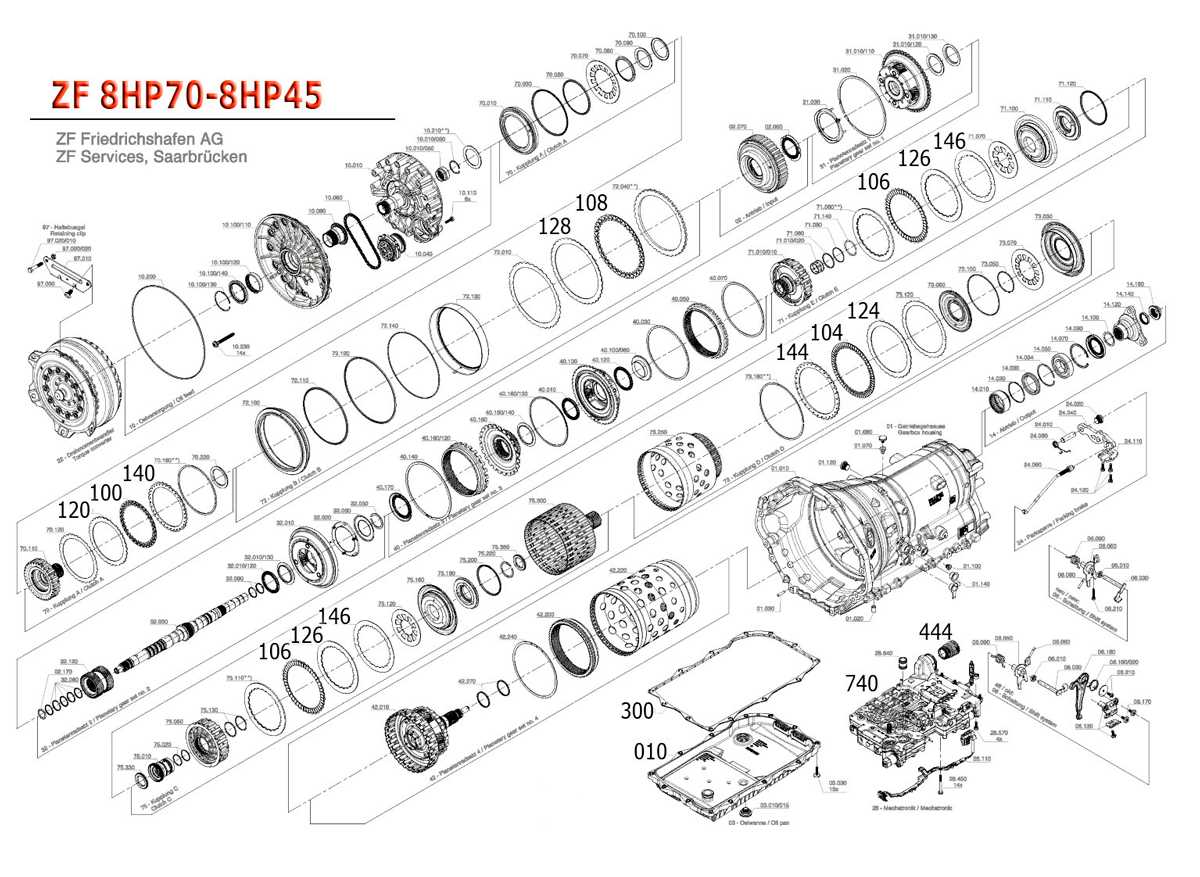
The complexities of modern automotive transmissions require a thorough understanding of their components and functionality. This section delves into the intricacies of a particular transmission system, focusing on maintenance practices and troubleshooting techniques. The aim is to empower vehicle owners and technicians with the knowledge necessary to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
By exploring various operational principles, users can gain insight into the unique challenges associated with this type of drivetrain. Whether you’re an experienced mechanic or a passionate car enthusiast, this guide will provide valuable information to address common issues and enhance your understanding of the system’s workings.
Moreover, it is essential to familiarize oneself with the specific features and functions of the transmission in question. Armed with this knowledge, individuals can make informed decisions regarding service procedures, potential upgrades, and repairs, ultimately leading to a smoother and more efficient driving experience.
ZF 8HP Overview and Features

