
This section provides essential insights into the upkeep and servicing of a widely recognized agricultural machine. It is designed to assist users in understanding the various components and their functions, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the equipment. Knowledge of these aspects is crucial for anyone looking to maintain efficiency and reliability in their operations.
By exploring common issues and their resolutions, this guide aims to empower operators with the tools needed for effective problem-solving. Understanding the intricacies of the machinery can significantly enhance its functionality and minimize downtime, which is vital in the demanding world of agriculture.
In the following sections, you will find detailed information that covers key maintenance practices and troubleshooting techniques. Whether you are a seasoned operator or a newcomer, this guide will serve as a valuable resource for achieving the best results from your equipment.
Ford 3000 Repair Manual Overview
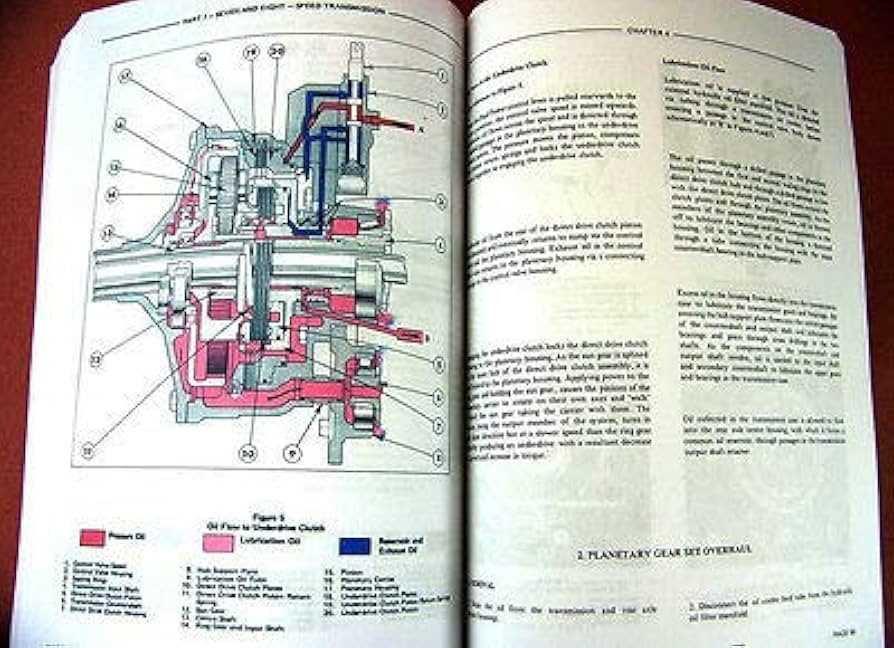
This section provides an insight into the comprehensive guide designed for the upkeep and troubleshooting of a specific agricultural vehicle model. The guide aims to assist users in understanding the necessary procedures for maintenance and addressing common issues that may arise during operation.
Key Features
The document includes various essential elements that enhance user experience and ensure effective management of the vehicle. Some of these features include:
- Detailed descriptions of components
- Step-by-step maintenance procedures
- Diagnostic tips for common problems
Table of Contents

| Chapter | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Introduction to the vehicle and its specifications |
| 2 | Routine maintenance tasks and schedules |
| 3 | Troubleshooting and repair procedures |
| 4 | Parts and tools required for maintenance |
Common Issues and Solutions

