrivers: A set of both flathead and Phillips screwdrivers will cover most fastening needs.
- Pliers: These are invaluable for gripping, twisting, and cutting tasks.
- Socket Set: A comprehensive socket set allows for quick adjustments and can reach fasteners in tight spaces.
- Torque Wrench: Ensures that bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications, preventing over-tightening.
- Multimeter: Useful for diagnosing electrical issues, measuring voltage, and testing continuity.
Equipping yourself with these basic tools not only prepares you for a variety of challenges but also instills confidence in handling different projects effectively.
Step-by-Step Repair Procedures

This section provides a comprehensive guide to addressing common issues associated with small engines. Each step is designed to be clear and straightforward, ensuring that you can follow along with ease. Understanding the process will help you restore functionality effectively and safely.
1. Gather Necessary Tools and Materials: Before starting, collect all essential tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and replacement parts. Having everything on hand will streamline the process and minimize interruptions.
2. Disconnect Power Source: Always ensure that the engine is turned off and disconnected from any power supply. This safety measure is crucial to prevent accidents during the procedure.
3. Inspect and Clean Components: Begin by examining all parts for wear or damage. Clean the components thoroughly to remove any debris or buildup that could affect performance.
4. Replace Worn Parts: If any components are found to be damaged, replace them with high-quality substitutes. Ensure that new parts match the specifications required for optimal operation.
5. Reassemble Engine: After addressing all necessary repairs, carefully reassemble the engine. Ensure that all screws and bolts are tightened to the recommended torque specifications.
6. Test Functionality: Once reassembly is complete, reconnect the power source and conduct a test run. Observe the engine’s performance to confirm that issues have been resolved.
7. Regular Maintenance: To prolong the lifespan of your engine, implement a regular maintenance schedule. Routine checks and cleanings will help prevent future problems and ensure smooth operation.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity

Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring that machinery operates efficiently over time. By following a few simple guidelines, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your equipment and reduce the likelihood of unexpected failures.
Routine Inspections

- Check for leaks or signs of wear on a regular basis.
- Inspect all moving parts for proper lubrication and functionality.
- Ensure that filters are clean and replace them as needed.
Proper Storage

- Store the equipment in a dry, sheltered area to prevent rust and corrosion.
- Cover the machinery to protect it from dust and debris.
- Keep it out of direct sunlight to avoid damage from UV rays.
By implementing these practices, you can maintain optimal performance and longevity, ensuring your investment remains productive for years to come.
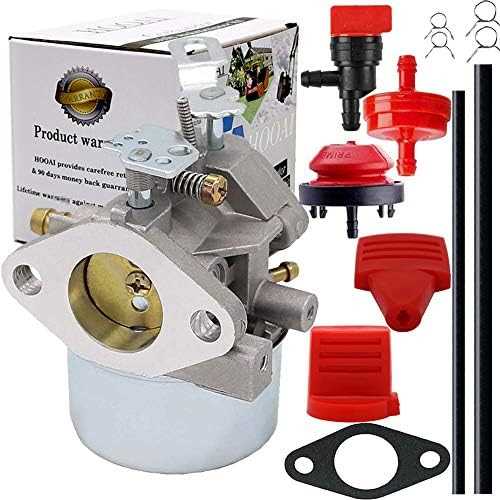
Understanding Tecumseh H50 Parts