The ZF transmission system represents a significant advancement in automotive engineering, designed to enhance performance and efficiency. This sophisticated transmission is engineered to provide seamless gear shifts, improving overall driving dynamics. It integrates innovative technologies that optimize power delivery while ensuring a smooth and responsive driving experience.
Key characteristics of this transmission include:
- Adaptive Gear Shifting: Utilizes advanced algorithms to analyze driving behavior, enabling precise gear changes based on the driver’s needs.
- Compact Design: The transmission’s design facilitates easy integration into various vehicle platforms, contributing to space efficiency.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: Enhancements in the shifting mechanism result in reduced fuel consumption without sacrificing performance.
- Robust Durability: Constructed with high-quality materials, ensuring long-lasting performance under demanding conditions.
- Multi-Mode Operation: Offers different driving modes, allowing drivers to select settings that best suit their preferences, from sporty responsiveness to comfort-oriented driving.
This advanced transmission system is widely adopted in various vehicles, reflecting its versatility and capability to meet the demands of modern automotive engineering.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips

Understanding the typical problems that may arise in advanced transmission systems is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. This section provides insights into frequent complications and effective strategies for addressing them, ensuring the longevity and reliability of your vehicle’s transmission.
Frequent Problems
One of the most common challenges faced by users involves erratic shifting behavior. This can manifest as delays, harsh engagement, or slipping during acceleration. Additionally, abnormal noises, such as grinding or whining, often indicate underlying mechanical issues. Another issue is fluid leakage, which can lead to insufficient lubrication and overheating, potentially causing severe damage if not promptly resolved.
Troubleshooting Approaches

To effectively troubleshoot these issues, start by conducting a thorough inspection of the fluid levels and quality. Ensuring the correct type of fluid is used is vital for the system’s performance. If shifting irregularities persist, scanning for error codes can provide valuable insights into specific malfunctions. Regular maintenance checks, including software updates and component examinations, can prevent many of these issues from developing in the first place.
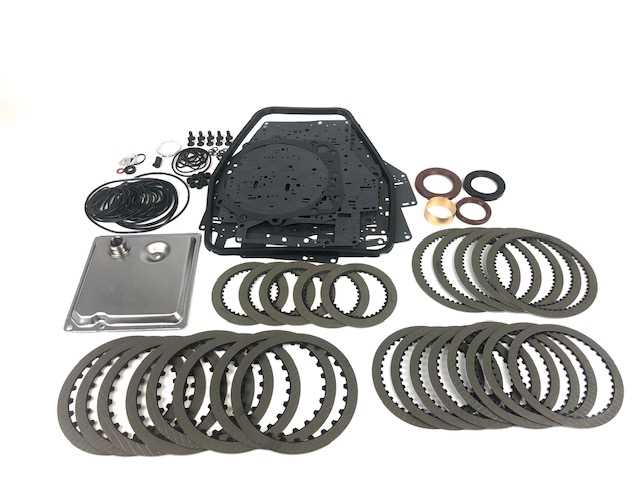
Essential Tools for Repairing ZF 8HP

When working on complex transmission systems, having the right equipment is crucial for ensuring efficiency and precision. Each task requires specific instruments that facilitate the process and enhance the quality of the work performed. This section highlights the key tools needed for effective service and maintenance.
| Tool | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Torque Wrench | A precision instrument used to apply a specific torque to fasteners. | Ensures that bolts are tightened to manufacturer specifications to avoid damage. |
| Transmission Jack | A specialized jack designed for lifting and supporting transmissions. | Provides stability and safety while accessing components. |
| Seal Puller | A tool used to remove seals and gaskets without damaging the housing. | Facilitates easy replacement of seals during disassembly. |
| Fluid Pump | A device for transferring fluid to and from the transmission. | Helps in maintaining proper fluid levels and changes. |
| Diagnostic Scanner | A tool that reads error codes from the vehicle’s computer. | Identifies issues and provides insights into electronic malfunctions. |
Step-by-Step Repair Procedures