This section addresses frequent challenges encountered with agricultural machinery and offers practical solutions to enhance performance and longevity. Understanding these common problems can help operators maintain their equipment effectively.
Engine Performance Issues
- Hard Starting: This may be caused by a weak battery or faulty ignition system. Check battery connections and replace worn-out components.
- Overheating: Insufficient coolant or a malfunctioning thermostat can lead to overheating. Regularly inspect the coolant levels and replace the thermostat if necessary.
- Poor Fuel Efficiency: Clogged fuel filters or improper fuel mixtures can affect efficiency. Clean or replace filters and ensure the correct fuel type is used.
Hydraulic System Problems
- Slow Response: This could indicate low fluid levels or contaminated fluid. Check and refill hydraulic fluid, and replace if it appears dirty.
- Leaking Seals: Worn or damaged seals can lead to fluid leaks. Inspect seals regularly and replace any that show signs of wear.
- Noisy Operation: Unusual noises may suggest air trapped in the system or insufficient fluid. Bleed the system and ensure proper fluid levels are maintained.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
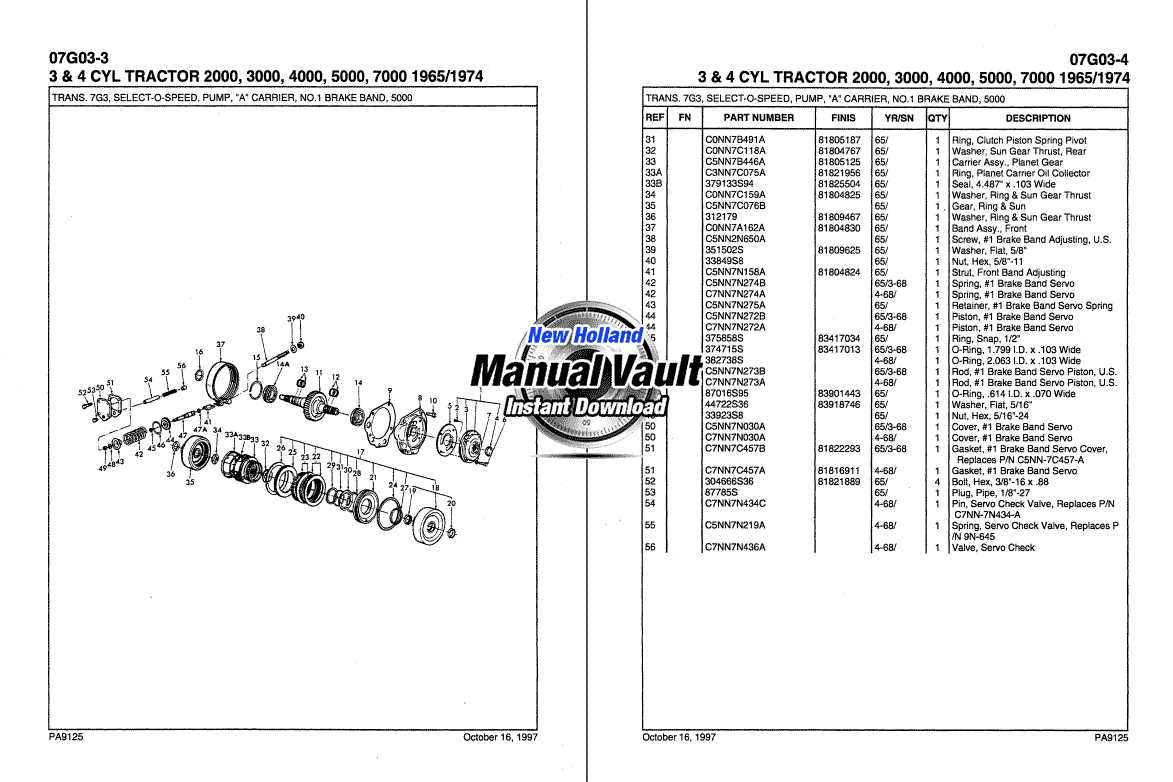
Ensuring the durability and efficiency of your machinery requires regular upkeep and attention to detail. Implementing a systematic maintenance routine can significantly extend the lifespan of your equipment while optimizing performance.
Regular Inspections
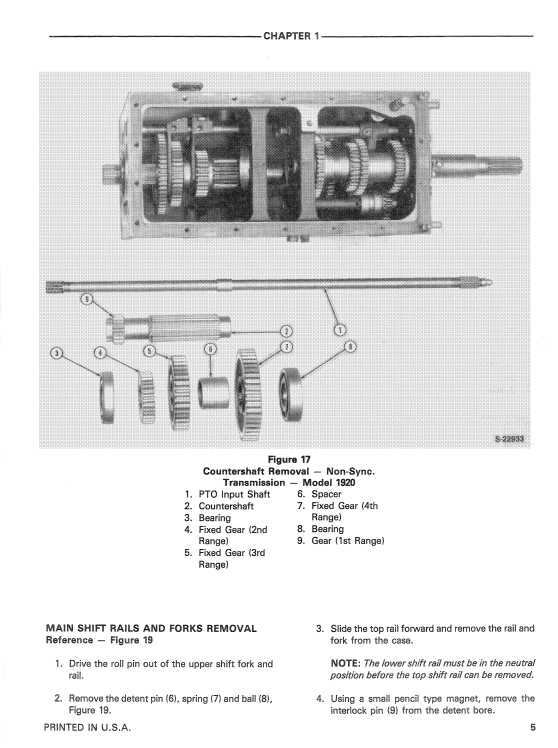
Conducting routine checks on vital components can help identify potential issues before they escalate. Focus on the following areas:
- Fluid levels: Regularly check and top up engine oil, coolant, and hydraulic fluid.
- Filters: Replace air and fuel filters as recommended to maintain optimal airflow and fuel efficiency.
- Belts and hoses: Inspect for wear or damage and replace as needed.
Proper Cleaning