Grasping the components of small engines is crucial for effective maintenance and troubleshooting. Each part plays a vital role in the overall functionality, ensuring optimal performance. Familiarity with these elements allows for better decision-making when it comes to service and upgrades.
Key Components Overview
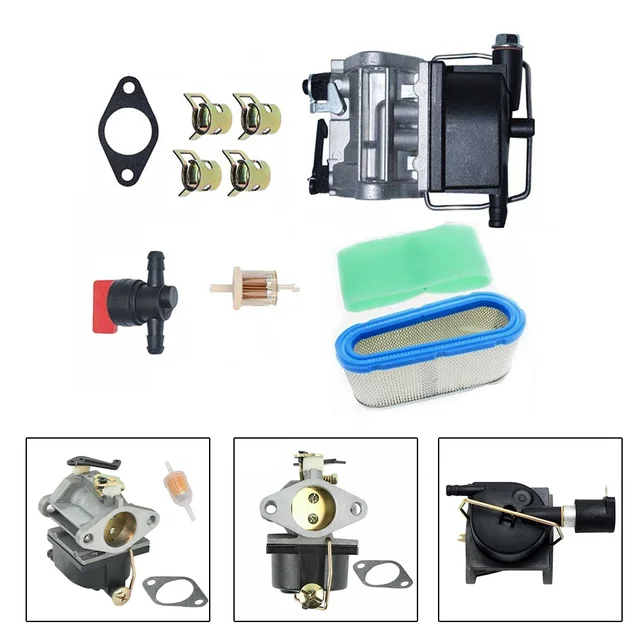

Every engine is composed of several essential parts, each designed to perform specific functions. Understanding these components can help in diagnosing issues and planning for replacements or enhancements. Here are some of the main elements:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cylinder | Houses the piston and allows for combustion. |
| Piston | Moves up and down to create pressure for combustion. |
| Carburetor | Mixes air and fuel for combustion efficiency. |
| Crankshaft | Translates linear motion of the piston into rotational motion. |
| Ignition System | Generates a spark to ignite the fuel-air mixture. |
Importance of Understanding Components

Knowing how each part operates and interacts with others is essential for anyone involved in engine care. This knowledge not only facilitates smoother operation but also extends the lifespan of the equipment. Furthermore, being informed about component upgrades can lead to enhanced performance and efficiency.
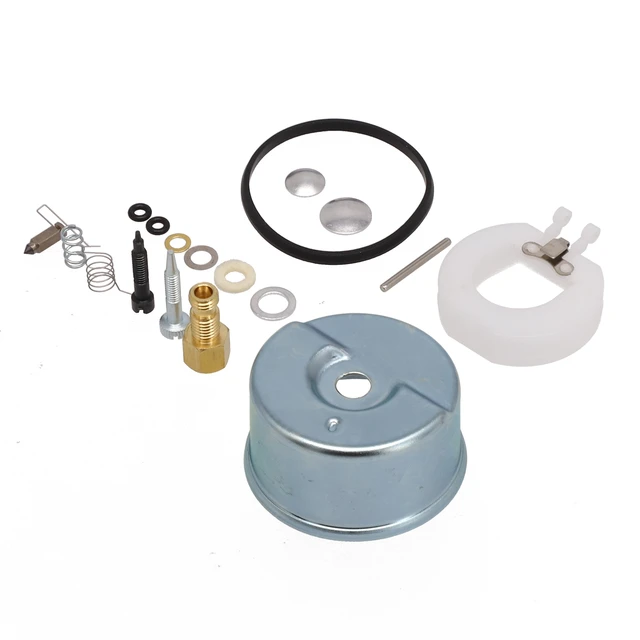
Fuel System Repair Guidelines
The functionality of an engine largely depends on the efficiency of its fuel delivery system. Proper maintenance and troubleshooting are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity. This section outlines key steps to diagnose and address common issues within the fuel system, promoting smooth operation and reliability.
Inspecting Fuel Lines: Start by examining the fuel lines for any signs of wear or damage. Cracks, leaks, or blockages can significantly hinder fuel flow. Replace any compromised sections to maintain a steady supply.
Cleaning the Carburetor: A dirty carburetor can lead to poor engine performance. Disassemble the unit carefully, paying attention to the jets and passages. Use a suitable cleaning solution to remove deposits and ensure all components are free from obstruction.
Checking Fuel Filter: A clogged fuel filter can restrict fuel flow, causing erratic engine behavior. Regularly inspect and replace the filter as necessary to guarantee clean fuel reaches the engine.
Examining Fuel Quality: Poor-quality fuel can introduce contaminants into the system. Always use fresh fuel from reputable sources, and consider adding a fuel stabilizer to prevent degradation during storage.
Adjusting Fuel Mixture: An improper air-fuel mixture can lead to inefficient combustion. Follow manufacturer specifications to adjust the mixture, ensuring the engine runs smoothly and efficiently.
Testing Fuel Pump: Ensure the fuel pump is functioning correctly by checking for adequate pressure. A malfunctioning pump can result in insufficient fuel delivery, impacting overall performance. Replace the pump if it fails to meet the required specifications.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can effectively maintain and enhance the fuel system’s performance, ultimately extending the lifespan of the engine.
Ignition System Diagnostics