This section outlines a systematic approach to addressing common issues that may arise during the maintenance of automotive transmission systems. By following these detailed guidelines, technicians can ensure efficient troubleshooting and effective solutions to restore functionality.
The process begins with a thorough inspection, followed by disassembly, assessment of components, and reassembly. Each step is crucial for diagnosing and resolving the problems effectively.
| Step | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Inspection | Carefully examine the transmission for leaks, unusual noises, or warning lights. |
| 2 | Disassembly | Remove the necessary components to access the internal mechanisms. |
| 3 | Assessment | Evaluate individual parts for wear and damage, noting any that require replacement. |
| 4 | Replacement | Install new components where needed, ensuring all parts meet specifications. |
| 5 | Reassembly | Carefully reassemble the transmission, following manufacturer guidelines to avoid errors. |
| 6 | Testing | Conduct tests to confirm proper operation and identify any remaining issues. |
Following these steps methodically will enhance the likelihood of successful repairs, ensuring the transmission operates smoothly and reliably.
Fluid Specifications and Maintenance
Ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the transmission system requires adherence to specific fluid requirements and regular maintenance practices. This section delves into the essential characteristics of fluids used in modern transmission systems and highlights the importance of routine checks and changes to maintain functionality and efficiency.
Recommended Fluid Types
It is crucial to select the appropriate transmission fluid to facilitate smooth operation and prevent damage. The following table outlines the specifications of recommended fluids, including their properties and typical applications.
| Fluid Type | Viscosity | Specifications | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Synthetic ATF | SAE 5W-30 | Meets or exceeds OEM standards | High-performance applications |
| Mineral-Based ATF | SAE 10W-40 | API GL-4 or equivalent | Standard usage in older systems |
| Low Viscosity ATF | SAE 0W-20 | Specific for certain newer models | Enhanced fuel efficiency |
Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance is vital to ensure the transmission system operates efficiently. Key practices include routine fluid level checks, periodic fluid changes, and replacing filters as necessary. Adhering to manufacturer guidelines regarding service intervals will help prevent premature wear and costly repairs.
Replacing Components: A Comprehensive Guide
This section provides an in-depth look at the process of substituting parts within complex transmission systems. Understanding the intricacies involved in component replacement is essential for maintaining optimal performance and ensuring longevity. This guide aims to equip technicians and enthusiasts with the necessary knowledge and techniques to carry out effective replacements.
Before initiating the replacement process, it is crucial to gather all required tools and components. Proper preparation can significantly reduce the time spent on the task and minimize the risk of errors. Ensure that you have access to the appropriate specifications and manuals, as they contain valuable information regarding the specifications and fitting of each part.
When removing a component, follow a systematic approach to avoid damage to surrounding elements. Start by disconnecting any electrical connections and securing the area to prevent contaminants from entering the system. Carefully label all connections to facilitate reassembly. Utilize the proper techniques to remove fasteners and components, ensuring not to strip screws or cause harm to the housing.
Once the faulty part is extracted, inspect it for wear and damage. This examination can provide insights into the underlying issues that led to its failure. When installing a new component, adhere strictly to the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding torque specifications and installation sequences. Ensuring that components are correctly aligned and seated can prevent future complications and enhance the system’s overall efficiency.
After installation, it is advisable to conduct thorough testing to verify the functionality of the new part. Monitoring the system for any unusual sounds or behaviors can help identify potential issues early on. Regular maintenance checks post-replacement are also essential to ensure continued performance and reliability.
Transmission Diagnostics and Testing

Effective assessment of a vehicle’s transmission system is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Proper diagnostic procedures can identify potential issues before they escalate, saving both time and resources. This section focuses on various techniques and tools used to evaluate transmission functionality, highlighting common symptoms and methods of testing.
Common Symptoms of Transmission Issues

- Slipping gears or unexpected changes in gear
- Unusual noises such as grinding or whining
- Fluid leaks under the vehicle
- Warning lights illuminated on the dashboard
- Poor acceleration or loss of power
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques

- OBD-II Scanner: Utilize an On-Board Diagnostics II scanner to retrieve error codes that can indicate specific transmission malfunctions.
- Fluid Inspection: Examine the transmission fluid for color, odor, and viscosity; degraded fluid can signal potential problems.
- Road Test: Perform a comprehensive road test to assess the vehicle’s shifting performance and responsiveness under various driving conditions.
- Pressure Testing: Measure hydraulic pressure within the transmission system to ensure it meets manufacturer specifications.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a thorough visual examination of external components, including wiring, connectors, and mounts for signs of wear or damage.
Understanding the Control Module Functions
The control module plays a crucial role in the operation and efficiency of advanced transmission systems. Its primary responsibility is to manage and optimize various functions, ensuring that the transmission responds accurately to the driver’s inputs and the vehicle’s operational conditions. By coordinating multiple components, the control module enhances performance and contributes to a seamless driving experience.
Key Responsibilities
One of the main functions of the control module is to process information from various sensors throughout the vehicle. This data includes engine speed, vehicle speed, throttle position, and more. By analyzing this information, the module can make real-time adjustments to shift timing and firmness, improving acceleration and fuel efficiency. Additionally, it monitors the system’s health, identifying potential issues before they lead to significant failures.
Adaptation and Calibration
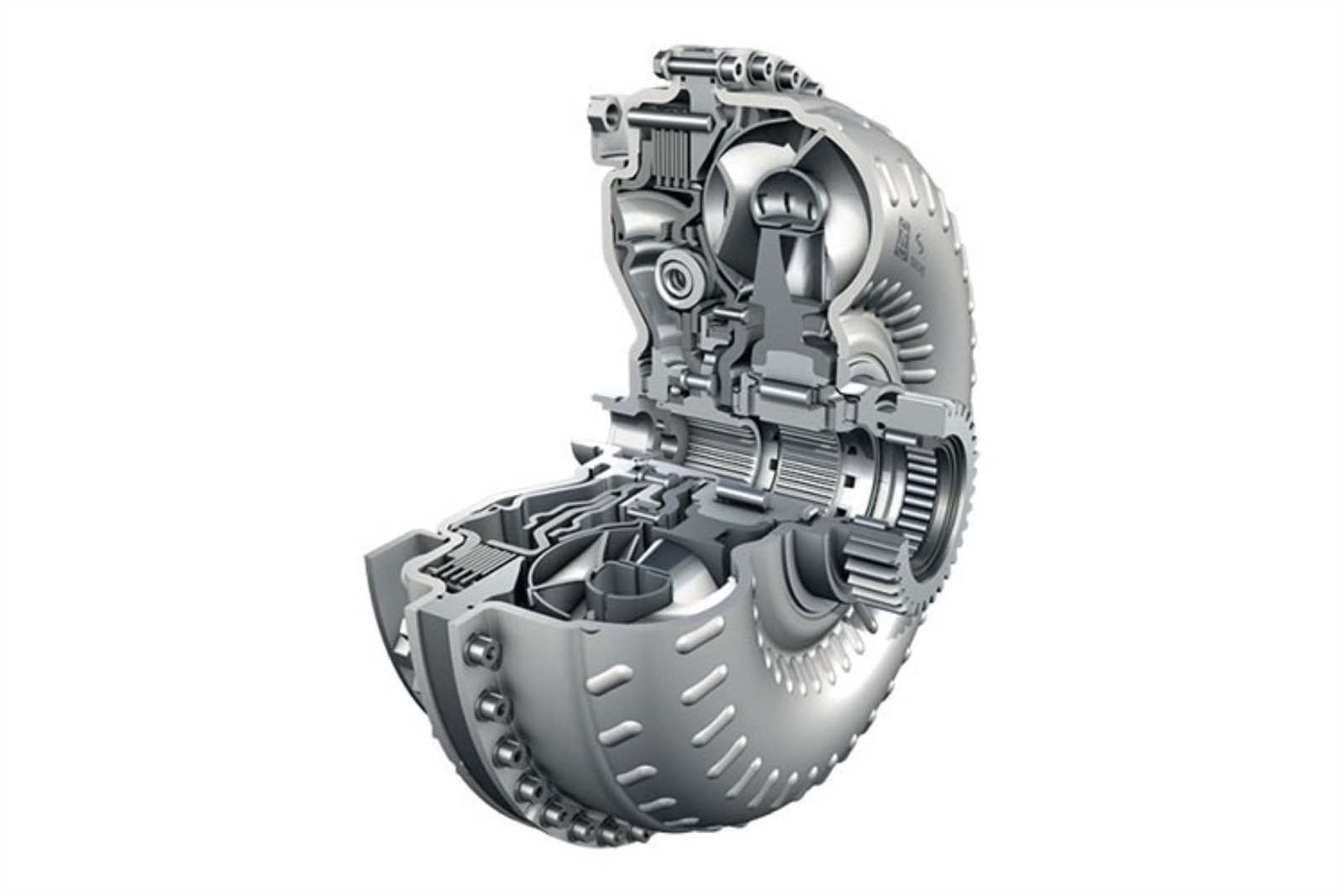