Keeping your equipment clean not only improves functionality but also prevents corrosion and buildup. Follow these steps:
- Remove dirt and debris from the exterior regularly.
- Clean out any accumulated material from under the chassis.
- Use appropriate cleaning agents for different surfaces to avoid damage.
Regular maintenance and cleaning are essential practices that will ensure the reliability and efficiency of your machinery for years to come.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
This section provides a comprehensive approach to identifying and resolving common issues encountered during operation. By following a systematic process, users can effectively diagnose problems, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the equipment.
Identifying the Problem
Begin the troubleshooting process by clearly defining the symptoms. This will help in narrowing down potential causes. Consider the following steps:
- Observe any unusual sounds or vibrations.
- Check for warning lights or indicators.
- Review any recent changes or maintenance performed.
Systematic Diagnosis
Once the problem is identified, proceed with a structured approach to diagnose the issue:
- Inspect the fuel system for blockages or leaks.
- Examine the electrical connections and battery condition.
- Check the oil levels and condition for signs of contamination.
- Test the hydraulic system for pressure and leaks.
By carefully following these steps, users can efficiently troubleshoot and address issues, ensuring smooth operation of the machinery.
Engine Components and Specifications
This section provides an overview of the essential parts and characteristics of the engine, focusing on the various elements that contribute to its functionality and performance. Understanding these components is crucial for maintaining and optimizing the operation of the machinery.
Key Components
The primary elements of the engine include the cylinder block, crankshaft, camshaft, and pistons. Each part plays a vital role in the combustion process and overall efficiency. The cylinder block serves as the main structure housing the cylinders, while the crankshaft converts linear motion into rotational motion. The camshaft controls the opening and closing of the valves, ensuring the correct timing for optimal airflow and exhaust. Pistons move within the cylinders, driving the power generation process.
Specifications Overview
Specifications such as engine displacement, horsepower, and torque ratings are critical for assessing performance. Engine displacement, measured in liters or cubic inches, indicates the volume of the engine’s cylinders and is directly related to power output. Horsepower reflects the engine’s ability to perform work, while torque measures the rotational force available to drive machinery. These specifications guide users in selecting the right engine for their specific applications.
Transmission Problems and Repairs

The transmission system is essential for the proper functioning of any vehicle, as it transfers power from the engine to the wheels. Various issues may arise over time, leading to performance problems. Understanding these common complications and their solutions is crucial for maintaining optimal operation.
Common transmission issues include:
- Slipping Gears: This occurs when the transmission unexpectedly changes gears or fails to engage properly.
- Unresponsive Shifting: Difficulty in shifting between gears can indicate internal problems.
- Fluid Leaks: Any sign of fluid under the vehicle may signal a leak, which can lead to serious damage.
- Noisy Operation: Unusual sounds during gear changes can indicate wear or damage.
To address these issues, consider the following repair steps:
- Check the transmission fluid level and condition. Low or dirty fluid can cause several problems.
- Inspect for leaks and replace any damaged seals or gaskets.
- Examine the shifting mechanism for wear and tear, making adjustments or replacements as necessary.
- If issues persist, seek professional diagnosis to assess internal components and ensure thorough repairs.
Regular maintenance and prompt attention to symptoms can prevent more severe complications and prolong the lifespan of the transmission system.
Electrical System Diagnostics
The electrical system is crucial for the proper functioning of machinery, as it powers various components and ensures their efficient operation. Diagnosing issues within this system requires a systematic approach to identify malfunctions and implement effective solutions.
Key Steps in Diagnosing Electrical Issues:
- Visual Inspection: Start by examining wiring, connectors, and components for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Testing Voltage: Use a multimeter to check voltage levels at different points within the system to ensure they meet specified standards.
- Continuity Testing: Conduct continuity tests to confirm that circuits are complete and functioning as intended.
- Component Testing: Isolate and test individual components, such as switches, relays, and sensors, to determine their operational status.
By following these steps, one can systematically troubleshoot the electrical system and restore functionality efficiently. Regular maintenance and prompt diagnosis of issues can help prevent larger problems in the future.
Hydraulic System Maintenance
Proper upkeep of the hydraulic system is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the machinery. Regular attention to various components can prevent costly failures and maintain efficiency.
Key maintenance tasks include:
- Regularly checking fluid levels and quality.
- Inspecting hoses and connections for leaks or wear.
- Replacing filters as needed to ensure clean fluid circulation.
- Monitoring the operation of pumps and cylinders for unusual noises or performance issues.
It is also important to follow these guidelines:
- Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance intervals.
- Use appropriate hydraulic fluids that meet specified standards.
- Keep the system clean and free of contaminants.
- Document all maintenance activities for future reference.
By adhering to these practices, you can enhance the reliability and functionality of the hydraulic system over time.
Body and Frame Repair Techniques