The ignition system is a crucial component in ensuring optimal engine performance. Diagnosing issues within this system can help identify problems that may lead to decreased efficiency, misfires, or starting difficulties. This section provides guidance on how to systematically assess the ignition system to ensure it operates correctly.
Common Symptoms of Ignition Issues
Identifying the signs of malfunction in the ignition system is the first step towards effective troubleshooting. Common symptoms include:
| Symptom | Possible Cause |
|---|---|
| Engine won’t start | Faulty spark plug or ignition coil |
| Rough idling | Worn ignition components |
| Backfiring | Improper timing or defective ignition module |
| Decreased power | Weak spark or electrical issues |
Diagnostic Steps
To effectively diagnose ignition system problems, follow these steps:
- Check the spark plugs for wear and proper gap.
- Test the ignition coil’s output with a multimeter.
- Inspect wiring and connectors for damage or corrosion.
- Examine the ignition timing using a timing light.
By following these diagnostic procedures, one can pinpoint issues within the ignition system, ensuring reliable engine performance.
Safety Precautions During Repairs

Ensuring safety while performing maintenance on machinery is crucial. Proper precautions not only protect the individual working on the equipment but also contribute to the longevity and efficiency of the unit itself. Following a set of guidelines can help mitigate risks associated with mechanical tasks.
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, safety goggles, and steel-toed boots.
- Disconnect power sources before starting any work to prevent accidental activation.
- Ensure the workspace is clean and well-lit to avoid tripping hazards and to enhance visibility.
- Use tools that are in good condition and specifically designed for the task at hand.
Additionally, it is important to follow these best practices:
- Read any relevant documentation to familiarize yourself with the equipment before beginning.
- Keep a first aid kit readily available in case of emergencies.
- Do not work alone; have someone nearby in case assistance is needed.
- Dispose of any hazardous materials according to local regulations.
By adhering to these safety measures, individuals can help ensure a secure environment during maintenance activities, reducing the likelihood of accidents and injuries.
Finding Replacement Parts Easily
Locating the right components for your equipment can often feel overwhelming. However, with a few strategic approaches, you can streamline the process and ensure you find exactly what you need without unnecessary hassle.
Utilize Online Marketplaces: One of the most efficient ways to source spare parts is through various online platforms. Websites dedicated to outdoor equipment and machinery often have extensive inventories. By using specific keywords related to your model, you can quickly narrow down your options.
Join Community Forums: Engaging with fellow enthusiasts in online forums or social media groups can provide valuable insights. Members frequently share their experiences, recommend suppliers, and may even have spare parts available for sale.
Check Local Dealers: Local retailers and authorized dealers can be excellent resources for acquiring original components. Establishing a relationship with a dealer can also lead to helpful tips and information regarding upcoming sales or special orders.
Explore Salvage Yards: For those seeking budget-friendly solutions, salvage yards can be a treasure trove of usable parts. While this option may require more time and effort, the potential savings can be significant.
Use Part Lookup Tools: Many manufacturers provide online tools to help you identify the correct components based on model numbers or descriptions. These tools simplify the selection process and can often link you directly to purchasing options.
By employing these strategies, you can effectively enhance your search for replacement components, ensuring your machinery remains in optimal working condition.