Another vital aspect of the control module is its ability to adapt to different driving conditions and driver preferences. Through various calibration settings, it can adjust shifting behavior to suit performance-oriented driving or more economical operation. This adaptability ensures that the transmission remains responsive and efficient, catering to the unique needs of each driver and driving situation.
Upgrades and Performance Enhancements
Enhancing the capabilities and efficiency of an automotive transmission system can lead to significant improvements in overall vehicle performance. By focusing on various modifications and refinements, enthusiasts and technicians can unlock the full potential of their drivetrain, resulting in better responsiveness, increased power delivery, and improved fuel efficiency.
Performance Chips and Tuning: One of the most effective ways to boost performance is through the use of performance chips or tuning software. These modifications allow for adjustments to engine parameters, optimizing power output and torque delivery to suit individual driving preferences.
Upgraded Components: Replacing standard parts with high-performance alternatives can also contribute to enhanced operation. Components such as clutches, torque converters, and fluid coolers are crucial for ensuring efficient power transfer and longevity. Selecting upgraded variants can significantly improve reliability under demanding conditions.
Fluid Selection: Utilizing specialized transmission fluids designed for performance applications can lead to smoother shifts and improved lubrication. The right fluid can enhance thermal stability and reduce wear, further extending the lifespan of the system while maintaining optimal performance levels.
Regular Maintenance: Maintaining a rigorous schedule of inspections and routine servicing is essential for ensuring that all enhancements function as intended. Regular fluid changes, component checks, and diagnostics can help prevent potential issues and sustain the benefits of any upgrades implemented.
Expert Recommendations for DIY Repairs

When tackling complex automotive tasks, it’s essential to approach the project with careful planning and consideration. Knowledgeable enthusiasts and professionals alike emphasize the importance of understanding the system components and utilizing the right techniques for successful outcomes.
Preparation is Key