This section focuses on various methods to address issues related to the outer structure and framework of vehicles. Understanding these techniques is crucial for maintaining the integrity and performance of the machine.
When approaching repairs, consider the following essential techniques:
- Assessment: Begin with a thorough evaluation of the damage. Look for signs of rust, dents, and structural weaknesses.
- Alignment: Ensure that the framework is properly aligned. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear and handling issues.
- Welding: Utilize welding methods to fix cracks and reinforce weak areas. Different types of welding can be applied based on the material and extent of damage.
- Panel Replacement: In cases of severe damage, replacing entire panels may be necessary. Ensure proper fit and secure attachment.
- Rust Treatment: Treat any areas affected by corrosion. This involves cleaning, applying rust inhibitors, and repainting to prevent future issues.
- Finishing Touches: After repairs, inspect the surface for any imperfections. Sanding and repainting may be required for a smooth finish.
By applying these techniques, one can effectively restore the vehicle’s body and frame to optimal condition, ensuring both safety and aesthetics.
Essential Tools for Repairs

When it comes to maintaining machinery, having the right equipment is crucial for efficient and effective service. The following tools are indispensable for anyone looking to perform maintenance tasks, ensuring that work can be done smoothly and accurately.
Basic Hand Tools
- Screwdrivers: A variety of sizes and types, including flathead and Phillips, are essential for loosening and tightening screws.
- Wrenches: Both adjustable and fixed wrenches are necessary for dealing with nuts and bolts of different sizes.
- Pliers: Needle-nose and standard pliers can assist in gripping, twisting, and cutting tasks.
- Socket Set: A comprehensive socket set allows for quick and easy fastening of bolts, especially in tight spaces.
Specialized Equipment

- Torque Wrench: This tool ensures that bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications, preventing damage.
- Multimeter: Useful for electrical diagnostics, a multimeter helps measure voltage, current, and resistance.
- Oil Filter Wrench: This specialized wrench aids in removing and installing oil filters with ease.
- Diagnostic Scanner: A vital tool for identifying issues within electronic systems, enhancing troubleshooting efforts.
Having a well-stocked toolkit equipped with these essential instruments will make any maintenance task more manageable and efficient.
Parts Replacement Procedures

This section outlines the essential steps for efficiently replacing components in your machinery. Understanding these procedures ensures optimal performance and longevity of the equipment.
Preparation Steps

Before starting the replacement process, follow these initial steps:
- Gather all necessary tools and replacement parts.
- Review the specific instructions for the part being replaced.
- Ensure the work area is clean and organized.
Replacement Process

Follow these guidelines to successfully replace the part:
- Power down the machinery and disconnect it from any power source.
- Carefully remove any coverings or protective components.
- Loosen and detach the old part using the appropriate tools.
- Install the new component, ensuring it is securely fastened.
- Reassemble any coverings and reconnect the power source.
- Conduct a thorough inspection to ensure everything is in place.
By adhering to these procedures, you can maintain the functionality and reliability of your equipment.
Safety Precautions While Working
Ensuring safety during maintenance tasks is crucial for preventing accidents and injuries. It is important to follow specific guidelines to create a secure working environment. Awareness of potential hazards and taking appropriate measures can significantly reduce risks associated with machinery handling.
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves, goggles, and sturdy footwear. This gear acts as a barrier against injuries from sharp objects, chemicals, or falling debris. Regularly inspect your equipment for any signs of wear and replace them as necessary to maintain effectiveness.
Maintain a clean and organized workspace. Clutter can lead to accidents, so ensure that tools and materials are stored properly when not in use. Keep pathways clear to facilitate easy movement and reduce the chance of trips and falls.
Understand the machinery before operation. Familiarize yourself with the user guidelines and safety instructions. This knowledge helps in recognizing warning signs and understanding the equipment’s functions, leading to more informed decision-making during tasks.
Be aware of your surroundings. Always keep an eye on other workers and equipment in the vicinity. Effective communication is key; use signals or verbal cues to ensure everyone is aware of potential hazards.
Handle tools and equipment with care. Improper usage can result in injury, so ensure that you are trained in the correct handling techniques. Always use the right tool for the job to prevent accidents and enhance efficiency.
By adhering to these safety measures, you contribute to a safer working environment, ultimately protecting yourself and others from potential harm.