- Research the specific system thoroughly to familiarize yourself with its functions and parts.
- Gather all necessary tools and equipment before starting the project to minimize interruptions.
- Create a dedicated workspace that is clean and well-lit to ensure safety and efficiency.
Step-by-Step Approach
- Begin with a comprehensive assessment of the system, noting any visible signs of wear or damage.
- Follow a logical sequence when disassembling components to avoid confusion during reassembly.
- Document each step with photos or notes to help with the reassembly process.
- Utilize quality replacement parts from trusted sources to ensure longevity and performance.
- Test the system thoroughly after completing the work to confirm that everything operates as intended.
Preventive Maintenance for Longevity
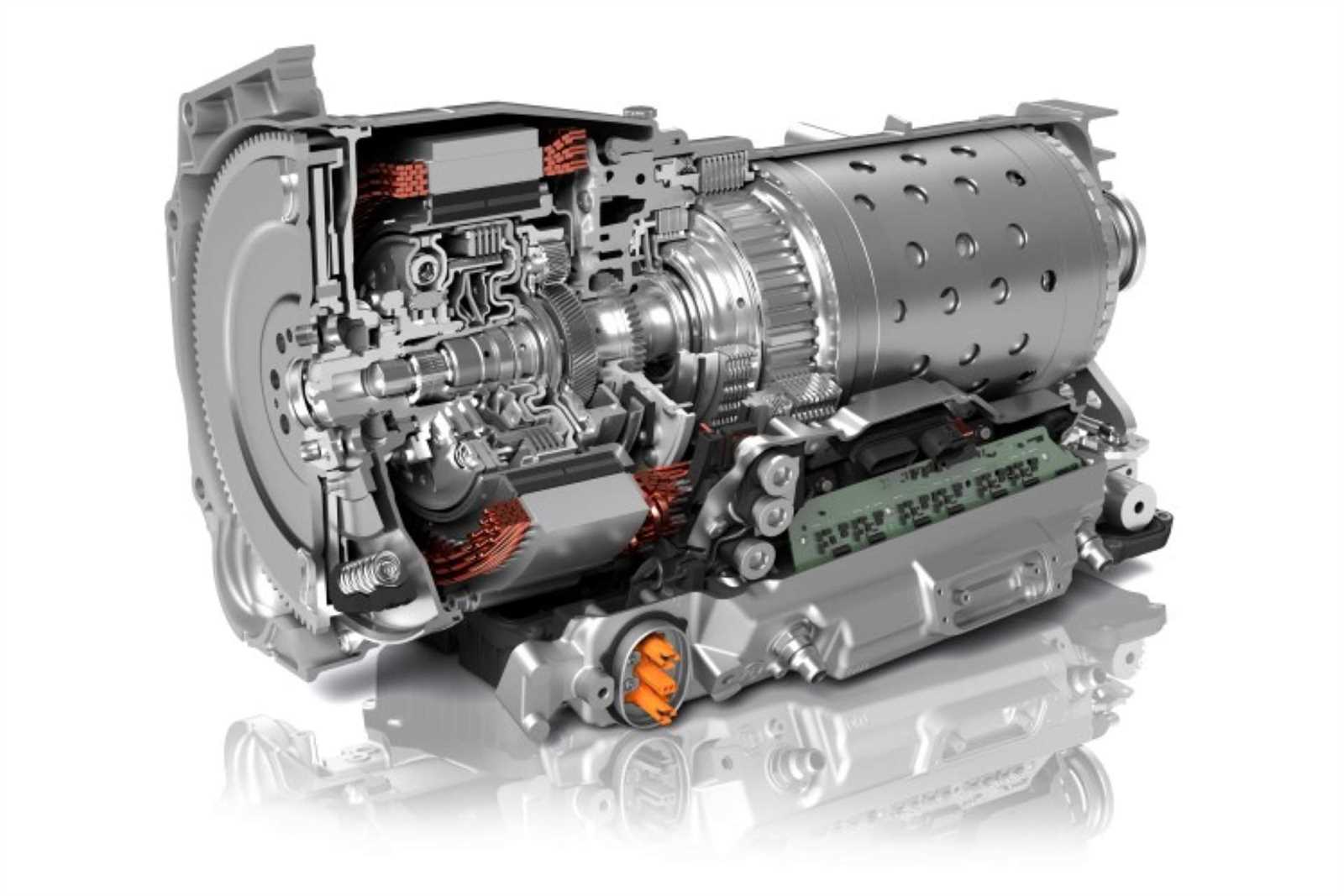

Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring the extended lifespan and optimal performance of complex mechanical systems. By implementing a proactive maintenance strategy, users can significantly reduce the risk of unexpected failures and enhance the reliability of their equipment. This approach not only saves time and money but also contributes to a safer operational environment.
Key areas to focus on for effective preventive care include fluid levels, component inspections, and timely replacements. The following table outlines essential tasks and recommended intervals to maintain peak functionality:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Check and top up fluid levels | Every 5,000 miles or annually |
| Inspect for leaks and wear | Every service interval |
| Replace filters | Every 15,000 miles |
| Examine belts and hoses | Every 30,000 miles |
| Perform software updates | As needed |
By adhering to these guidelines, operators can ensure their systems remain in excellent working condition, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and prolonged service life.